Double-decker Boeing 747. Uncomfortable seats in the cabin
Boeing 747- the very first wide-body aircraft in the history of aviation, as well as one of the most recognizable airliners in the world. He even got an informal nickname - "Jumbo Jet" (Jumbo Jet). For 37 years, the Boeing 747 held the record for the largest passenger capacity, and today it is the longest passenger aircraft on the planet. Its history began in 1969, and since then Boeing has been constantly improving the design of this airliner family.
Story
 The need to develop the Boeing 747 arose during the boom in air travel in the 1960s. The Boeing 707, which dominated the US air travel market at the time, was already struggling to keep up with the growing flow of passengers. Prior to this, Boeing had already been developing a large transport aircraft for the US Army, but then the corporation lost to the Lockheed project and their C-5 Galaxy aircraft.
The need to develop the Boeing 747 arose during the boom in air travel in the 1960s. The Boeing 707, which dominated the US air travel market at the time, was already struggling to keep up with the growing flow of passengers. Prior to this, Boeing had already been developing a large transport aircraft for the US Army, but then the corporation lost to the Lockheed project and their C-5 Galaxy aircraft.
In 1965, design engineer Joe Sutter, who was working on the Boeing 737 at the time, was appointed chief designer of the Boeing 747. He began his job by identifying the needs of airlines. At the time, it was believed that huge aircraft would soon be superseded by supersonic aircraft. Therefore, the 747 was originally designed as a cargo-passenger aircraft. Over time, it was even planned to completely re-equip all aircraft into cargo ones. The cockpit was placed on the upper deck specifically in order to be able to convert the nose of the aircraft into a cargo ramp.
In 1966, the Boeing Corporation completed the design and presented the configuration of a new aircraft, designated 747. The original design was a fully double-deck aircraft, however, some difficulties arose with this configuration, and the scheme was abandoned in favor of the "humped" version. The first customer was Pan Am, which ordered 25 Boeing 747-100s.
Moreover, thanks to Pan Am recommendations, important changes were made to the design of the aircraft, in particular: the wingspan was increased, the placement of the landing gear was changed, and the maximum takeoff weight was increased from 272155 kg to 308443 kg.
jumbo jet
Not surprisingly, the early press reports that followed Boeing's official announcement were heavily loaded with adjectives that signified significance. Everything about the Boeing 747 was on a gigantic scale, and very soon it was called a bulky aircraft (“jumbo-sized”), which led to the nickname “Jumbo Jet” (bulky jet liner).
Production
 The decision to start production of the Boeing 747-100 was made on July 25, 1966. following additional orders from Japan Airlines and Lufthansa.
The decision to start production of the Boeing 747-100 was made on July 25, 1966. following additional orders from Japan Airlines and Lufthansa.
Boeing made a promise to Pan Am to deliver the first aircraft by 1970 - that is, it was necessary to develop, build, test and certify the aircraft in less than 4 years. The work went very quickly, but the enormous costs of the corporation for the construction and development of the aircraft almost put Boeing on the verge of bankruptcy.
The problem was that Boeing didn't have the hardware to produce such gigantic aircraft. Especially for the release of the Boeing 747, a new factory was built in the small town of Everett, Washington, which became the home for a new family of aircraft. For reference, today in this workshop, Boeing assembles models: 747, 767, 777, 787. And the building itself has a record volume of 13.3 million cubic meters.
Especially for the Boeing 747, Pratt & Whitney developed a huge turbofan engine with a high bypass ratio - JT9D. In order to increase the level of safety and flight performance of the aircraft, 4 redundant hydraulic systems and slotted flaps were installed on the 747, which made it possible to use the aircraft on relatively short runways.
 While testing the aircraft for airworthiness certification, Boeing developed an unusual training device known as the Waddell Van, named after Boeing 747 test pilot Jack Waddell. The device consisted of a mock-up of a Boeing 747 cockpit mounted on the roof of a truck. Such a simulator was designed to teach pilots to steer a giant airliner from a high position in its cockpit.
While testing the aircraft for airworthiness certification, Boeing developed an unusual training device known as the Waddell Van, named after Boeing 747 test pilot Jack Waddell. The device consisted of a mock-up of a Boeing 747 cockpit mounted on the roof of a truck. Such a simulator was designed to teach pilots to steer a giant airliner from a high position in its cockpit.
On September 30, 1968, the Boeing 747 was rolled out of the hangar for public display, and on February 9, 1969, it made its first test flight.
Boeing has invested heavily in the development of this aircraft. A few months before the delivery of the first 747-100, the company was forced to turn to bankers for additional funding to complete the project. During this period, Boeing's debt to investors amounted to about $2 billion. Boeing President William Allen later clarified, "It was too big a project for us."
But, despite all this, the Boeing 747 was a massive success. In the wide-body aircraft segment, the airliner held a monopoly for many years. And, of course, it paid off.
Airlines and Boeing 747
 At first, major airlines were somewhat skeptical about the new aircraft. The fact is that at the same time, McDonnell Douglas (taken over by Boeing in the 90s) and Lockheed were also developing three-engine wide-body aircraft much smaller than the 747. Many airlines believed that the 747 would not justify itself on long-haul routes and would not economical, like McDonnell Douglas DC-10 and Lockheed L-1011 TriStar aircraft. In addition, the fact that, due to its size, the 747 may not be suitable for airport infrastructures, raised doubts.
At first, major airlines were somewhat skeptical about the new aircraft. The fact is that at the same time, McDonnell Douglas (taken over by Boeing in the 90s) and Lockheed were also developing three-engine wide-body aircraft much smaller than the 747. Many airlines believed that the 747 would not justify itself on long-haul routes and would not economical, like McDonnell Douglas DC-10 and Lockheed L-1011 TriStar aircraft. In addition, the fact that, due to its size, the 747 may not be suitable for airport infrastructures, raised doubts.
First of all, the concern of air carriers was caused by the high fuel consumption of the Boeing 747 (compared to the three-engine aircraft described above). Many airlines immediately announced their reluctance to purchase this aircraft due to the threat of a sharp increase in ticket prices.
As a result, the concerns of air carriers were justified. The fuel crisis of the 1970s caused a rapid rise in oil prices, and as a result, a reduction in air travel. Airlines faced the problem of the unprofitability of the Boeing 747: due to high ticket prices, the planes flew half empty. American Airlines installed pianos and bar counters instead of seats to attract passengers, but these measures were not enough. Subsequently, the company converted all aircraft into cargo aircraft, then sold them. After some time, Continental Airlines did the same with their aircraft.
