The technology of the dispatcher of the Dispatching Point of the Circle of the Krasnoyarsk city of Krasnoyarsk. Air traffic controllers (air traffic controller)
The daily record for take-offs and landings at Domodedovo airport is 724 operations. The maximum hourly intensity when operating from two parallel runways is 43 aircraft. All of them are controlled by air traffic controllers working at the Command and Control Post (KDP) or “tower” (from the English word “TOWER”). In total, 6 dispatcher shifts of 10 people each work at Moscow Domodedovo Airport. The profession of an air traffic controller occupies one of the first places in terms of psycho-emotional stress on the human body. Today we will talk about people whose actions daily affect the lives of tens of thousands of passengers...
The Moscow Automated Control Center, located near Vnukovo Airport, is responsible for all aircraft in the sky over Moscow. The Domodedovo Air Traffic Service Center is a structural subdivision of the branch "Moscow Center for Automated Air Traffic Control" (this phrase was specially written down verbatim during the visit). The Center is responsible for ensuring the safety, regularity and economy of aircraft flights in the area of Domodedovo Airport:
1. 
Domodedovo has 2 runways (runways). Each of them is responsible for its own dispatchers. The tower houses the workplaces of the flight director, the senior controller, the controllers of the Launch Control Station (ATC) and the Auxiliary Approach Control Center (AAC):
2. 
The area of responsibility of the launch controller (RTD) includes the control of aircraft in the airspace, which includes sectors of climb after takeoff and the final stage of landing, as well as the runway and taxiways:
3. 
The air traffic controller also manages the movement of special vehicles, the lighting system on the runway and taxiways, and performs all the necessary additional operations:
4. 
I imagined the dispatcher as a stern man, in big headphones, yelling something into a microphone and staring intently at a round kinescope, along which a green strip runs in a circle, like in old Soviet films. It turned out not to be the case at all. They don’t use headphones, kinescopes are not round and not green, and not only men, but also very charming girls work as dispatchers:
5. 
At the dispatcher, all aircraft located near the airport are marked on the monitor screen. He sees whether they are climbing or descending, at what height they are and at what speed they are flying:
6. 
7. 
8. 
From the tower you can see the entire territory of the airport. Modern equipment is installed here, including an automated information display system. The airfield surveillance system provides control over the movement of any means on the airfield.
If the dispatcher is suspicious, then he can use binoculars:
9. 
If the lane is occupied, then the traffic controller turns on a special runway occupancy display with an audible signal:
10. 
In addition, on the tower there is an ATIS controller (automatic information transmission service in the airfield area) - on the left in the photo, a flight director (shift supervisor), a senior controller and substitution controllers (on the right in the photo):
11. 
Each dispatcher is entitled to a 20-minute rest every 2 hours. At this time, it is replaced by the substitution manager:
12. 
The actions of dispatchers are supervised by a senior dispatcher. He constantly moves from one dispatcher to another and controls their actions (in the photo he is on the left):
13. 
There is also a flight director on the tower (on the left in the photo). He is responsible for organizing the work of the shift staff:
14. 
The minimum time between aircraft landings is 2 minutes, and between take-offs from 1 to 3 minutes, depending on the aircraft classification. The atmosphere on the tower is calm and quiet. When the dispatcher conducts a radio exchange with the aircraft crews, then everyone falls silent, or they say in a low voice:
15. 
16. 
17. 
To get to the tower, the dispatcher must go through the door with a porthole:
18. 
Here you need to attach a special card to the lock and confirm your fingerprints:
19. 
The dispatcher gets to the tower via a spiral staircase:
20. 
The tower is also notable for its balcony. From here you have a great view of the airport:
21. 
22. 
23. 
24. 
25. 
26. 
27. 
28. 
29. 
Globe Domodedovo:
30. 
Well, a view of the road leading to Domodedovo:
31. 
Can you track up to 20 moving objects at the same time?
Do you have the ability to see and evaluate the interaction of objects in three-dimensional space?
Will you be able to make one right decision in 25 seconds and manage to give commands to emergency services?
Do you have at least ICAO level 4 aviation English?
You are not subject to stress and external noise and light influences?
Are you in perfect health?
Do you have a fast reaction time?
Can you work in a team?
If you answer “no” to at least one of these questions, this profession is not for you. The Moscow Center for Automated Air Traffic Control (MC AUVD) employs people who not only meet all the requirements listed above, but also have individual, unique professional skills, without whose control not a single aircraft will take to the skies today ...
So what calls people to this complex and responsible profession, the price of a mistake in which is extremely high? Is there a share of romance in this aviation specialty, love for the sky, for aviation, or is everything decided by a fairly high, by today's standards, salary and prestige?
Let's try to figure it out, and the deputy director of the MC AUVD Alexander Povaliy will help us with this. Alexander Pavlovich has worked at the center for more than 40 years...
And it all started back in 1981 ... Then Moscow air traffic controllers began to master the TERCAS system, which was new for that time. The Swedish equipment was installed in the newly built technological building of the MC AUVD. This system is still in use today, along with two redundant modern monitors. In a separate simulator class, equipment similar to the main equipment is installed, on which both the dispatchers themselves and the trainees train ...
