How to put silicone bait on a hook. Installation of silicone baits. Use this bait for
Blessed Akhtuba!...
Abundance, variety of river fish species and absolutely “mind-blowing” local beauty attract a huge number of fans of fishing and outdoor recreation to these places during the entire period of open water.
Someone can’t sit still and wants to walk along the spinning rods, pull a large perch in eriks or troll pike perch and pike in the channels of Akhtuba, Mangut and Kharabalyk from a boat, and someone who is tired of the stormy city bustle I want to sit quietly with a fishing rod or donkey on a gentle sandy bend or in a backwater under centennial willows ...
What is peaceful white fish caught on in the Lower Volga? There are many baits and baits for this - from simple ones that can be obtained directly at the place of fishing, to cleverly prepared in advance. But for catching large peaceful fish, it is not enough to have the right bait for fishing - you also need to be able to properly put it on the hook. The fact is that most large specimens of leucorrhea, such as bream, silver bream, blue bream, roach, rudd, ide and representatives of many other species, including crucian carp and the famous Astrakhan carp, become experienced and cautious with age. They are already "not fooled on the chaff" and, using experience and intuition, you have to build on the hook, at times, absolutely incredible works of fishing art.
If we talk about the most common, classic nozzles and baits, then almost all of their types can be reduced to the following: worms, water larvae, flying insects, dough (bread crumb, mastyrka, etc.) and whole grains of cereals and legumes.
Getting or preparing the right bait for fishing is only half the battle. You also need to correctly put the bait on the hook. For different types of baits, different ways of planting are used, which I will discuss later. The figure below shows the main ways to fix the bait.
MOTH (Fig. 1)
The baiting of bloodworms, larvae of harmless mosquitoes of the family Chironomidae, living in benthic silt, is usually done by carefully passing the sting of the hook behind the head (dark ball) through the first segment. Depending on the size of the larva and hook, bloodworms can be planted in any quantity. The main thing is not to tear the delicate skin, 
Almost ALL types of peaceful fish (bellows) are caught on the bloodworm, as it is their usual natural food. This bait is indispensable in winter, early spring and late autumn, when fish, prone to digging up invertebrates from the bottom soil, prefer bloodworms to all other baits. But it must be remembered that bloodworms attract really large fish only in places of their usual feeding, near silty backwaters, ilmens, overgrown channels. Where the bloodworm does not live in principle (for example, the cores of the Akhtuba, Mangut, Kharabalyk channels), it makes no sense to catch bloodworms, especially considering the size of the fish caught. And this happens to be from 0.5 to 11-12 kg of weight.
You can store this bait in the refrigerator at positive temperatures (from 0 to +5), in a cool room or just in a box on a litter, but in any case, you need a lot of air and moisture to store the bloodworm, it is better to distribute it for storage in a thin layer on a saucer with damp cotton cloth.
Bloodworms are usually caught with a float rod or by placing it on a mormyshka. Bloodworms are often used as a bait for a combined sandwich-type bait, when the bait is made up of bait (worms, larvae) and herbal ingredients (dough, grains, legumes).
Fish such as bream, blue bream, roach, ide, rudd, vobla, crucian carp, small carp are perfectly caught on bloodworms throughout the entire period of open water. It is logical that you should not use such a relatively small bait for catching large species of fish and fish that collect food not from the bottom and feed on the current.
WORMS (Fig. 2)
Several types of earthworms () are also one of the most common baits for fishing for linen and some types of predatory fish.  So, for example, if almost any fish respects an ordinary earth or dung worm, then a small catfish, sometimes up to 10-15 kg in weight, and a large carp are happy to peck at a bunch of “creeps”, real giants among worms.
So, for example, if almost any fish respects an ordinary earth or dung worm, then a small catfish, sometimes up to 10-15 kg in weight, and a large carp are happy to peck at a bunch of “creeps”, real giants among worms.