New aircraft: McDonnell Douglas DC-10, Lockheed L-1011 TriStar, and later - captured a large part of the wide-body aircraft market. With the release of these aircraft, many air carriers almost immediately abandoned the 747 in their favor.
Boeing 747 evolution
 Since entering the airline industry in 1970, the Boeing 747 has continued to be upgraded. Almost immediately after the base model 747-100, modifications appeared: 747-100B (a model with increased takeoff weight), as well as 747-100SR (a model with an increased number of passenger seats, but a shortened flight range).
Since entering the airline industry in 1970, the Boeing 747 has continued to be upgraded. Almost immediately after the base model 747-100, modifications appeared: 747-100B (a model with increased takeoff weight), as well as 747-100SR (a model with an increased number of passenger seats, but a shortened flight range).
In 1971, Boeing released a modification that differed from the base model with more powerful and reliable engines, as well as increased takeoff weight. The aircraft was offered in both passenger and cargo versions. Modification 747-200SR appeared in 1976.
In 1980, the model was released. The upper deck of the aircraft has become longer, respectively, and the passenger capacity has increased. More modern engines were put on the plane, thanks to which the speed and takeoff weight of the liner also became greater.
But the design of the liner underwent serious changes with the release of the modification. First of all, the cockpit has changed: computers were installed on the aircraft that calculate various flight parameters, the data on which are displayed on the displays (Glass Cockpit). Thus, the control of the aircraft was optimized, and the crew was reduced from 3 to 2 people.
 As for the fuselage, composite materials were used in its design, which made it possible to reduce the weight of the aircraft. Wingspan compared to 747-300 was increased by 4.8 meters. The liner received modern powerful and reliable engines. Take-off weight and flight range, compared with previous modifications, have been significantly increased.
As for the fuselage, composite materials were used in its design, which made it possible to reduce the weight of the aircraft. Wingspan compared to 747-300 was increased by 4.8 meters. The liner received modern powerful and reliable engines. Take-off weight and flight range, compared with previous modifications, have been significantly increased.
The interior has been redesigned to give the passenger as much personal space as possible. And in general, the aircraft has become quieter, more powerful and faster than all previous modifications of the Boeing 747.
In 1996, Boeing showed off designs for the 747-500X and 747-600X. However, the development of these versions could cost about 5 billion dollars, so there was not much interest in them. In the end, many of the ideas proposed for the 747X family were implemented on the 747-400ER (extended range version), which entered commercial service in 2002.
The last aircraft of the 747-400 modification was released in 2009.
747-8 - a new generation long-haul liner
 On November 14, 2005, Boeing Corporation announced the launch of a new airliner development program. The aircraft was completely redesigned in accordance with the technologies introduced into the new liner. It was assumed that the 747-8 will have the same engines and cabin as the 787, and it also partially (in some channels) uses a fly-by-wire control system. Boeing said the new aircraft will be quieter, more fuel efficient and more environmentally friendly than previous versions of the 747. As an evolution of the 747-400 already in use, the 747-8 will save on staff training and interchangeable parts.
On November 14, 2005, Boeing Corporation announced the launch of a new airliner development program. The aircraft was completely redesigned in accordance with the technologies introduced into the new liner. It was assumed that the 747-8 will have the same engines and cabin as the 787, and it also partially (in some channels) uses a fly-by-wire control system. Boeing said the new aircraft will be quieter, more fuel efficient and more environmentally friendly than previous versions of the 747. As an evolution of the 747-400 already in use, the 747-8 will save on staff training and interchangeable parts.
In October 2006, Boeing approved the cargo version of the 747-8 Freighter. Construction of the first 747-8 Freighters began at the Everett, Washington plant in early August 2008.
The first flight, cargo Boeing 747-8F made February 8, 2010. And on March 20, 2011, the passenger Boeing 747-8 went on its first flight.
Technology in 747-8
 When creating the 747-8, new Boeing advances in technology and aerodynamics were applied. Recall that both versions of the aircraft began to be developed back in 2005, and by 2006 both of them differed from the 747-400 by a fuselage lengthened by 5.6 m.
When creating the 747-8, new Boeing advances in technology and aerodynamics were applied. Recall that both versions of the aircraft began to be developed back in 2005, and by 2006 both of them differed from the 747-400 by a fuselage lengthened by 5.6 m.
After receiving all the certificates, the 747-8 became the longest passenger liner in the world, surpassing the previous record holder by 90.5 cm.
With a maximum takeoff weight of 442 tons, the 747-8 is the heaviest aircraft (among both civilian and military) created in the history of the United States. Compared to the 747-400, the main technical changes are in the wing, which has been completely redesigned. The sweep angle and power set of the wing is retained to reduce costs, but the wing has become thinner and wider, with completely recalculated aerodynamics. The pressure distribution and bending moments of the wing are different, moreover, it now holds more fuel. The outer sections of the flaps on the wing are single-slotted, and the inner sections are double-slotted.
 The 747-8 uses ridged wingtips similar to those used on the , and they are different from the 747-400 winglets. These wingtips are designed to reduce tip vortices, reducing wake and drag, and thereby reducing fuel consumption. Another attempt to reduce weight was the availability of a fly-by-wire control system for most of the lateral controls.
The 747-8 uses ridged wingtips similar to those used on the , and they are different from the 747-400 winglets. These wingtips are designed to reduce tip vortices, reducing wake and drag, and thereby reducing fuel consumption. Another attempt to reduce weight was the availability of a fly-by-wire control system for most of the lateral controls.
The increased fuel capacity of the redesigned wing, compared to the 747-400, avoids radical changes to the stabilizer design to accommodate additional fuel, which allows for additional fuel savings.
The 747-8 keel remained the same, 19.35 m high. To reduce weight, a composite material, carbon fiber, was partially used in the 747-8 airframe design.
Boeing 747 modifications
To summarize: the development of the first modification - the Boeing 747-100 began in 1966. In 1971, the operation of the 747-200 began. In 1980, the 747-300 was born, and in 1985, the 747-400. Operation of the new generation of Boeing 747-8 aircraft began in 2010.