Workplaces are quite comfortable even today, despite the past years and the commissioning of new systems and equipment. The warm light of a large round screen, black matte skin panels - everything is set up so that the dispatcher is completely immersed in the space he controls, without being distracted by external noise and irritants. It is believed that an experienced dispatcher already sees a picture in his head, which will be displayed on the monitor only after a few minutes. All his commands are mentally prepared in advance and are only waiting for the issuance. But this is in a normal, calm environment. And if suddenly an emergency situation on board or the weather begins to surprise - the load increases significantly ... Therefore, the time spent at the monitor (screen) is strictly limited and after a couple of hours the dispatcher gives up his place to a colleague, and he goes to the rest room for 20 minutes ...
Structurally, the center is divided into two large components: ADC - aerodrome control center and ADC - area control center. ADC manages air traffic in the areas of airfields and approach zones (a space with a radius of 100 km from Moscow). ADC has 9 sectors (4 directions), which have both geographical boundaries and altitude division. The lower approach sector is from 1800 to 3600 meters, the upper approach sector is already higher. Each sector has its own radio frequency (VHF range). In the areas of airfields, the aircraft are transferred under the control of the Krug controller. His area of responsibility is almost immediately after the plane takes off from the ground, and during the landing approach - until the fourth turn ...
ACC manages air traffic on air routes (23 sectors, 530 controllers). There are usually no sharp maneuvers on the echelons, so everything is calmer and the size of the sectors is correspondingly larger than in the ADC. Sectors are divided only by geographical principle without height division. The ACC sectors border with the same sectors of other ATC centers of the country and neighboring states: St. Petersburg, Rostov, Samara, Ukraine and others. Each dispatcher has access to his sector, which he regularly confirms. To work in another sector, a separate internship and training is required, followed by certification and obtaining the appropriate permit (there is a salary supplement for each additional sector)
In 2007, due to the transition to a new ATC system, it was decided to build a new Air Traffic Control Center. The equipment of the center and the software were entrusted to the Almaz-Antey Air Defense Concern ...
The new building is beautiful and spacious. The eye is pleased with a pleasant combination of colors and finishes. Lots of glass and sky blue...
The air traffic controller controls the aircraft throughout the entire flight period - from starting the engines and taxiing out of the parking lot and ending with the arrival of the aircraft at the parking lot after the pilot has landed. Its main function is to ensure the safe, orderly and regular movement of aircraft within its assigned area of responsibility. Taking into account the specifics and distribution of controlled areas and objects, an algorithm for working in the new traffic control center was created. The location of the workplaces of air traffic controllers corresponds to the geographical directions of the approaches. Additional sectors are responsible for going beyond the zones. Reserve sectors are also equipped with identical equipment, which will be required after the transition to the new airspace. Separately equipped places for senior controllers and controllers-operators and the flight director. All are gathered in a single room, but spatially somewhat separated from each other ...
Konstantin Vitalyevich Oleinik, head of the ADC (regional dispatch center), spoke in detail not only about the general tasks and structure of the new center, but also about the specific equipment of the air traffic controller workplace. First of all, of course, these are large modern monitors with anti-glare coating, which provide information about the movement of aircraft, the meteorological situation and many additional parameters necessary to obtain a complete picture of the air situation in the control zone. Additional monitors are responsible for the main and backup radio communications with both the aircraft in the air and with ground services and controllers of neighboring areas. Another additional monitor is reserved for auxiliary information ...
Now the system is working in test mode without radio communications, but with the real situation in the control zones. Testing is carried out by the dispatchers themselves, who alternately take a shift at a new center during their duty. The engineering staff is simultaneously debugging equipment ...
One of the important factors in ensuring convenience in the workplace is its ergonomics. For example, chairs, in addition to the basic requirements for them in maximum convenience and comfort, must also be strong enough, with a metal base that can withstand constant hours of stress ...
In the hall there is always the same-smooth soft lighting at any time of the day and optimal climatic conditions are maintained regardless of the time of year. Commissioning of the new automated system is planned for this year, so dispatchers need to get used to their new jobs. It is the air traffic controller who takes measures to maintain safety in the event of a difficult air situation and special flight situations by providing safe intervals of longitudinal, vertical and lateral separation. Behind the outward calm lies a huge inner tension and responsibility, which is the higher, the more complex the sky is - in such an endless, huge, and at the same time so cramped .... These “invisible people” are the hope of all those who are currently in the cockpits, at the helms or sidesticks of their ships. They trust and believe that in any situation they will be helped and prompted, they will do everything possible to safely return to earth ...
But what if the soul demands to see the planes not in the form of symbols on monitors, but really, with your own eyes, to hear the sound of their engines, a rapid takeoff and a soft landing? And here is the solution. But for this we have to move here, to the control tower of the airfield ...