Worms are baited in several ways (see diagram). For small fish (white bream, roach, rudd), a large worm can be cut into fragments, and for large fish, on the contrary, several pieces can be planted in a bunch. Sometimes, for greater attractiveness of the bait, the worm is put on the hook so that the part hangs from the sting (it is very mobile for a long time and effectively provokes the fish to bite). In addition, when catching large fish, the closed sting of the hook causes her less alertness.
On the worm during the entire period of open water, you can successfully catch bream, roach, rudd, perch, small perch and roach.
A worm is indispensable when fishing with a combined bait - a “sandwich”. In this case, the sting of the hook is usually clogged with steamed grains of corn or wheat, which in turn prevents the worms from slipping off the hook. For worm fishing, there are also special hooks that have notches on the back to better hold the bait.
GRASSBUCKER, LOCUST, WASTE, CYCADA (Fig. 3)
 Many species of river fish that feed constantly or periodically on flying insects are well caught during their mass appearance. Grasshoppers, wasps, cicadas, large moths and similar animals are perfect as such bait. Such insects are planted from the cephalothorax under the head from below on a hook with a long forearm in such a way as not to damage the tissues in the dorsal part, and the sting would barely protrude from the soft abdomen. In this case, the insect will remain mobile for a long time, which is important for attracting hunting fish.
Many species of river fish that feed constantly or periodically on flying insects are well caught during their mass appearance. Grasshoppers, wasps, cicadas, large moths and similar animals are perfect as such bait. Such insects are planted from the cephalothorax under the head from below on a hook with a long forearm in such a way as not to damage the tissues in the dorsal part, and the sting would barely protrude from the soft abdomen. In this case, the insect will remain mobile for a long time, which is important for attracting hunting fish.
In this way, on Akhtuba, in the course and in the thickets, they catch fish that feed on insects that have fallen to the surface of the water: ide, chub, large rudd, sabrefish, perch. Periodically, crucian does not disdain such bait.
For such fishing, a wire rod with a self-loaded float and a long leash or tackle with a bombard is most often used, which is used to catch a cast with a pull or in wiring, lowering the bait downstream. The bait in this case can float on the surface or slowly sink a few centimeters, which can be easily achieved using small foam balls on a leash or small pellets, and when fishing with bombards (sbirulino) with a brace, you just need to choose the right type of bombard - they are floating , slowly and quickly sinking.
When casting such tackle, a sufficiently heavy float or bombard allows you to send a light floating bait very accurately and far, even in windy weather.
DRAGONFLY LARGER (Fig. 4)
Dragonfly larvae and mayflies are also often successfully used as bait when catching peaceful and predatory fish. They are caught from the bottom, in shallow waters and in thickets of aquatic plants - their natural habitat, where they are the usual food for many species of river fauna, including ide, roach, ruff, crucian carp, small pike perch, chub and many other fish.
It is easy to find them right on the spot. To do this, it is enough to pull a bunch of aquatic plants or algae ashore and carefully examine them. On the hook, such larvae are planted from the head and through the soft abdomen. It is not necessary to try to keep the larvae mobile, on the contrary - when fishing from the bottom, a live larva will constantly climb into the thick of algae and silt, falling out of sight of the prey desired by the fisherman.
Caddis Larva (Fig. 5)
 This larva of a water butterfly, which builds a tube house from any available material (sand, fragments of shells, particles of dead plants, etc.), is also easy to get right on fishing in any shallow water near the coast, where they sometimes inhabit the bottom in large numbers. Carefully pulling the larva out of the house, it is planted on the entire hook, starting from the back.
This larva of a water butterfly, which builds a tube house from any available material (sand, fragments of shells, particles of dead plants, etc.), is also easy to get right on fishing in any shallow water near the coast, where they sometimes inhabit the bottom in large numbers. Carefully pulling the larva out of the house, it is planted on the entire hook, starting from the back.
They catch the caddis larva from the bottom, where it is a favorite food for all juvenile fish and some large fish, such as ide, chub, crucian carp, tench and bream.
B MAYFLY BUTTERFLY, DRAGONFLY, CENTILED MOSMUT (Fig. 6)
When baiting these fairly gentle flying insects, you should carefully select the size of the hook and choose hooks with a thin forearm. These types of bait for fishing on Akhtuba in the summer are great for catching most fish that prey on insects that fall on the surface of the water: chub, ide, sabrefish, rudd, medium-sized asp.