 On the upper deck of the first modification of the Boeing 747-100 there was a living room. It is noteworthy that she had only 6 portholes (3 on each side). Later, when airlines adapted the upper deck for business class, Boeing offered the installation of 10 windows as an option.
On the upper deck of the first modification of the Boeing 747-100 there was a living room. It is noteworthy that she had only 6 portholes (3 on each side). Later, when airlines adapted the upper deck for business class, Boeing offered the installation of 10 windows as an option.
Boeing 747-100 aircraft are equipped with Pratt & Whitney JT9D-3A engines.
The modification does not have a cargo version, although later the old passenger aircraft were converted into cargo ones. A total of 167 Boeing 747-100 series aircraft were produced.
747SR (Short Range)
 Japanese airlines approached Boeing to create a version of the aircraft capable of carrying large numbers of passengers on the country's domestic flights. Thus, the Boeing 747SR was born - an aircraft with a shortened flight range, but a significantly increased passenger capacity. Early versions of this modification could accommodate up to 498 passengers, while later versions were equipped with 550 or more seats. The Japanese enthusiastically accepted this modification. It was very fuel efficient, and most importantly, the aircraft resource was provided for a greater amount of time than conventional modifications of the Boeing 747, thanks to the reinforced fuselage and landing gear.
Japanese airlines approached Boeing to create a version of the aircraft capable of carrying large numbers of passengers on the country's domestic flights. Thus, the Boeing 747SR was born - an aircraft with a shortened flight range, but a significantly increased passenger capacity. Early versions of this modification could accommodate up to 498 passengers, while later versions were equipped with 550 or more seats. The Japanese enthusiastically accepted this modification. It was very fuel efficient, and most importantly, the aircraft resource was provided for a greater amount of time than conventional modifications of the Boeing 747, thanks to the reinforced fuselage and landing gear.
747SP (Special Performance)
 The modification of the Boeing 747SP was developed in 1976. This aircraft was created in order to seriously compete with the DC-10 and L-1011. The fact is, because of its size, Boeing was often unprofitable on medium-busy routes, and lost to McDouglas and Lockheed on them. The development of the Boeing 737 and 747 took too much money from the company, so Boeing did not have the opportunity to create a fundamentally new aircraft. Instead, the 747 had a shortened fuselage and some optimization of the aircraft parameters specifically for light traffic routes.
The modification of the Boeing 747SP was developed in 1976. This aircraft was created in order to seriously compete with the DC-10 and L-1011. The fact is, because of its size, Boeing was often unprofitable on medium-busy routes, and lost to McDouglas and Lockheed on them. The development of the Boeing 737 and 747 took too much money from the company, so Boeing did not have the opportunity to create a fundamentally new aircraft. Instead, the 747 had a shortened fuselage and some optimization of the aircraft parameters specifically for light traffic routes.
In addition to the shortened fuselage, the 747SP has an increased fin surface area and modified wing mechanization. 747SP took on board up to 220 passengers. The maximum flight range was 10,500 km at a cruising speed of 980 km/h.
Prior to the introduction of the Airbus A340, the 747SP had the longest range of any passenger aircraft and was popular with transoceanic carriers. Despite its technical advantages, the 747SP did not become as popular as the manufacturer had hoped. Only 45 aircraft of this modification were built. Most of them are still operated mainly in the Middle East. One aircraft was later converted into a flying astronomical laboratory - SOFIA (Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy). It has a telescope with a diameter of 2.5 meters.
747-100B
 Modification 747-100B was developed simultaneously with 747SR. It differs from the usual modification 747-100 in increased takeoff weight and additional fuel tanks. For the Japanese airlines JAL and All Nippon Airways, the 747-100В SR modification was specially produced, intended for the transportation of 550-624 passengers on routes of 3000-3500 km. Aircraft 747-100B served as the basis for the creation of various modifications of passenger and cargo aircraft 747-200B, -200F, -300, -400, SP and others. The aircraft is equipped with a conventional avionics complex with electromechanical means of data indication.
Modification 747-100B was developed simultaneously with 747SR. It differs from the usual modification 747-100 in increased takeoff weight and additional fuel tanks. For the Japanese airlines JAL and All Nippon Airways, the 747-100В SR modification was specially produced, intended for the transportation of 550-624 passengers on routes of 3000-3500 km. Aircraft 747-100B served as the basis for the creation of various modifications of passenger and cargo aircraft 747-200B, -200F, -300, -400, SP and others. The aircraft is equipped with a conventional avionics complex with electromechanical means of data indication.
 Introduced in 1971, the Boeing 747-200 had more powerful engines and increased takeoff weight, allowing for longer range. The first 747-200s on the upper deck had only 3 windows on each side, but later Boeing finally abandoned this scheme and new passenger aircraft already had ten windows on both sides. The latest modification, the 747-200B, produced since the 1980s, has been extended to 10,800 km. On the basis of the Boeing 747-200 airframe, modifications were built for the US Air Force: E-4A - a military command post, VC-25A - a liner for transporting the US president.
Introduced in 1971, the Boeing 747-200 had more powerful engines and increased takeoff weight, allowing for longer range. The first 747-200s on the upper deck had only 3 windows on each side, but later Boeing finally abandoned this scheme and new passenger aircraft already had ten windows on both sides. The latest modification, the 747-200B, produced since the 1980s, has been extended to 10,800 km. On the basis of the Boeing 747-200 airframe, modifications were built for the US Air Force: E-4A - a military command post, VC-25A - a liner for transporting the US president.
The Boeing 747-200B is an upgraded version of the 747-200 with more powerful engines and more fuel.
The Boeing 747-200C and 747-200F were designed to carry cargo. The 747-200F is a purely cargo aircraft, while the 747-200C is a convertible version, the aircraft can be easily converted from passenger to cargo.
Modification 747-200M Combi can carry passengers and cargo at the same time. The ratio is changed by rearranging the bulkheads.
Like the 747-100, many 747-200 passenger aircraft were later converted to cargo.
 Boeing 747-300 - originally conceived as a three-engine version of the Boeing 747SP, but this idea was quickly abandoned due to low market demand for such a model.
Boeing 747-300 - originally conceived as a three-engine version of the Boeing 747SP, but this idea was quickly abandoned due to low market demand for such a model.