The tower, or rather the Vnukovo air traffic service center (ATS VTs), is a branch of the ATMS MC ...
Oleg Viktorovich Fedoseev, the head of the traffic service of the VTs ATS, began his story about the Vnukovo control tower with a simulator to simulate a real airfield situation. It is used to train the dispatcher from the workplace from which he will have to work in the future. The equipment installed here is similar to the one on the tower. It is possible to simulate any situation, both weather and technological, in order to work out a clear and well-coordinated algorithm of the air traffic controller's action ...
The professional skills of tower controllers are very different from those of their counterparts in the ATC center. The picture here is rather two-dimensional, but it also requires increased attention. At the same time, dozens of pieces of equipment, aircraft, service personnel move across the field. Incoming aircraft “hang” in the sky and take-off boards soar, there is movement along taxiways, constant requests for engine starts follow ...
At the same time, the dispatcher has to keep a huge amount of information in his head (it doesn’t matter if it’s an apron, taxiing or start) - analyze and predict the development of the situation, know all the designations of taxiways and main tracks, parking numbers, weather conditions, friction coefficient, repair work areas and all kinds of restrictions and prohibitions . Be ready and instantly respond to any emergency situation on the field - whether it is an aircraft leaving the runway, or a fox suddenly appearing on the field from a nearby copse ...
Control over the movement of everything that can move on the platform is carried out simultaneously both on monitors and visually - the terminal building is clearly visible from a height of 40 meters ...
Quite recently, the airport introduced the next stage of an integrated system for monitoring the position of aircraft and special equipment on the CrossPoint apron using the GLONASS satellite navigation system. During the next stage of implementation, the equipment of all airport apron equipment was completed - more than 800 units. The basic function of the CrossPoint system is to display the actual position of aircraft, both in parking lots and in the process of taxiing along the airfield, as well as special equipment on the apron, with the preservation of historical information about all movements for several months ...
It’s good when the weather allows you to see the aircraft’s approach visually, but it also happens that you have to wait for the moment of landing only according to the report of the crew, wait and hope that the pilot will cope, which means that, for his part, the dispatcher did everything correctly and accurately, did everything that depended on him. At such moments, the nerves are strained to the limit, and the sense of responsibility is aggravated as much as possible ...
The tower offers a view of the entire airfield. Those sectors that for some reason fall into the “dead zones” are equipped with special additional video surveillance cameras. The controller must see and control every meter of the airfield. Additional radars track the coordinates of landing and taking off aircraft until they are transferred to the circle controllers ...
Sports are given a special place in the MC AUVD. It has its own football and hockey teams. Sections for volleyball, arm wrestling, tennis, etc…
The corridor between the buildings is occupied by photographs on the "Wall of History" - a chronicle of front-line, labor and sports exploits of the workers of the center. There is something to remember and something to be proud of for new generations. For the most part, people come to work at the center consciously and for a long time, as a rule, as long as their health and age allow, so there is practically no staff turnover. Despite all the difficulties and difficulties, a colossal nervous load and the constant need to improve personal skills and qualifications, the profession of an air traffic controller becomes the main and beloved for him for life ...
So what is it like to be an air traffic controller? What makes young people consciously choose this particular path to aviation, because the competition for training in the specialty of air traffic control is always quite high ...
Difficult? - Yes very!
Responsibly? - Probably too much!
Hard? - And how! The profession of an air traffic controller occupies one of the first places in terms of psycho-emotional stress on the human body. But the feeling that it depends on you, your team, exactly how the planes fly, at what height, with what course and speed. Understanding that it is you, and no one else, helps them see and interact with each other, share this endless sky, feel free, easy and, most importantly, SAFE in it, as if in a vast ocean. Isn't this the very romance of the profession, for the sake of which a person goes to all these hardships and trials ... Everyone who is somehow connected with aviation has “his own” sky. For air traffic controllers, it’s like this - a lifetime ...
Aviation professionals who control and maintain the air traffic of airplanes, helicopters and other aircraft are called air traffic controllers. Their place of work is airports and military airfields. The main task of the representatives of this profession is to ensure the safe, regular and orderly movement of air transport. To do this, you need to know:
- air navigation (a science that studies methods and means of air transport control);
- aviation meteorology (atmospheric processes, their impact on aviation activities);
- separation rules and instructions (dispersion of aircraft over a certain distance so that there is no collision between them).
The work of an air traffic controller is organized in such a way that he can control all stages of the movement of an aircraft or other air vehicle, from takeoff to landing. At the same time, the airspace is divided into certain zones assigned to a separate dispatcher specialist, who manages the flight specifically within his area. Therefore, air traffic controllers have a different area of specialization:
