Types of Schengen visas
Currently, there are categories of states that have decided to simplify the process of checking passports and control the movement of immigrants.
In addition, they decided to simplify the rules for entry and movement around the area. This category includes the main European representations, united by a single Schengen area.
The residents are able to cross the border between these states with the complete absence of any possible restrictions.
Full list of Schengen countries:
- Austria;
- Belgium;
- Hungary;
- Germany;
- Greece;
- Denmark;
- Iceland;
- Spain;
- Italy;
- Latvia;
- Lithuania;
- Luxembourg;
- Malta;
- Netherlands (Holland);
- Norway;
- Poland;
- Portugal;
- Slovakia;
- Slovenia;
- Finland;
- France;
- Czech Republic;
- Switzerland;
- Sweden;
- Estonia;
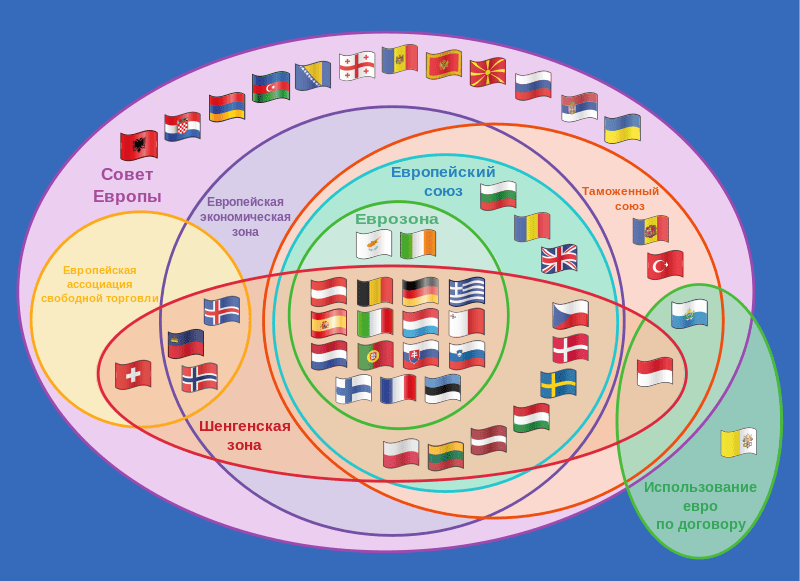
CountriesEuropean Community:
- Austria;
- Belgium;
- Bulgaria;
- Great Britain;
- Hungary;
- Germany;
- Greece;
- Denmark;
- Ireland;
- Spain;
- Italy;
- Cyprus;
- Latvia;
- Lithuania;
- Luxembourg;
- Malta;
- the Netherlands;
- Poland;
- Slovakia;
- Slovenia;
- Portugal;
- Romania;
- Finland;
- France;
- Croatia;
- Czech Republic;
- Sweden;
- Estonia.
Members of the Eurozone and their location on the map:
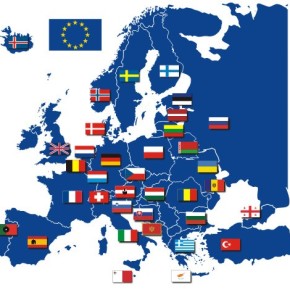
- Austria;
- Belgium;
- Germany;
- Greece;
- Ireland;
- Spain;
- Italy;
- Cyprus;
- Latvia;
- Lithuania;
- Luxembourg;
- Malta;
- Netherlands;
- Portugal;
- Slovakia;
- Slovenia;
- Finland;
- France;
- Estonia.
Citizens of countries outside these communities must obtain permits for entry.
Types of Schengen visas
A person who is going to visit one of the above zones is recommended to study main types of entry permits and how they are issued.

- Type "A": airport: this visa allows presence in the area of the local terminal. Other types of movement are strictly prohibited.
- Type "B": is provided to a person moving around a foreign region by public transport. Its validity period is from 1 to 5 days.
- Type "C": is provided to certain categories of citizens for free entry into the region. These include: guests, tourists and business travelers. It is also called short term. Its effect is less than 90 days.
For guests, this visa is issued only if there is an invitation from a person who is a citizen of this country.
A tourist visa is issued only for those citizens who carry out tourist trips. Other activities for this category of citizens are prohibited.
It should be remembered that it has some limitations. For example, for the import of funds. Information about this can be obtained by contacting the consulate in person.
Its validity period is from 15 to 90 days.
Businessmen are granted the right to enter only for the period of business meetings and negotiations. Registration of the entry visa is carried out by the inviting company.
It must be remembered that this visa is not required for persons with a visa-free entry type, i.e. belonging to one of the above countries.