The designation 747-300 was assigned to a new aircraft that appeared in 1980. On the liner, the upper deck was significantly enlarged, due to which the passenger capacity also increased.
Based on the 747-300, the 747-300M (cargo-passenger) and 747-300SR (short haul) variants were created. A distinctive feature of the new aircraft was a straight staircase connecting the upper and lower decks. On earlier aircraft, a spiral was installed. The maximum flight range of the Boeing 747-300 is 12,400 km.
 Model 747-400 is the most popular modification. This aircraft has added vertical wingtips (winglets). The cockpit was improved with new avionics, and therefore there was no need for a flight engineer. Were installed: additional tail fuel tanks, improved engines. In addition, the aircraft is distinguished by an increased degree of comfort.
Model 747-400 is the most popular modification. This aircraft has added vertical wingtips (winglets). The cockpit was improved with new avionics, and therefore there was no need for a flight engineer. Were installed: additional tail fuel tanks, improved engines. In addition, the aircraft is distinguished by an increased degree of comfort.
The Boeing 747-400 is 25% more efficient than the 747-300 and twice as quiet.
There are the following variants of this modification: 747-400M (cargo), 747-400F and 747-400SF (cargo). Specially designed for Japan's domestic routes, the 747-400D held the world seating capacity record until 2005, accommodating up to 594 people. It was then replaced by the Airbus A380, which in a single-class configuration can accommodate 853 passengers.
Modification 747-400ER - an aircraft with an increased flight range.
747-8 Intercontinental
 747-8 Intercontinental, or simply 747-8I, began construction on November 14, 2005. The aircraft is capable of carrying up to 467 passengers in a three-class configuration, for a distance of up to 15,000 km, at a speed of 0.855 M. Compared to the 747-400, the 747-8I carries 51 passengers and 2 cargo pallets more, and the cargo compartment has increased by 26%.
747-8 Intercontinental, or simply 747-8I, began construction on November 14, 2005. The aircraft is capable of carrying up to 467 passengers in a three-class configuration, for a distance of up to 15,000 km, at a speed of 0.855 M. Compared to the 747-400, the 747-8I carries 51 passengers and 2 cargo pallets more, and the cargo compartment has increased by 26%.
Despite initial plans to make the passenger variant shorter than the cargo variant, both modifications are the same length, making it easy to convert the 747-8I to a cargo version (a convertible variant that allows conversion from one variant to another and vice versa). Upper deck 747-8I extended. Boeing said the 747-8I is 30% quieter, 16% more fuel efficient and 13% cheaper than the 747-400 compared to the 747-400.
In 747-8 there are some changes on the decks. Most notable are the curved staircase connecting the decks and the larger main entrance for passengers. The interior of the 747-8's main cabin is similar to the advanced interior of the Boeing 787. The overhead luggage racks are curved, their center row appearing to be attached to the curved ceiling, rather than being integrated into the curve of the ceiling as on. The windows are the same size as the 777, which is 8% larger than the 747-400. 747-8 is equipped with an LED lighting system that can create a psychologically comfortable stay on board the aircraft. The LED system also provides greater reliability and lower operating costs.
747-8 Freighter
 Cargo version of the new generation liner 747-8. As on the 747-400F, the upper deck is shorter than on the passenger modification, inserts with a total length of 5.575 m are made directly before and after the wing in the fuselage. The total aircraft carrying capacity is 140 tons, and the flight range is 8130 km. On the main deck there is room for four more cargo pallets, and on the lower deck there is room for two additional containers and three additional pallets.
Cargo version of the new generation liner 747-8. As on the 747-400F, the upper deck is shorter than on the passenger modification, inserts with a total length of 5.575 m are made directly before and after the wing in the fuselage. The total aircraft carrying capacity is 140 tons, and the flight range is 8130 km. On the main deck there is room for four more cargo pallets, and on the lower deck there is room for two additional containers and three additional pallets.
Compared to the 747-400ERF, the 747-8F has a higher payload but a slightly shorter range. When Boeing released the −400ERF, with a MTOW 16t more than the 747-400F at 397-410t, it allowed air carriers to fill up more fuel, use it mid-flight and land at the same landing weight as the 747. -400F. This increased the range of the 747-400ERF compared to the 747-400F. Cargo aircraft often carry mechanisms or monoblock cargo, which requires an aircraft with a larger payload and landing weight.
For transport aircraft, it is customary to indicate the flight range with maximum load, and not with maximum fuel. The increase in the maximum takeoff weight of the 747-8th by 29 tons directly determines the weight of the aircraft without fuel, but with cargo. This caused the 747-8 to take off when fully loaded with incomplete fuel tanks. In flights without maximum load, the aircraft can take more fuel and increase the flight range.
Compared to the 747-400ERF (a cargo version of the 747-400 for long distances), the 747-8F has more payload capacity, but less (by 900 km) flight range.
747 LCF Dreamlifter
 The 747 LCF Dreamlifter is a special version of the Boeing 747 designed to transport large aircraft parts.
The 747 LCF Dreamlifter is a special version of the Boeing 747 designed to transport large aircraft parts.
In October 2003, Boeing announced that due to the lengthy shipping times, Boeing 787 parts would be transported to the final assembly site by air. For these purposes, we decided to convert the Boeing 747-400. The first test flight of the aircraft took place on September 9, 2006.
During testing of the aircraft, Boeing President Scott Carson jokingly apologized to the "father of the Boeing 747," Joe Sutter: "I'm sorry about what we did to your plane."
Thanks to the Boeing 747LCF (Large Cargo Freighter), a 787 wing made in Japan can be delivered to the US in just one day, not a month. The volume of the transport compartment Dreamlifter - 1840 cubic meters.
Special versions of the Boeing 747
 Boeing VC-25 is a special designation for the military version of the Boeing 747 passenger aircraft.
Boeing VC-25 is a special designation for the military version of the Boeing 747 passenger aircraft.
The VC-25 is best known for its role as "Air Force One", the US Air Force's name for the aircraft carrying the President of the United States. The two aircraft produced with tail numbers 28000 and 29000 are an early modification of the Boeing 747-200B, but with flight equipment and engines from the Boeing 747-400ER. While Air Force One formally refers to the aircraft only when the President of the United States is on board, it is not uncommon for the term to be applied to the VC-25 as a whole.