- Airfield control tower - here they schedule a flight plan for the day, in coordination with other airport services, control the situation in the air during flights, and maintain constant communication with the crews of the vehicles.
- "Taxiing" - checks the movement of vehicles on the territory of the airfield, allows or prohibits towing, starting the engine of the car, taxiing.
- "Start and landing" - are engaged in the management of the takeoff and landing of aircraft.
- "Circle" - controls the movement of cars in the take-off zone with a radius of 50 km from the airfield.
- "Approach" - manages the flight at an altitude of 2100-5700 m, allows landing in turn, determining time intervals.
- The regional center - controls the movement of aircraft at an altitude of 2100-17000 m.
- Point of local airlines - operates in the area of the local airfield at an altitude of 1500 m and below.
- Local control center - occupies the area of the administrative region far from major airports, flight control at an altitude of up to 1500 m.
The control and guidance of the movement of aircraft and other air assets is carried out by monitoring the situation in the air using a special monitor. In this case, meteorological conditions, aircraft schedules, etc. are necessarily taken into account.
Air traffic controllers do not have the right to make a mistake, since the lives of other people depend on their observation and reaction. Therefore, the organization of their work is aimed at preventing errors in flight control.
Dispatch service operates day and night - 24 hours a day. Because of this, in order to avoid nervous and psychological stress, air traffic controllers go out to perform their duties in shifts.
Air traffic controller skills
Employers, when hiring a person for the position of an air traffic controller, take into account such qualities as personality:
- resistance to emotional and psychological stress;
- the ability to distribute attention;
- care and responsibility;
- resourcefulness and self-control;
- initiative and organizational skills;
- Analytical mind;
- developed visual-motor coordination of movements.
In this case, the air traffic controller must know:
- device and principles of operation of dispatching equipment;
- the construction of aircraft machines to give advice on the rapid elimination of any problems during the flight;
- English (or another foreign language, depending on the place of work);
- professional terms.
In addition to all of the above, it is desirable to have one of the diplomas of higher education in the specialty "Operation of aircraft and air traffic management", "Air traffic control".
Pros of being an air traffic controller:
- work is not related to physical activity (women of different ages can work);
- comfortable working conditions (indoors, sitting);
- the right to early retirement (men - from 50 years old (work experience of at least twelve and a half years), women - from 45 years old (with ten years of work experience)).
Salary of a Russian air traffic controller in 2019
The average salary of an air traffic controller per month is about 120 thousand rubles. Such information is provided on the website http://ru.zarplat.info/air traffic controller. Already today there is information about the salary increase for air traffic controllers by 30% in 2018.
Here you can also view vacancies in such companies of the Russian Federation: Strela - 90,000 rubles / month, AC 1st class - 72,000 rubles / month, Air Navigation of the North-West - 65,000 rubles / month, "Vanguard" Sosnovy Bor - 250,000 rubles / month.
How to become an air traffic controller
In Russia, there are not so many universities where you can get the profession of "air traffic controller". These are the Moscow State Technical University of Civil Aviation (Moscow), the State University of Civil Aviation (St. Petersburg), the Higher Aviation School (Ulyanovsk), the Higher Military Institute. V.M. Komarova (Yeisk). St. Petersburg State University of Civil Aviation has its branches in Khabarovsk and ATK GA, after studying in which you can get a secondary vocational education.
Every three years, air traffic controllers take special advanced training courses, after which they confirm their current certificate and capacity in accordance with the requirements.
Experts remind
An air traffic controller is one of the most responsible professions, which is associated not only with aviation technology, but also with human lives.
On a day that happens once every 4 years - February 29 - we managed to get to the most important strategic facility, where security is provided much more seriously than at the airport: even paranoid people in the USA do not have such an inspection at the entrance!
Meet the Moscow Center for Automated Air Traffic Control. It is here that dispatchers sit, controlling all aircraft over the most active part of the European territory of Russia in terms of movement. In the west, the center's area of responsibility is limited by Ukraine and Belarus, in the north - by the territories of St. Petersburg and Vologda dispatchers, and in the south and east - by Rostov and Kazan. 58-59% of all Russian traffic is right here: hypercentralization in our country is observed in all industries, and, despite the trend towards, it continues to grow in the Moscow region.
At the same time, Moscow airports are now hindering each other's development. For example, the same one, next to which the dispatch center is located, could serve 10 times more passengers (we are talking about the terminals themselves), but here Moscow is around and it is difficult to implement effective schemes for using airspace (and even the lanes intersect, that is, work maybe only one). The opening (Zhukovsky) will not change much: there will be very little traffic and this airfield is mainly used for experimental aviation, plus you can enter there only from one side - from the other (course 123), again, Moscow and the airport will be in the air " intersections." Ostafyevo is also too close: in general, the farther the airport from Moscow, the better, but the development of airports or Tver has remained in the plans so far.
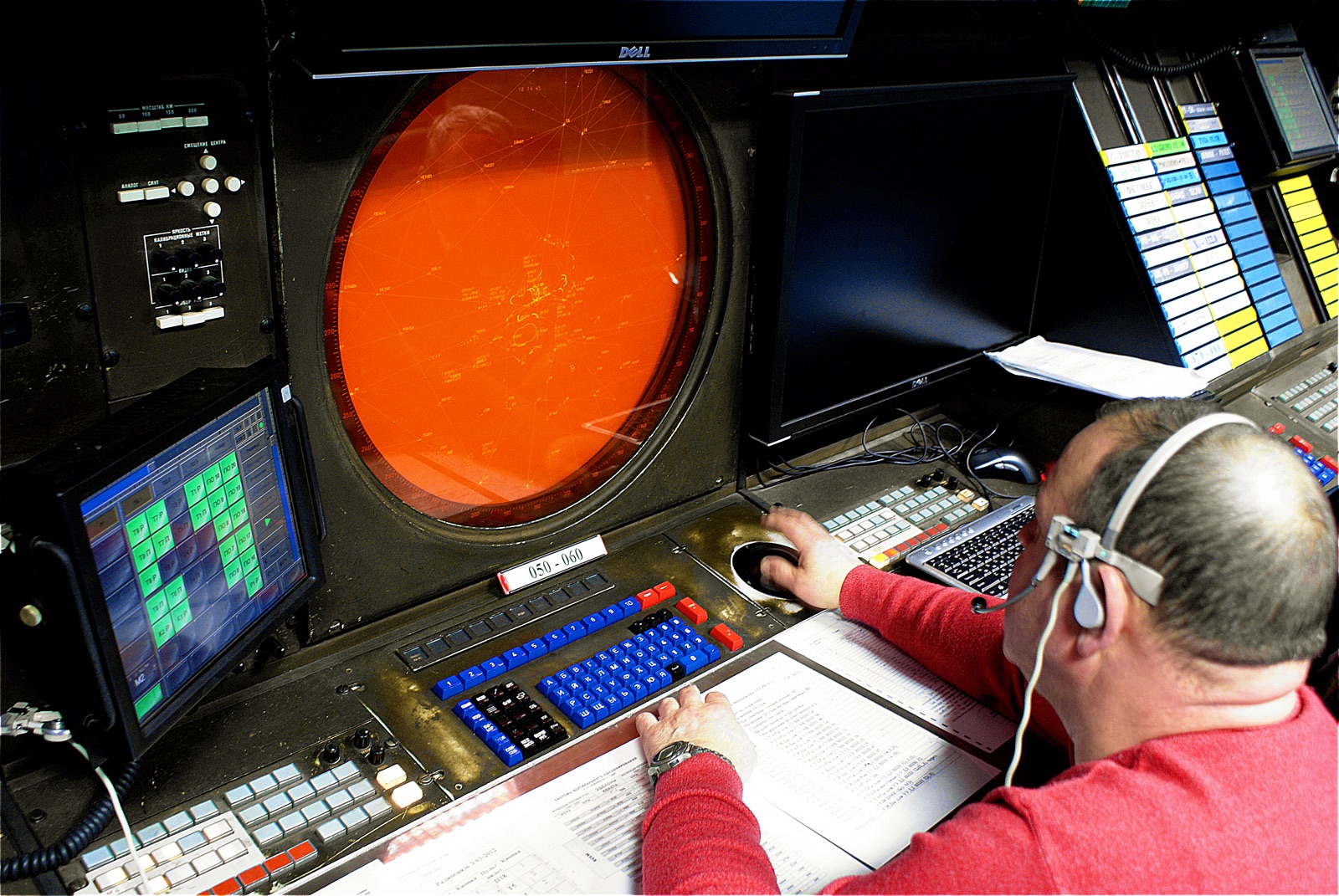