In addition, the entry visa also has the following types:
- C1– stays in the country for up to 30 days;
- C2 and C3– up to 90 days at 6 and 12 months;
- C4– presence up to 90 days, however, valid from 1 to 5 years.
It should be remembered that in cases of the likelihood of termination of stay in the country or a return planned during the trip, it must be indicated in the process of filling out documents.
- A multivisa ensures entry only through the state that issued the permit. Its duration is 180 days, as well as 1 and 3 years. Features of its provision and use depend solely on individual circumstances and on the state from which the entry is made.
Restrictions: it provides multiple entry, but it should not exceed 90 days.
Citizens can make multiple entries into the country until the limit for visiting is spent.
One of the most common visas is the C1 type. Its advantages are based on the ease of obtaining, since the rest are very difficult to obtain.
If this visa is obtained, a multiple-entry visa may be granted on the next visit.
- Type "D": carries out entry for a long time and stay in the country for more than 90 days. It also provides for the provision of residence in the Schengen area and any movement within the area for a period not exceeding three months.
- TypeFTD: issued only to vehicles moving from the borders of the Russian Federation and to Kaliningrad.
- TypeLTV: granted for a short time when traveling within the country whose consulate issued it.
A state can apply such a visa in its area at any time it needs and also cancel it without hindrance.
How to apply for a Schengen visa?
It is quite easy to get a long Schengen to any country if you follow the rules.
Documents to be presented at the embassy:
- Foreign passport (real and those that have expired);
- 3 photos;
- Accounting documents;
- Certificate from the bank on the status of the personal account;
- Papers on family and social status and on the position of the individual in society;
- Insurance;
- Copies of all pages of an identity document.
Addresses of the embassies of the Schengen countries:
- Austrian: Starokonyushenny lane, 1;
- Belgian: st. Malaya Molchanovka, 7;
- Republic of Bulgaria: st. Mosfilmovskaya, 66;
- Great Britain: Bolshoy Savvinsky lane, 12, building 18;
- Republic of Hungary: st. Mosfilmovskaya, d.62;
- Germany: Leninsky prospect, 95 "A", (entrance from the side of Akademika Pilyugin street);
- Greece: Trubnikovsky lane, 23;
- Spain: Bol. Nikitskaya st., 50/8;
- Incoming kingdoms of Spain: Stremyanny Lane, 31/1;
- Institution accepting documents to Spain: Cow Val 1A, building 2;
- Italy: Yakimanskaya Embankment, 10;
- Canada: Starokonyushenny lane, 23;
- Cyprus: Povarskaya st., 9;
- Republic of Lithuania: Borisoglebsky per. 10;
- Maltese: st. Koroviy Val, 7, apt. 219;
- United States of Mexico: B. Levshinsky lane, 4;
- Netherlands: Kalashny lane, 6;
- Norway: st. Povarskaya, 7;
- Republic of Poland: st. Klimashkina, 4;
- Portugal: Groholsky per., 3/1;
- America: Bolshoi Devyatinsky lane, 8;
- Finland: Kropotkinsky lane, 15-17;
- France: st. B. Yakimanka, 45;
- Center of France: st. Marxistskaya, 3, building 2;
- Czech Republic: st. Y. Fuchik, 12/14;
- Switzerland: trans. Ogorodnaya Sloboda, 2/5;
- Sweden: Mosfilmovskaya st., 60.
Consular fee
When applying for it at the embassy: is 35 Euro

The following are exempted from its payment:
- Citizens who are related to any citizen from the Schengen countries
- People crossing the border for health purposes
- People belonging to the category of persons with limited liability, as well as persons accompanying them
- Students and other persons crossing the border for educational purposes
Consular fee at the visa department or consulate: in addition to the usual consular fee, an additional service fee is also paid, its size depends on the country of visit:
- Greece: 880 rubles, through a travel agency - 70 Euro; child – 25 Euro
- Spain: 1180 rubles, with urgent registration an increase of 55 Euro
- Italy: 1350 rubles
- Germany: category "D" - 30 Euro, category C - 35 Euro
- France: 1124 rubles
- Czech Republic: 35 Euro, urgently 70 Euro. Issued exclusively at the embassy
- Bulgaria: 54 EUR
- Finland: At the Moscow Embassy 21 Euro, in other cities 25 Euro
- Cyprus: Since 2016, the issuance of electronic and regular provisions has been allowed. With independent registration, the procedure is free, in travel agencies it is 100 Euro
Travel agencies: two fees are paid, plus the services of a travel agency.
Extension of the Schengen visa
If the visa has expired, and staying in the country is required for certain circumstances, citizens can apply for an extension of the visa.