VC-25s often operate in conjunction with Marine One, a helicopter that takes the President of the United States to the airport in circumstances where ground transportation is not suitable. If the first lady or vice president of the United States is present on board, but not the president himself, the aircraft is assigned the code designation "Air Force One Foxtrot".
Despite the fact that the VC-25, like a regular Boeing 747, has 3 decks with a total area of 370 m², the interior has been converted for presidential needs. The lowest deck is for luggage and food supplies. The aircraft has a food warehouse with a cold store with a total capacity of more than 2,000 standard rations. Meals can be prepared in two kitchens, which together can feed about 100 people at a time. Since the luggage capacity of the aircraft only corresponds to that of the passengers, a presidential flight is usually preceded by an air convoy of transport aircraft (usually at least one C-5 Galaxy) carrying helicopters, a motorcade of cars, and other equipment necessary for the presidential entourage.
The VC-25A is capable of covering 12,600 km without refueling (corresponding to 1/3 of the length of the equator) and can accommodate more than 70 passengers. Each VC-25A costs approximately $325 million.
The main passenger area is on the middle deck, and the communication system and aircraft cabin are on the upper deck. There are 3 exits on the plane - two on the lower deck and one on the middle one. Usually the president enters through the main entrance on the middle deck, while passengers and journalists board through the entrance in the aft part of the lower deck. The conditions for the press and other passengers are the same as in the first class cabin of a regular Boeing 747.
On board the VC-25, medical equipment includes an operating table, a supply of medicines and other medical supplies that may be needed during emergency medical care.
 President George W. Bush, Jr., equipped Air Force One with a treadmill during his tenure. On each flight, there is a medical staff on board. The aircraft cabin is divided into seats for guests, senior staff, the US Secret Service, security services and media representatives.
President George W. Bush, Jr., equipped Air Force One with a treadmill during his tenure. On each flight, there is a medical staff on board. The aircraft cabin is divided into seats for guests, senior staff, the US Secret Service, security services and media representatives.
The presidential section includes a bedroom with two sofas that can be converted into a bed, a toilet, a shower and a personal office. These rooms, including the President's office, are mostly located on the starboard side, on the port side there is a long corridor. The aircraft rooms are fully equipped with telecommunications systems (including 85 telephones and 19 televisions). There are also secret and non-secret fax and digital communications.
The US Air Force is currently looking to replace Air Force One with the Boeing VC-25 (two heavily modified Boeing 747-200Bs). Boeing is reportedly considering offering the 747-8 alongside the Boeing 787 variant. On August 11, 2010, the South Korean government announced that it was considering purchasing the 747-8 as a presidential aircraft.
 E-4B - air command posts (ACP) for the president, secretary of defense and other members of the senior leadership of the United States, in the event of a nuclear war and the destruction of ground control structures. Among themselves, these liners are sometimes called “doomsday planes”.
E-4B - air command posts (ACP) for the president, secretary of defense and other members of the senior leadership of the United States, in the event of a nuclear war and the destruction of ground control structures. Among themselves, these liners are sometimes called “doomsday planes”.
The first 3 E-4As were built based on the Boeing 747-200 airframe at the Boeing factory in 1974-1978.
In 1979, an upgraded E-4B was built. Outwardly, it was distinguished by the presence of a large fairing that covered the satellite communications antennas on top of the fuselage above the upper deck. In 1980, all three E-4As were redesigned as E-4Bs. All aircraft equipment is protected from the electromagnetic pulse (EMP) of a nuclear explosion. There is a filtering system from radioactive dust in the intake and air conditioning systems for ventilation of the cabin and compartments.
The aircraft is equipped with equipment for receiving fuel from tanker aircraft. With periodic refueling in the air, the aircraft can stay in the air for a week (maybe more). The period of its duty in the air is limited only by the working life of the oil in the oil systems of engines. Full air-to-air refueling of the E-4B requires two fully fueled KC-135 tankers.
 Military experimental version of the Boeing 747, with a high power chemical laser installed in the nose of the aircraft. The aircraft is intended for US missile defense.
Military experimental version of the Boeing 747, with a high power chemical laser installed in the nose of the aircraft. The aircraft is intended for US missile defense.
747 Shuttle Carrier
The aircraft is used to transport the Space Shuttle aerospace aircraft from alternate spaceports to the main launch site at Cape Canaveral. The shuttle is attached to the fuselage from above.
KC-33A is a tanker aircraft designed to refuel fighters in the air.
747 SOFIA
SOFIA stands for Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy. In a word - an observatory aircraft. It is intended for space exploration. It is a joint project of NASA and the German Aerospace Center.
The aircraft is based on a modification of the Boeing 747SP. A large door was installed on the liner in the aft fuselage, it is designed to be opened in flight so that scientists can study the sky through the telescope installed behind it.

Specifications:

The Boeing 747 400 is a jet 2-deck passenger aircraft designed to carry more than 500 passengers. This modification of the Boeing can fly up to 14 thousand kilometers. Today, air transportation on this liner is carried out by Rossiya Airlines.
The history of the creation of the aircraft
This modification of the Boeing was created on the basis of the Boeing 747 300. In the mid-80s, the 300th modification of the Boeing did not allow to realize all the capabilities of Boeing Airplanes. In view of this, it was decided to create a new modification of the liner, which will be distinguished by an increased level of fuel economy, a longer flight range, an improved cabin and a 10% reduction in operating costs. The development of the new vessel began in 1985, and the first roll-out of the 400 took place in January 1988. By that time, about 100 orders for the production of the Boeing 400 had been received.
The first official flight of the new vessel took place on April 29, 1988. The new modification B747 stayed in flight for more than 2 hours. Test pilot James Lesh and his crew were satisfied with the results of the test tests, which allowed this vessel to receive an airworthiness certificate. On January 26, 1989, the first 400 was handed over to Northwest Airlines. And after 2 weeks, the first passenger flight of this liner took place along the route Minneapolis - Phoenix.
Interior configuration
The cabin scheme of the Boeing 747 400 of Rossiya Airlines provides for the division of seats into 2 categories: economy and business. In economy class, the distance between the seats is no more than 90 cm. At the same time, the seats recline only 60 degrees. For the convenience of economy class passengers, each seat has a folding table.
Thanks to the special design of the seats in the business class, they can be transformed into an almost full-fledged bed. The advantage of this is also considered to be a greater distance between the seats. Another plus is a special menu for passengers, free drinks and access to Wi-Fi.