TERKAS - development of the 1970s, began to be operated in 1981.
The control center was opened in 1981. There was no modern equipment in the USSR at that time, and therefore, as is usually the case, the Varangians were called in - in the sense, they bought the TERKAS system from the Swedish company Stansaab (later it became known as Datasaab, and then was bought by Ericsson). A whole story was connected with this purchase: some of the components of the system were American-made, and the Swedes could not obtain export licenses for them (restrictions on the export of dual-use products against Russia are still in effect in the United States). And then the Swedes relabeled these components and smuggled them to Moscow through Soviet diplomats. This was later revealed, and in 1984 Ericsson agreed to pay a fine of more than $3 million for export patent infringement.

Now a warm lamp "TERKAS" is used for training dispatchers, and in the very center new equipment of Russian production, developed by the St. Petersburg Institute of VNIIRA, is being launched. While debugging and development is underway, the start of work is scheduled for April.
More in the video:
Approximately 530 dispatchers work in MC ATC. There are at least 10 people in one shift, of which, on average, 2 are on vacation, one is on sick leave, i.e. 7-8 go out, and at least 5 work at the same time.

They have strict health requirements - almost like pilots - and work is considered harmful: they retire at the age of 50 (and women - at 45, they are 15-18% here), vacation - 67 days, there are allowances for harmfulness, sanatorium - spa treatment, and the working week consists of 36 hours. However, there are many more applicants than places: the average salary here is 180 thousand rubles, and they also give an interest-free loan in the amount of 1.9 million, which can be used as a down payment on a mortgage. After 3 years of work, you can buy air tickets to anywhere in the world for 50% of their cost, and after 7 years you can fly for free. The dispatchers have their own football and hockey teams, and even a gym right in the Mission Control Center - however, you can only go to it after the shift, because you suddenly get injured?