For this you need:
- Find out the name and opening hours organizations dealing with this issue.
- Give a clear and concise reason extensions: force majeure and emergency circumstances related to the illness of the citizen himself or a close relative.
- Collect documents confirming the right to extend the visa and fill out a questionnaire.
- Apply accordingly on the extension of the visa, as well as a passport. In addition, you must provide a valid visa and documents on the right to extend. The extension of the visa is carried out for a period not exceeding 90 days. The appeal process takes 10 business days.
- In case of refusal need to issue new entry documents.
Appeal against refusal of a Schengen visa
There are precedents when the state refuses extradition.

What is causing the rejection:
- Misuse valid entry documents - the consulate strictly controls the flow of incoming and outgoing tourists.
- Threat to security and violation of agreements between states.
- Submission of false information about a citizen when applying for a visa.
- Expired personal documents.
- The purpose of visiting the country is permanent residence.
- The questionnaire was filled out incorrectly.
Upon receipt of a refusal, a citizen should write documents for appeal. Its registration must be carried out in accordance with the laws of the country of entry.
Each country has its own procedure for filing an appeal and specific competent authorities considering them:
- Belgium: the complaint is sent to the State Council in the form of a petition, written in a certain form, executed by registered mail within 30 days from the date of receipt of the letter of refusal.
- Denmark: documents are submitted without any specially established procedures to the Ministry of Immigrant Affairs. The document must indicate personal data, permanent place of residence, all data on the written application. In case of repeated refusal, the document is submitted to the Danish court.
- Finland: the decision to refuse a Finnish visa is not subject to change
- France: the reasons for the refusal are not subject to publicity if the citizen is related to another person residing in Europe, and also if there is a notice of violations in the information center. In this case, the tourist draws up a complaint to the Commission. Papers to appeal the decision are submitted no later than 60 days from the date of the decision to refuse. The commission, when considering, may refuse extradition or give letters of recommendation to the Minister of Foreign Affairs. When a negative decision is made by the Commission, a citizen may submit documents for appeal no later than 2 months from the date of receipt of the decision to the State Council. The Council of State does not have the right to decide on the issuance or refusal of a visa. Considering that the appeal made by the Commission is accepted, the Minister for Foreign Affairs shall decide otherwise. Papers are also submitted to the State Council, provided that the previous documents of appeal have not been considered.
- Germany: documents are submitted to the authorized bodies that are reviewing the verdict. Papers are provided within one month. All competent authorities can be found at the Embassy.
- Italy: the competent authorities notify of the negative opinion in a language accessible to the applicant. A citizen within 60 days has the right to apply for a review of the decision to the Administrative District Court of the Lazio region.
- Luxembourg: a request for a review of the case is submitted to the Administrative Tribunal within three months. You should be aware that this body does not make decisions on the issuance of visas. If a negative conclusion is issued again, the case is returned for reconsideration.
- Netherlands: Appeal papers are submitted within one month.
- Norway: documents for revision are submitted within three weeks. If the paper is submitted to the consulate, then for its consideration it is sent to the Office of Foreigners.
- Spain: the duration of the appeal is two months. Papers are filed at the Tribunal Superior de Justicia de Madrid.
- Sweden: verdicts are considered unilaterally and a cancellation complaint cannot be filed.
Schengen rules
These rules are based on the fact that any person who has received the opportunity for freedom of movement in another country must comply with the strict implementation of the rules and regulations provided for in that country by law.

Rules:
- Initial entry only through the country that issued the visa.
- When a citizen is in several places of stay A visa is obtained where the stop takes the most time. The main country is clarified before the process of processing any documents.
- If you have a multivisa for a period of 2180 days, the period of a single stay of a citizen should not exceed 90 days.
New rules
In 2015, the Visa Information System was created, containing information about all citizens entering and moving in the Schengen area.
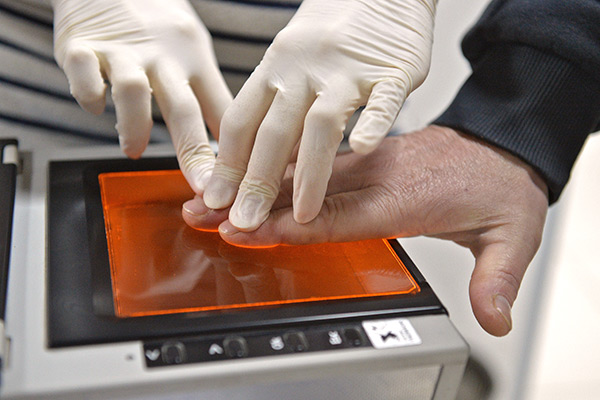