The main feature of this liner is its division into lower and upper decks. The standard number of seats on the lower tier is 470. This deck is designed exclusively for economy class passengers. The basic configuration of the seats is 3:4:3. However, there are exceptions. For example, a 2:4:2 layout is used at the tail end of a vessel, and a 2:3:2 layout is used at the bow.
Important! On the lower deck there are 3 blocks of bathrooms: in the tail, between the 20th and 22nd lines, as well as at the 43rd-44th rows. The Boeing 747 400 also has dressing rooms (54-59 rows) and catering units (31-34 rows). The descent from the upper deck is located near the 31st row.
The upper deck of the liner is represented by both business and economy class. Business class seats are located from the first to the third line. Starting from the 5th row, the “higher economy class” begins. The upper tier is located in the nose of the aircraft. For the convenience of passengers of the upper tier, 2 blocks of bathrooms are equipped. The capacity of the standard upper deck is 41 seats (business - 12 and economy - 29).
Should know! There are 3 main schemes for the Boeing 747 400 of Rossiya Airlines. The EI-XLM scheme differs significantly from the standard version. In accordance with this layout, passengers can take Super Space seats on the lower deck of the aircraft. These are economy class seats with improved features. They are in the bow of the lower deck. At the same time, in EI-XLM, the entire upper deck is represented exclusively by business class seats.
Choosing the best seat on the plane
The best places on the Boeing 400 are considered to be rows 1-3 of the upper tier. This is where the business class is located with comfortable seats and monitors with a diagonal of 15.4 inches. The distance between the lines in this class is more than one and a half meters. Seats on the 5th line of the upper deck differ in increased convenience. Despite the fact that they represent the economy class, passengers occupying these seats will have a lot of free legroom. In addition, the increased comfort of the passengers of the upper tier is ensured by the presence of displays with a diagonal of 8.9 inches.
On the lower deck, seats from lines 10 to 12 are considered places of increased comfort. The comfort of these places is due to the fact that the seats are installed in pairs - 2 chairs are more comfortable than 3 or 4. These seats are intended for passengers with children. It is here that the mounts for the baby cradles are installed.
Should know! On the lower deck, the countdown starts from the 10th line.
The plan of the lower deck makes it possible to classify seats E and F in rows 17-19 among the best places on this vessel. These seats also use paired seating. 31 lines can be noted, which is characterized by a lot of free space. However, it is due to the fact that there is a bathroom nearby. In addition, place 31C is located directly next to the stairs from the upper tier.
In the EI-XLM modification, lines 1 to 4 can be classified as the best seats. It is here that the seats of the Super Space category are located.
Bad places: how not to make a mistake
It's no secret that the double-decker Boeing 747 400 has a few bad seats that can really ruin your flight experience. First of all, it is worth noting the places in the 29th line. In this row, the backs of the seats do not recline due to the proximity to the emergency exit and the bathroom. The same applies to the 19th line. Seats A, D, E and L do not recline. The rest of the seats in this row, although postponed, have significant limitations.
Holders of tickets for seat C on lines 32-34 will experience significant discomfort due to the constant plying of other passengers. This is due to the fact that these seats are in close proximity to the stairs leading to the second floor. Passengers traveling in rows 43, 54, 70 and 71 will not have the best flight experience. Due to the proximity of the emergency exits, the chairs in these places are not transformed. When studying the location of seats on this plane, it is also worth paying attention that the rows located near the bathrooms (20-22, 27-29, 41-46 and 69-71 rows) will not be the best option.
On the upper deck, it would be a mistake to buy tickets to the last row. The main disadvantage of this line is the proximity of the toilet. In addition, there is a staircase to the lower deck nearby.
Before buying a ticket for a flight operated by a Boeing 747 400, passengers should pay attention to a few very important nuances:
- You should not buy tickets for seats located near the office premises. Queues are always formed here, which creates discomfort and unnecessary noise.
- If you have a long-distance flight, then you should not take tickets for seats where the seat does not unfold.
- Passengers with small children should buy tickets to the nose of the aircraft. But for those who do not want to hear children's crying and noise, on the contrary, it is not recommended to purchase tickets in this part of the liner.
- For daytime and morning flights, it is worth buying tickets for seats near the porthole.
- Seats D and G, located in the middle of the cabin, are uncomfortable due to the constant movement of passengers and flight attendants.
Watch a video about the flight on the Boeing 747-400 Russia
The wide-body double-deck airliner of the Boeing Corporation was created at an impressive pace. For four years, the aircraft was designed and produced, and the pilots were trained at the same time. The year 1970 was marked by the launch of the first double-deck airliner Boeing-747 into commercial operation.
The transport company was founded in 1934 in Leningrad. After many years of work, in 2011 it was reorganized into OJSC Rossiya Airlines. The carrier has its head office in St. Petersburg, and the fleet is based at Pulkovo International Airport.
The commercial management of the company has been with Aeroflot since 2014. Rossiya Airlines is one of the ten best carriers in Eastern Europe and is one of the country's most punctual airlines.
Since 2016, the company's bases have been opened in several Russian cities, and the network of routes has been expanded. At a rapid pace, Rossiya is becoming number two after the parent company in the Aeroflot Group.
In the same year, Rossiya replenishes its aircraft fleet with nine Boeing-747-400ERs, previously owned by Transaero, renews the fleet livery, and establishes the tradition of naming aircraft after Russian cities.
Currently, flights are being made on almost 100 domestic routes, the international geography is expanding, it has already reached one and a half dozen countries.
The airline from the northern capital has become the official carrier of the Zenit football club.
This dynamically operating company annually increases passenger turnover and has excellent growth rates.
How to choose the best seats, interior layout
Boeing-747-400, owned by the company Russia, can accommodate 522 passengers on two decks (there are aircraft with 477 and 461 seats).

The cockpit is located on the upper deck. It is followed by three rows of comfortable business class. The rows are more than one and a half meters apart, and the seats are arranged according to the 2/2 scheme. The seats here are much wider, and LCD monitors are built into the backs.

5 row. Favorable seats, a screen in front, and plenty of legroom.
Behind row 9 of the upper saloon is a toilet, and next to it is a staircase leading to the lower deck. These places may cause minor disturbance during the flight.