The advantage of this bait is its availability, since it is easy to get these insects in the appropriate season right while fishing in coastal grass, reeds and bushes.
Most often, flying insects are caught from the surface with a wire rod or fly fishing.
FLY, GADDLE, GADDED (Fig. 7)
Many species of flies live near stagnant and flowing water bodies of the Lower Volga. They are the usual food of medium-sized fish that gather food from the surface of the water: chub, ide, sabrefish, rudd, roach and others.
A live large fly is put on a hook in front through the cephalothorax and then the stinger is removed through the end of the abdomen. At the same time, the husband remains mobile for a long time and creates ripples on the surface of the water with his wings, which quickly attracts hunting fish to the place of fishing.
The most common large flies suitable for bait near the water are dung and blowflies, murmuring flies and horseflies.
In the same way, they put a bear on a hook - a large earthen insect, on which catfish and carp are successfully caught.
Maggot (Blowfly Larva) (Fig. 8)

Maggots come in different sizes, up to 3 cm long, and different shades (from white to greenish and dark pink). Maggots are put on the sting of the hook behind the head (black dot on the thin end of the larva) so that the whole body remains to hang freely. The maggot is very tenacious and has a strong shell, so it remains mobile for a long time on the hook.
Maggots are often used in combined baits along with worms and various vegetable baits.
Maggots should be stored in a box with air access in a very cold place (+2 + 8 degrees C), then they do not pupate for a long time, up to 2 weeks. If desired, you can feed them with boiled egg white, steamed bran, etc.
HRUSH GRUB AND BARBEET (Fig. 9)
These rather large whitish larvae are often found in compost heaps, humus and rotten wood. They are suitable for fishing from the bottom of large fish: carp, catfish.
They should be planted very carefully so that the body of the larva does not leak out, and without damaging the head, so that the larva remains mobile.
FILAMENTAL ALGAE (Fig. 10)
 They are easy to find in the summer on various objects in stagnant and running water, where they sometimes form extensive green-brown fouling, called "mud" and mulberry in the common people.
They are easy to find in the summer on various objects in stagnant and running water, where they sometimes form extensive green-brown fouling, called "mud" and mulberry in the common people.
These algae are the food of fish such as tench, crucian carp, roach, grass carp and silver carp.
They catch them with a float rod, and make a hook attachment by tying a bunch of fibers with a loop, as in the diagram. The remaining free tail hides most of the hook, which the fish sucks in when biting, gradually taking the bait from the tail.
DOUGH, BREAD (Fig. 11)
These vegetable baits are very popular among anglers and are used for catching all cyprinids except asp, grass carp and silver carp. Fine  this bait works when catching carp, carp and carp in the summer.
this bait works when catching carp, carp and carp in the summer.
The dough and rolled bread crumb, as well as balls of mastyrka and semolina are put on a hook with a short forearm so that the nozzle must cover the sting, otherwise it may alert the fish. These baits are mainly used when fishing with a float rod, as they have little strength and weak hold on the hook.
To improve the properties of such baits from bread, dough and cereals, you can dip the finished bait along with the hook in vegetable hemp, linseed or sunflower oil - this way they become more water resistant.
STEAMED GRAINS (Fig. 12)

Depending on the size of the hook, which in turn depends on the size of the intended prey and the size of the bait, one to several grains or beans are planted in such a way that the hook is hidden as much as possible (for peas and beans) or that the bait forms a "beard" under the forearm of the hook (as in the figure), for example, when planting elongated grains of oats and wheat.
Such a bait holds on the hook very well, allows you to catch even bottom tackle and is often used in combination with animal baits - worms, maggots.
Of course, there are many more exotic baits for catching whitefish and other peaceful fish, when using them on Akhtuba you should be guided by your own experience, intuition and common sense. The main thing is not to be afraid to experiment, because fishing is a very creative and exciting process.