The new rules require:
- Bring high quality photos a citizen with fingerprints: they are stored for about 5 years in the database and are provided to any country party to the agreement
- Multivisa, is obtained and updated according to the data in the database. A new visa is granted after 5 years.
- The system contains information about all previously written petitions and decisions on them.
Get travel medical insurance
Entry to the Schengen zone for Russians
In order to get into the Schengen zone, Russian citizens need to obtain a type "C" visa, which can be single and multiple.

- Single entry visa: exercise the right to enter once or twice, but for a period not exceeding 90 days. It should be remembered that with it the first entry rule necessarily applies, i.e. through the country that issued the visa.
- Multiple entry visa: a citizen is granted the right of several entries for a certain period. This period is marked on the visa.
They are: tourist (30 days, 1 and 2 years); educational (study time), business (5 years); guest and working (working hours or by invitation).
To grant Russian citizens the right to enter the Schengen area, it is necessary to issue the following list of documents provided above.
The situation with the Schengen agreement in connection with the flow of illegal immigrants
Emigrants are increasingly trying to penetrate the cheap Schengen countries. In connection with the aggravation of this situation in the countries that are parties to the agreement, passport control is in effect. It operates in Germany, Austria, France, Denmark, Sweden, Norway.
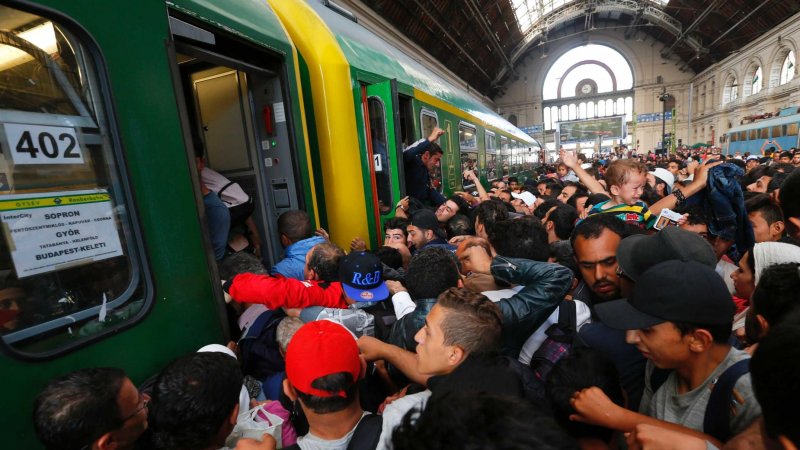

Hungary fenced itself off from Croatia, Serbia and Slovenia, so in these countries the question is raised about the application of additional security measures up to 2 years.
Towards EU membership/ Candidate countries
The main countries candidates for joining the European Union are:
- Spain;
- Macedonia;
- Serbia;
- Turkey;
- Montenegro.

Potential Candidates
Countries that are not members of the European Union but are seeking to join it include:
- Bosnia;
- Herzegovina.
UK and Ireland – separate visas required
These countries are included in the Schengen Agreement, but have reserved the right to carry out personal passport control on the territory of their country.
Until 2016, tourists visiting the UK were free to travel to Ireland. However, these conditions did not apply in reverse order.
Bulgaria, Romania and Cyprus are not included in the Schengen
Bulgaria and Romania have been preparing for the entry into the Schengen zone for 8 years. However, there are no clear dates for their entry yet.

Countries such as France, the Netherlands and Germany prevent the entry of Romania and Bulgaria. With the advent of 2016, the situation has not changed.
The planned entry date was the spring of 2016, but due to political repression by illegal immigrants, many note that this issue has not been resolved.
Croatia prepares to join the Schengen
2013 was marked by the fact that Croatia entered the EU zone. However, it is still missing from the Schengen Agreement.

This situation suggests that the national visa obtained in this country does not give the right to enter the Schengen area.
The original entry date was July 2015. However, the situation for 2016 shows that there are no changes on this issue either.
When planning trips to countries that are part of the Schengen area, it is necessary to clearly study the procedure for processing documents for issuing a visa, as well as the addresses and opening hours of embassies.
Before going to the embassy, it is necessary to analyze possible questions from the employees of this institution.
In advance, you should familiarize yourself with the competent authorities and the procedure for filing an appeal in case of refusal.