The lower deck accommodates 470 passengers, there are 71 rows. The distance between the rows is 78 centimeters, a monitor is mounted in each back of the seats. Most of the interior is made according to the 3/4/3 scheme.
In the bow 10, 11 and 12 rows are arranged in two chairs on both sides of the aisle. It is convenient to travel together, these are places of increased comfort. Passengers with children can interfere with a calm flight, as there are supports for prams nearby.
19 row. Next to them are emergency exits and the backs of seats A, F, E, L can be blocked, and the backs of the remaining seats will be limited in reclining.
20,21,22 rows. There are toilets on both sides, which is not very pleasant. Aircraft of this class make long flights, and there are many people who want to visit the bathrooms. Immediately behind 22 there is a wall next to it, which will presumably prevent the unfolding of chairs.
29 row. Seats A, L do not have folding seats, due to emergency exits. There are toilets close by.
In the 31st row, A, B, C will be good places. There is free space in front of them and you can stretch your legs, sitting comfortably. The tables recline from the armrests - minus these places. Unfavorable is the proximity of the stairs at place 31C.

32-33 rows. Their place C is near the stairs.
In the rows behind which emergency exits and bathrooms are located (43, 54, 70, 71), the seat backs are limited in unfolding. It is necessary to find out this fact when buying tickets, having familiarized yourself with the scheme of the liner.
44.45 rows can be excellent places to travel, a good space in front of them is favorable for relaxation. However, the proximity to the bathrooms can overshadow the flight.
67-70 rows. Here, the outer seats near the windows stand two by two. Good location for passengers traveling as a couple.
Last row, 71. The rear seats are not comfortable, but some people need closeness to the bathroom.
Today, Russia is the only carrier that has aircraft of this brand. Aircraft operate charter flights, and the lower deck is oriented towards tourist traffic, tickets for these seats are sold at a reduced price.
Assuming a trip, it must be remembered that the Boeing-747-400 of the Russian company has different seating options. It is worth finding out where it is more convenient to sit, where the best view from the window is.
History, characteristics and modifications of the Boeing 747
At the end of the sixties, the development of a new Boeing liner began, it was supposed to have the qualities declared by the potential customer Pan American:
- Capacity for more passengers
- Capacities to fly long, intercontinental distances
- Large size (for capacity and load capacity)
- Ability to quickly convert to a cargo aircraft
It was decided to abandon the location of the upper cabin along the entire length of the aircraft, fearing for a decrease in aerodynamic conditions. The cockpit is at the top. Pilots also had to learn to fly from a high cockpit level.
A new factory was specially built to assemble the giant machine. The cost of building the aircraft paid off later, when the Boeing 747 gained popularity among carriers and travelers.
In the early 1970s, when fuel prices were too high, some airlines-owners converted aircraft to cargo needs. Nevertheless, the Boeing 747 flew, and new models appeared that could extend its life.
So, in the middle of the 2000s, a modification of the Boeing 747-400ER appeared, nine of which the Russian airline has in its fleet.
The Boeing 747-400 aircraft is an updated and modified model with improved characteristics. Outwardly, the B-747-400 is distinguished from the previous brothers by the vertical wing tips (not on all models). The crew is reduced to 2 people, thanks to electronic control. Noise and fuel efficiency is higher. Engines 4 pieces, turbofan.
Flight parameters B-747-400
- Crew - 2
- Passenger capacity - 524
- Aircraft length - 70.6 meters
- Height - 19.4 meters
- Wingspan - 64.4 meters
- Fuselage coverage - 6.5 meters
- Cabin width - 6.1 meters
- Empty weight of the liner - 180800 kilograms
- Maximum speed - 988 km / h
- Range with a full load - 14205 kilometers
- Motors - CF6-80, 4 turbojet installations
The double-deck Boeing-747-400 is gradually losing ground, yielding in efficiency and age to younger and more economical airliners. However, it has not yet fully developed its allotted resource, and is operated by many of the world's leading air carriers.
News
In 2018, a service station for Boeing wide-body aircraft owned by Aeroflot Group opens in Belgium. Maintenance will be carried out by Volga-Dnepr Technics Moscow. In the future, it is planned to open several more linear stations where it will be possible to repair and carry out technical inspections of Boeing-747, Boeing-777 aircraft. Such stations were founded by VDTM in the air harbors of Moscow (three main airports), Krasnodar and Krasnoyarsk. According to the management of the service company, a service station will soon open in Vladivostok.
The Boeing 747-400 is a sought-after jet airliner designed primarily for long-haul flights. And if you choose the right seat in the cabin, even a very long journey will fly by unnoticed. How to choose the best places? First you need to familiarize yourself with the cabin layout in order to know what places are located near the toilet room, emergency exit, above the wing of the aircraft, on the upper and lower decks. Considering these and other factors, you need to choose a place that suits your requirements and wishes so that your trip is as comfortable as possible.
Aeroflot Boeing 747-400 cabin layout
Depending on the total number of seats in the cabin and the ratio of the number of seats in business class and economy class, several models of Boeing 747-400 airliners are produced. Consider the scheme of the most common Aeroflot airliner with 522 seats.
There are two decks in the cabin of a Boeing aircraft: upper and lower.
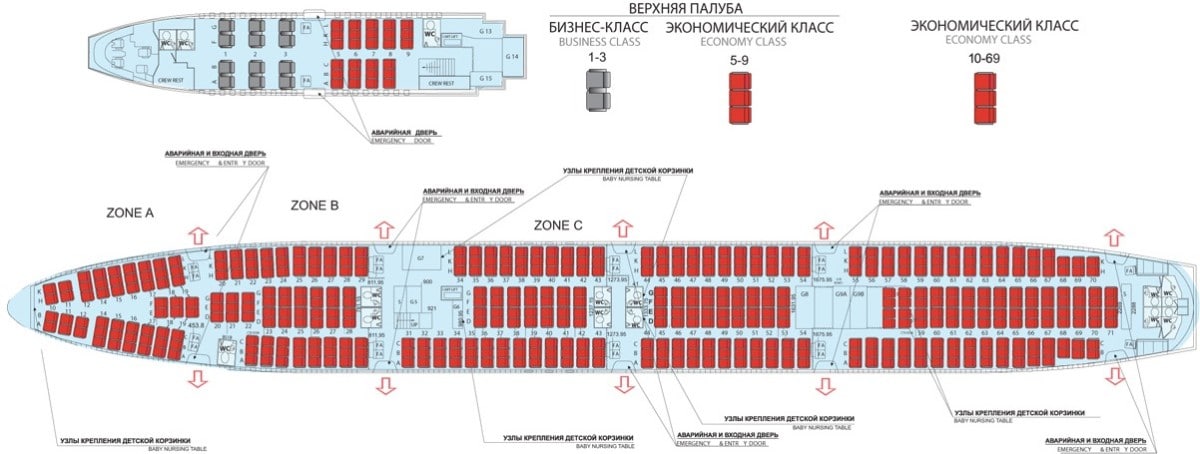
Business Class
The business class is located on the upper deck - these are rows 1 to 3. Wide seats are placed in two, there is a large distance between them, about one and a half meters. You can safely stretch your legs, turn on a movie on an excellent monitor that is built into the wall of the chair, and enjoy the flight.