For almost every angler, the first bait with which he began to catch was a worm. The reason for this is the availability and versatility of the bait. Using a worm for fishing, everyone noticed that someone fish bites reliably, while someone has constant idle bites or does not bite at all. In the process of fishing, it turned out that the effectiveness depends on whether the angler knows how to properly put the worm on the hook.
There are not many rules for baiting a hook with a worm, but the success of fishing depends on the observance of each of them.
Basic rules for planting a worm
- do not injure the worm unnecessarily. The mobility of the worm determines how quickly the bait is noticed by the fish. Only a very hungry one pecks at a drooping, passive worm;
- the fish should not pull the bait off the hook. For confident fixation of the worm, use barbed hooks, pierce several times or use clamps;
- the size of the hook, trophy and bait must match;
- use for fresh worm bait.
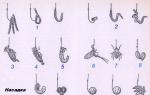
Ways to put a worm on a hook
- One worm at intervals. The bait is pierced at a distance of 1-1.5 cm in 2-3 places with a hook, the tip is hidden inside the worm. They catch silver bream, roach, ram, carp, perch, etc.;
- One worm in a ring. The worm is attached to the hook with two punctures in the area of the head and tail. Does not allow small fish to constantly pull the bait. Designed for catching large fish in places where there are a lot of little things. Used when fishing for a durable worm;
- One worm is pierced behind the head or in the middle of the body. Used for fishing in the presence of a confident bite. Used when fishing for a durable worm;
- One whole worm. From half to two thirds of the worm is strung on a hook. The tip of the sting of the hook, in order to avoid pulling the bait by the fish, slightly out. Restricts the movement of the bait, severely damages the worm. Suitable for catching small fish;
- Several worms (garland). 2-3 worms are baited with an interval of one hook. Suitable for catching big fish.
- Several small worms on one hook. For catching big fish
- 2-3-5 hearts bait for the head part. The bait remains mobile for a long time. Suitable for catching large fish in places where small things do not annoy.
- Piece (half) worm on one hook. Used for catching small fish on small hooks;
- Sandwich. After the worm, a grain of cereal or corn is planted on the hook. Together with the worm, a maggot is planted on the hook. In addition to the fact that the maggot is actively moving, it also prevents the fish from pulling the worm off the hook;
- Tackle from 2-3 hooks, tied on a leash at a distance of 2-3 cm. One worm on such a rig is sequentially put on hooks, starting from the top. The worm on the rig remains mobile and behaves naturally. They are used for planting large bait when catching trophy specimens.

What worms can be used for fishing
Worms are distinguished by color, size and habitat. For fishing purposes, the most commonly used:
- Muckworm . Sometimes the worm is called a maggot. Characteristic pungent smell, strong, often variegated, skin. Holds well on the hook. There are two types of dung worms. Brick-red worm - large, can be divided into parts. It is used for catching large specimens of crucian carp, carp, tench, silver bream, etc. The red-yellow worm is small. Small fish are caught on this worm - gudgeon, ruff, roach, etc .;
- Creep out . The second name of this worm is a large earth worm. Large, up to 30 cm long and up to 1 cm thick, worm. Lives in the deep layers of the soil. Prefers fertilized soils. Creeps out completely or partially to the surface at night. Suitable for catching big fish
- Earthworm. Length 5-15 centimeters. Pale pink or bluish color. Holds firmly on the hook. Used for bottom fishing, especially at night, such as burbot. It is not very popular with anglers;
- green worm . Gray or dark green color;
- Zheleznyak. Grey-smoky color. Length up to 15 cm. Lives in clay soil. Holds well on the hook. Used to catch predators;
- Subleaf . Red-blue or purple color. Delicate, easily torn. It can exceed the size of an earthworm and a dung worm. Not afraid of the cold. Requires secure fastening on the hook. Use a barbed hook or pierce the worm with a thin hook several times;
- water succulent. Almost transparent. Used for catching silver bream, perch, roach, rudd. Habitual object of food for fish;
- water worm . Brown-red or pale red color. Rough. Length up to 20 cm, thickness up to 0.5 cm. Easily torn. Large hooks required.