Doing sports, do not forget to remove the dumbbells
A typical schedule looks like this: a shift from 14:00 to 22:00, then an overnight stay in a rest room (dispensary) and a new shift from 8:00 to 14:30. Then, until 16:30, debriefing, study of documents, and from 21:30 to 8:30 - night duty, after which 3 days off.

Each dispatcher renews the certificate every two years, passing a medical examination. Quarterly, annual and pre-shift inspections are also carried out.
Initially, the dispatcher is assigned the third class - in the process of development it is easy to grow to the first (and there are 70% of them here). And in every possible way the study of the English language is stimulated: for its knowledge, the salary increases by 50%.

The best way to learn as air traffic controllers is at the St. Petersburg University of Civil Aviation (SPbGUGA), there are also graduates of the Moscow State Technical University, the Ulyanovsk Institute of Civil Aviation and a college in Krasnoyarsk.

You need to be able to distinguish aircraft visually


Airfield controllers have their own simulator
And by the way, the dispatch center is very active on social networks: Vkontakte (
“The number of air transportation in Russia is growing every year, both on domestic and international routes. New directions are opening, the country's airports continue to be developed by foreign airlines. People are used to flying: business trips, business trips, vacations - flights have long become something commonplace. However, few of the passengers climbing the ladder on board the aircraft think about who, in fact, manages all this huge flow of arriving and departing aircraft and how this mechanism, which is in continuous motion, is controlled. Today we will talk about this in a little more detail using the example of the Domodedovo ATS Center, which is a structural subdivision of the Moscow AOVD Center ... ”says Armen Gasparyan
(Total 27 photos)
Post sponsor: PPU pipes buy: Sale from the manufacturer of heat-insulated PPU steel pipes.

1. The functions of the center include ensuring the safety, regularity and economy of aircraft flights in the area of the Domodedovo airfield. Air traffic control in the area of the Domodedovo airfield is carried out using TOWER technology (Tower - Command and Control Center) in two languages: Russian and English.