Boeing 747-400 business class photo Aeroflot
Economy class
Rows 5 - 9 of the economy class are located on the upper deck, the seats are arranged according to the 3:3 scheme and are separated from the business class by a screen, not a partition, which makes the upper deck more comfortable. The most convenient for the economy class at this level is the fifth row because there is a lot of space in front and there are no seat backs that fall at the most inopportune moment. The least comfortable row on the upper deck is the last row, as it is located close to the bathroom and stairs, which creates certain inconveniences (smell and frequent passenger traffic).

Boeing 747-400 economy class photo Aeroflot
10 - 12 rows - economy class seats, which are located in the bow of the lower deck of the airliner, the seats are arranged 2 in a row. These seats can easily be called the most comfortable on the lower deck. Engine noise in this part of the aircraft is minimal, making them very attractive and most suitable for passengers with children.
Tourist class is a cheaper option for economy class
From the 14th row, the tourist class begins. Armchairs are arranged according to such schemes 3:3, 3:2:3, 3:3:3 and 3:4:3, which reduces the space between the seats and makes it difficult for passengers to move. Seats 17-19 of rows E, F are quite comfortable, since they are placed in 2.

Photo tourist class Boeing 747-400 Aeroflot
Seats at the emergency exit - 19, 29, 43, 54, 70 and 71 rows, have a significant disadvantage, which is manifested in the fact that the seat backs do not recline, which greatly complicates a long flight.
20, 31, 34, 44, 55 rows - places behind the emergency exit have a big plus in the form of additional space in front and free movement, even if there is a window seat, because you can get up without disturbing your neighbors. But chair 31A is slightly warped due to the emergency exit, which can lead to some discomfort.
Seats at the toilet rooms - 20, 21, 22, 28, 29, 42, 43, 44, 45, 70, 71 rows - have a number of negative qualities, such as: smell, frequent movement of passengers, pandemonium, noise, sound of drained water. Seats in rows No. 28, 42 are also inconvenient because the backs of the seats are motionless. But places D, E, F, G in the 45th row have free legroom. Row 31 has a lot of room in the front - you can stretch your legs, but it is placed near the stairs, like rows 32 - 34, which guarantees constant movement and noise.
If it is important for you to contemplate beautiful landscapes during the flight, then avoid purchasing tickets for seats above the wing of the aircraft (33 - 52 rows). But if you have aerophobia, then the seats in the center of the plane are most suitable for you, there is not so much chatter here, and such people are always calmer among neighbors.
The seats that are located at the end of the plane are considered the safest, but there is not enough free space for a comfortable flight. The advantage is that seats B, C, H, K 68 - 70 rows are arranged in pairs, but the backs of the seats can be fixed, and it is at the end of the aircraft that the technical rooms are located, as well as the bathrooms, which are the most loaded during the flight.
At the porthole, in the middle or at the aisle
If you want to admire the incredible scenery during the flight, then feel free to choose a seat by the porthole. But, if you are with a child or you often have a desire to take a walk, you should book aisle seats so as not to cause discomfort to yourself and your flight neighbors every time you want to get up. Well, the places in the middle are considered the least convenient - neither to sleep peacefully, nor to go out normally, and you may not even get an armrest. If you want to sleep during the flight, then you should not take an aisle seat, because you will be constantly disturbed by your neighbors, passengers and airline workers who move around the cabin of the airliner.
Best Places
- business class (1-3 row);
- economy class 5, 10, 11 and 12 (A, B);
- tourist class 34 (H, K, L), 55.
Good places:
- tourist class 17 - 19 (E, F), 31, 45 (D, E, F, G), 68 - 70 (B, C, H, K).
Worst places:
- economy class 9 row;
- tourist class 19 - 22, 28, 29, 42 - 45, 54, 70, 71.
Conclusion
Before booking a seat on an aircraft, you need to familiarize yourself in detail with the layout of the cabin in which you are going to fly and set priorities for yourself (at the window or at the aisle you want to fly, with a movable seat back or with extra legroom, in which part of the aircraft you prefer to travel). You can call the airline hotline and ask the manager about everything. After carefully considering and weighing all the pros and cons, choose a place that will be most comfortable for you. After all, a place that meets your preferences and requirements is the key to a comfortable flight.
Consider the situation using the example of a Boeing 747-400 cabin layout, a three-classof the LuftHansa airliner with 344 seats and let's decide what are the best seats in the cabin in the Boeing 740. Seats in the 1st and 9th row have the advantages of an empty
space in front of the seats. Seat on the 25th row is not so convenient,
because you can hear conversations and the noise of the neighboring
economy class. The seats of the 28th row located immediately behind the partition are not so
comfortable as standard.
Row 31 is next to the emergency exit and toilet. 32 row has the advantage of free legroom and more
free movement. Even though the proximity
toilet is recommended because of the freedom of movement. Row 42 is also not recommended, similar to row 28. 43 row has limited legroom.
56 row is located in the tail, toilets are located nearby, and chairs
do not recline or have a restriction.
One thing can be said about business class, all seats
good ones.
The advantage of seating near a window is that you can
view the picture overboard. Not disturbed by rising neighbors, but
to get up yourself, you need to disturb the entire row.
The seats located in the middle are the quietest.
The seating arrangement near the aisle gives the advantage of free
exit, but there may be increased anxiety from passing and
flight attendants.
4 row has the same advantages and disadvantages.
These little rules can help you decide where to place.