Where to dig worms
- Dung worms live in rotted manure, in various organic garbage dumps, in the ground of barnyards, in compost heaps. Digging with a pitchfork or rake. So the bait is less injured. Most often found in colonies. In those places where there is no fishing press, the extraction of this worm does not take much effort and time. Does not like heat;
- Crawling, in the warm season, is collected in parks, gardens at night with a flashlight. They also collect the worm in the early morning, after the dew has fallen, on park, garden paths and paths. When collecting bait at night, try not to direct the light of the lantern directly at the worm. Direct light, noise and trampling force the worm to hide in a mink. In order to hide in his house, the worm needs only half a second. It rarely crawls out of the mink completely, therefore, having caught the worm by the upper part, closer to the mink, it is gradually pulled out of the ground. Sometimes worms crawl out of burrows during drizzling rain. The habitats of creeps are easy to determine during the day by the presence of characteristic holes in the ground;
- The earthworm is collected in the beds or, after rain, on the paths. Rain floods the minks, and the worms are forced to leave them, crawling to the surface. They dig a worm with a pitchfork or a shovel in the same places where it appears after rain. Worms live in almost any meadow. If there is no shovel or pitchfork, the bait is found by tearing the sod from the ground;
- The green worm is harvested in the fatty soil of coastal meadows or under marsh tussocks;
- Ironstone lives in clay soil. Here it is dug with a shovel;
- The subleaf lives under compacted layers of fallen leaves, under dense layers of pine needles, under sawdust or under packed old straw. To determine the most likely habitat of the worm, they find lowlands, pits, small funnels that retain moisture;
- The water leaf is collected from the underside of the water lilies;
- The water worm is found in the muddy sections of rivers, near wharves, timber rafts and rafts. For extraction, a shovel is used, with the help of which the bottom soil is raked ashore.

Recommendations for choosing a method of planting when catching different types of fish
Each type of fish has its own specifics in feeding. Some species feed only at the bottom, others only at the surface, and others combine both. Fish also differ in the rate of consumption of the found food. Some species immediately grab everything that moves, others repeatedly try, pull, and only then swallow. Most often, the worm is used to catch fish from the bottom. Based on this specificity, anglers have developed the most successful recommendations for catching various fish species;
- On a carp. Use types of worm bait in which a long moving tail or tails remain, except when there are a lot of small carp in the reservoir. For catching large and medium crucian carp, a bunch of several small or medium worms is suitable. For catching small carp - pieces of a worm or its small specimens with the obligatory removal of the tip of the hook to the outside. On separate reservoirs the crucian prefers the worm already chewed by the previous bites. In this case, after baiting the hook, the tip of the worm is crushed;
- On the bream. You can use "crucian" bait methods. Does not like too voluminous bait. I really like the bait of a few pieces of a worm or a bunch of small worms. It can be useful, when planting a worm with a “stocking”, to move it above the hook onto the fishing line. For catching large specimens, a medium-sized crawl out with a tail hanging from the hook is used. The sting of the hook with all methods is hidden inside the worm;
- For carp . Most often, a dung worm is used in the form of a garland of several worms. It is very good to use a worm sandwich, pierced with an interval and a grain of corn, for carp fishing. The baiting of hair equipment with a worm pierced in two or three places has proven itself well. It is used for catching carp and a bunch of small worms pierced with a hook in the middle. It happens that it bites well on earthworms collected near a reservoir;
- For catfish. They use the largest of the worms - crawling out. 3-6 worms are put on the hook. The mouth of a catfish is huge and is able to swallow everything that is offered to it. For baiting worms, when catching catfish, in addition to a single hook, a double is used. It is useful to fix the worm on the hook with a stopper of animal or vegetable origin - maggot, live bait, leech, frog, locust, bear, corn, barley, river mollusk.