3. Everything that happens on the airfield of the airfield takes place only under the control and on the commands of the air traffic controllers. This applies not only to aircraft pilots, but also to ground technical services. True, for passengers, all this remains completely invisible throughout the entire time they stay within the walls of the airport complex and on board the aircraft.

4. After the aircraft is prepared for flight, the aircraft crew must obtain permission for this flight from the aerodrome control tower controller. Further, a few minutes before departure, the crew asks the taxi controller for permission to start the engines and, after receiving it, begins preparations for takeoff. The taxi controller also reports the route to the runway (RWY) and permits taxiing to the so-called preliminary start - a place on the taxiway immediately in front of the runway.

5. After the crew reports that the preliminary start is taken, the taxi controller transfers the aircraft under the control of the launch controller, who allows the execution of the line start, that is, taxiing directly onto the runway and aligning along its center line, reports the conditions for take-off and, after the crew reports on readiness, allows take-off .

6. After takeoff, the aircraft passes under the control of the Moscow air hub control center (MADC). It is sequentially serviced by controllers: circle and lower approach, which can make adjustments to the established procedure for entering the airway; then the upper approach, controlling the aircraft until it reaches the prescribed flight level and leaves the Moscow Air Zone (MVZ), and, finally, the controllers of the Area Control Center (ACC), who serve the aircraft at the flight level.

7. Let's talk a little more about the work of launch controllers, whose area of responsibility includes airspace, which includes the sectors of climb after takeoff and the final stage of the landing approach, as well as the maneuvering area (runway and taxiways).

8. To date, two parallel runways with courses 14L/32R and 14R/32L are operating at Domodedovo Airport, and the Heading Glideslope System (CGS) operates in all four directions, which allows aircraft with the appropriate equipment on board to automate the landing process to the maximum and ensure flight safety at meteorological minimum III-A category ICAO (with vertical visibility up to 15 meters and horizontal visibility up to 200 meters).

9. At the same time, as a rule, only two courses are operating, which are mainly determined by the direction of the wind. But course 32 is considered a priority, because. when landing on runway 32L and 32R, it is easier to create an interval between aircraft, while when landing on the 14th runway, the space for maneuver is limited by Moscow (flights above which are prohibited below 8000 meters), as well as Vnukovo and Ramenskoye.

10. For the effective operation of the two existing lanes, one more locator will have to be put into operation, which has already been built on the territory of the airport, but has not yet been interfaced with the existing TERCAS air traffic control system (TERCAS - Terminal and En-Route Control Automated System). Three radars: one each in Domodedovo, Vnukovo and Sheremetyevo provide full coverage of the cost center, the new radar will significantly improve the operation of existing systems and cover the range from the ground to a height of 500 meters at the most accurate possible level.

11. There are plans to build a third runway, and an area of 9,550 hectares has already been reserved for future construction. Also, in connection with the expansion and increase in the number of lanes, it is planned to build a new control tower up to 100 meters high.

12. Now the airport schedule is designed in such a way that at least 40 take-off and landing operations are performed every hour from 07:00 to 23:00 in order to distribute the load over time as evenly as possible. Over the next year, with the introduction of a new airspace structure in the cost center, with both lanes operating, Domodedovo Airport will be able to provide a throughput capacity of up to 90 takeoffs and landings per hour. In 2013, the peak load was 59 operations per hour.

13. In general, the capacity of the airport is even higher than the approach can provide. This is also due to the fact that earlier the distribution of flights between the airports of the cost center was determined mainly taking into account the geographical principle: Sheremetyevo served the northern and northwestern directions and all international flights, Vnukovo served the southern and southeastern directions, Domodedovo served the eastern direction.

14. At present, in the conditions of competition between airports, the geographical principle of the distribution of aircraft flows is no longer the key one, which, along with a ban on flights over Moscow, in turn increases the load on the cost centers.

15. The height of the existing tower is 42 meters, almost the entire territory of the airport is visible from it. An overview of those sections of the runway that are closed by structures is provided with the help of video cameras.

16. In a calm working atmosphere prevailing in the ATC procedure room, it is hard to believe that the people behind the consoles are representatives of one of the most stressful and responsible professions!
17. Dispatchers have 6 shifts, each with 10 people: a flight director, a senior dispatcher and 8 dispatchers (this is a payroll, in fact 6-7 people work at the same time). The dispatcher's work schedule should not exceed 36 hours per week. Dispatchers go on shift according to the schedule: day, morning, night. When leaving for a shift, a 15-minute briefing is carried out, another 15 minutes are spent on the acceptance / delivery of duty. After two hours of work, a 20-minute break is required, and at high intensity, close to airport capacity, a 10-minute break after each hour of work. After the night shift, three days off are provided. Vacation is 28 basic days and 39 additional days for harmful working conditions, which in total is 67 days.