- experiment with different types of worms;
- do not focus on one type of worm, because it is "sold in the nearest store";
- keep in mind that matching the size and type of fish, bait and hook is the key to successful fishing;
- the long tip of the worm can lure large fish, but attracts small ones;
- even in the absence of bites, change the worm every half hour;
- the supply of worms should not limit the angler's ability to change the bait;
- the worm should not burrow into the soil at the bottom of the reservoir;
- the worm is dipped in hemp, sunflower oil or garlic extract. Oil will give the bait a pleasant smell, garlic, in addition to the smell, will add activity;
- dung worm does not need additional smell.
The worm is undoubtedly the most popular and affordable bait for any angler, be it a city dweller or a rural dweller. There are a lot of options for putting a worm on a hook. Especially for this bait, barbed hooks were invented. The worm is used when catching fish on almost all types of fishing gear. The effectiveness of the worm does not lose its significance even in winter. Almost no angler goes fishing without this bait.
The vibrotail is still one of the most competitive baits today, allowing you to successfully catch all types of freshwater predatory fish. But as in any important business, the result of which depends on the performance of many successive effective operations in the aggregate that bring overall success, and fishing is just such an option, fishing with a vibrotail has a number of nuances.
It is about one of these nuances, and in particular, how to install a vibrotail, that we will talk today and try to analyze the main points of its competent execution.
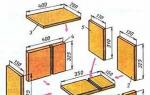
Silicone baits for jig are diverse in their shapes and types, and also differ in size and density of the material. All these factors should be considered during installation. Anyhow, how to put a silicone bait on a hook, throw it into the water and expect a successful bite is simply unreasonable. First of all, the fisherman must understand that the vibrotail can be equipped with various types of hooks, single, offset, double, tee, and this depends on the fishing conditions, the intensity of bites and the type of fish that the angler is counting on. The easiest way to plant a vibrotail seems to be on.
Important! Choose the place where the wide back of the vibrotail transitions into its narrow tail. This transition point should be the exit point of the hook from the body of the bait.

With a sting, we pierce the vibrotail at the location of the mouth of the artificial fish and string its body until the sting of the hook reaches the point of exit to the surface that we have chosen. We bring the tip in the back of the artificial fish to half the rounding of the jig head hook. This completes the installation.
Important! The hook of the jig head must correspond to the size of the vibrotail from the mouth of the fish to the point where the sting of the hook comes out on the surface of the back of the nozzle.
jig head selection
Initially, it is worth choosing a jig head based on a combination of three factors:
- hook size;
- head weight;
- bait size.
I explain that large silicone will require a long forearm, but not always a large mass of head load, because this factor depends on fishing conditions and on the depth of the reservoir.
The correct silicone nozzle on the offset
It is not much more difficult to correctly fit the vibrotail on the offset. This installation is successfully used for catching a predator in the snarled sections of reservoirs. Having picked up the offset, we pass it into the mouth of the fish and bring out the sting of the hook under the lower part of the vibrotail head. Then we stretch the hook along the body of the fish and pierce the belly of the silicone to its back through and through. We bring the tip of the offset machine strictly parallel to the back of the nozzle, trying to press the tip as tightly as possible to the body of the vibrotail. Installation completed. A silicone fish is mounted on a single hook without much difficulty, which cannot be said about mounting on a double and a tee.

Equipping a vibrotail with a twin
Requires selection of a hook with a long shank. Putting a vibrotail on a jig with just this type of twin greatly simplifies the task.
As in the case of installation on a single type of hook, we determine the point for piercing the bait, only now it will not be the exit point of the point, but the place where the double ring is inserted into the body of the nozzle and the point will not be on the back, but on the side. Having slightly parted the hooks of the double, we pierce the fish from the side through and through with one hook and string the silicone along the entire forearm. As a result, it turns out that the vibrotail will hang with its back between two double hooks. Then, pressing the ring into the body of the bait towards its mouth, we pass the silicone through until the fixing ring comes out of the body of the fish. The installation is almost completed, it remains only to spread the nozzle to the length of the entire forearm of the hook so that it gets its original geometric dimensions and does not deform.

Important! A deformed bait has a noticeably negative effect on the quality of its game during postings.