18. Charming Natalia for several years of work on the tower in Domodedovo managed to visit many difficult situations - such is the job of a dispatcher. But the thought of changing jobs never arose. Even in her youth, she chose this profession for herself, and it could hardly have been otherwise when the whole family worked at the airport. Girls in air traffic controllers used to be taken with great reluctance, but today the situation has leveled off. Young professionals are in great demand today, and this problem no longer exists.

19. Each controller passes a medical examination every two years, and every three years is required to receive a certificate of English proficiency in ICAO category IV. Dispatchers retire at the age of 50, but this does not mean that the employee should immediately quit. If the medical board allows, and it is almost the same for air traffic controllers as for pilots of civilian ships, then people continue to work. The main criterion in this case is health.

20. At the time of the survey, lane 14L was controlled by one controller, and the adjacent one (14R) by two. At that time, planned work was carried out at the end of runway 14L, and landing on it was not carried out, respectively, and the load was less. Whereas runway 14R worked for both takeoff and landing, and it was served by two controllers: the control controller (works directly with the aircraft crews - conducts radio exchange) and the support controller (controls traffic, provides interaction with other services, keeps a log of takeoffs / landings and assists management, including operation of runway lighting equipment). The senior dispatcher is responsible for the distribution of employees, guided by the current situation.

21. An electrical engineer on duty checks the runway lighting equipment (we hope that we will be able to get to know the operation of this equipment better next time). The runway lights are manually adjusted by the controller depending on meteorological visibility. The weather display shows visibility at three points: at the beginning, in the middle and at the end of the runway. The illumination intensity is selected according to the minimum meteorological visibility. If the visibility at least at one of the points is less than 600 meters, the dispatcher informs the crew of its values at all three points. If visibility is between 600 and 2000 meters, only one value is reported (in the touchdown zone). If the visibility is more than 2000 meters, its value is not reported at all. Crews receive all meteorological information, including visibility, from an automatic informant (ATIS - Automatic Terminal Information Service). At the request of the aircraft crew, the intensity of runway lights may be changed.

22. In general, over time, the work of the controller, having passed the stage of aircraft control, has been transformed more into a service. Nowadays, the main task of air traffic controllers is to provide crews with aeronautical and meteorological information, as well as the prevention of dangerous encounters.

23. To maintain a safe interval, the vectoring method is used (to a greater extent during landing approach). Vectoring is the provision of aircraft navigation guidance by indicating certain courses to crews based on the use of radar data. The main difference between the vectoring phase and other flight phases is that the responsibility for navigation in this case is assumed by the controller. Vectoring ends either with a clear indication to the crew of the need to continue navigation using their own means, or by bringing to a course that will allow them to independently (using the technical means of the landing approach system, for example, CGS) bring the aircraft to the landing straight, or by entering the visual maneuvering zone. This is done by changing either course or speed.

24. If there is a threat of a reduction in the safety interval on the pre-landing direct line, the controller may give the aircraft a go-around command. An interval of 5 kilometers is considered safe, and for a heavy aircraft (more than 136 tons) - 10 kilometers. The second possible reason for the go-around command may be the presence of obstacles on the runway. In all other cases, the decision to go-around is made by the pilot-in-command.

25. The head of the traffic service of the Domodedovo ATC center, Viktor Aleksandrovich Sitnikov, demonstrates a visual diagram, looking at which one can assess the degree of orderliness of air traffic. For comparison, green and red stripes on the left diagram indicate the daily trajectories of take-offs and landings of aircraft at London Heathrow Airport, and on the diagram on the right, the areas of overflight by aircraft of the Moscow air zone are colored in blue.

26. These are just the general basics of air traffic control at the airport, it is impossible to cover all the features of this complex and multi-level system within the framework of one story. But the main thing is that everything in it is subject to one common requirement - ensuring the order and safety of aircraft flights. The fulfillment of this global task, in conjunction with the work of other services, is the key to a pleasant flight for the passenger.

27. Well, about the magnificent views from the control tower, especially at sunset, you don’t even need to talk, it’s enough to see once - there really is a place for the eye to rest.
We would like to thank the press center of the Moscow Air Traffic Control Center and the press service of Domodedovo Airport for organizing this event and assisting in the photography. Special thanks to Viktor Alexandrovich Sitnikov, head of the traffic service of the Domodedovo ATS Center, for a very informative and interesting story about the work of dispatchers!