In most cases, deformations of the silicone bait occur from an incorrectly defined puncture site and from an incorrectly selected length of the shank of the vibrotail hook. With a sluggish bite, uncertain bites and frequent gatherings, it is reasonable to equip the jig bait using a tee in the installation. This mounting option allows you to increase the chances of notching a cautious and fastidious predator.
Read also about fishing and the correct selection of bait depending on the fishing conditions.
Equipped with a tee
To equip vibrotails with triple hooks, you will need additional unpretentious equipment in the form of a metal or plastic tube with a diameter of not more than five millimeters. The length is sufficient at 2 cm. The tube should be one and a half times the thickness of the mounted silicone bait. This device is needed in order to make a through hole in the body of the vibrotail for mounting the tee on the side.
Important! The hole must be optimal in diameter based on the size of the tee. A small hole will not allow symmetrical installation of the tee hooks, and a large hole with an increase in the play of the tee during wiring will worsen the quality of the nozzle play.
As in the first wiring diagrams, markings are made to determine the point of the required hole. The length of the tee forearm, excluding the attachment loop, will be our main guideline. We pierce the vibrotail with a pre-prepared tube, since silicone is malleable for these manipulations. Further, in the hole made towards the mouth of the fish inside the body of the bait, we thread the triple hook with a fastening ring through the front. Stretching the hole previously made by the tube, we transfer the first sting of the tee to the opposite side of the artificial fish.
With the second sting, we pierce the back through the same hole, bringing the tip parallel to the back of the silicone, but leave the third hook without any manipulation. In principle, the installation of a vibrotail on a tee can be considered complete. The disadvantages of this installation is its rather low permeability in fishing areas with vegetation. The best way to use silicone baits on tees is in clean areas of the reservoir.
The importance of equipping a vibrotail when fishing

The ability to correctly, competently and effectively equip vibrotails with various types of hooks allows you to use broader strategies when catching a predator. Indeed, such types of equipment, excluding only the attachment of a vibrotail to solid jig heads, make it possible to use silicone baits in conjunction with interchangeable hinged weights, the so-called cheburashkas among fishermen, as well as when fishing with a bombard under various fishing conditions. Equipping a vibrotail with an offset hook, double and tee can be safely called universal. After all, by manipulating the load of Cheburashka and the float of the bombard by type and weight, the bait can be used at different depths and at the same time perform various types of postings.
Well, by changing the types of hooks, they can be successfully caught in overgrown and snarled areas of the reservoir and with the passivity of the predator. Therefore, the arsenal of fishing lures for a lover of catching predators, representing freshwater reservoirs, should include all the types of installation discussed above. After all, equipment prepared at home will save valuable time on fishing, increase the angler's opportunities for a successful outcome of fishing, even despite the prevailing conditions of the fishing session.
Maggot is a versatile bait that can be used at different times of the year. This bait is loved by different types of fish, both small representatives of the ichthyofauna and trophy specimens. Beginning anglers face certain difficulties with putting the larvae on the hook. Incorrect installation leads to the absence of bites and a decrease in catch. The lure often dies faster than the fish can see it. How to put a maggot on a hook in order to make fishing interesting and effective? To begin with, you should get to know the bait better.
Some people throw up their hands in surprise when they hear the word maggot. But every angler can easily talk about this bait. In fishing shops you can buy bait in unlimited quantities. Maggot is sold in its natural form, in a dyed state, and even in canned form. Small portions of bait are added to the bait. What is maggot, and where can you find it?
Maggot (speck) is a blowfly larva. A large enough insect with a bluish-greenish tint to land on a piece of meat or fish for a few seconds to lay many eggs on the surface. After a couple of days, they will turn into white larvae 4 to 12 mm long. Previously, this is how anglers bred catchy bait.
Attention! Under favorable conditions, maggots can exist for about 10-14 days, after which pupation begins. In the refrigerator, the bait can be stored for six months.
The fly larva has the unique ability to change color. You can get yellow maggots by giving them chicken yolk. A red tint is obtained by adding a special dye to food.
Maggot is also able to change its smell. To do this, it is enough to add drops of anise to the sawdust to further interest the fish.
How does maggot attract fish?
Fly larvae are a storehouse of protein and other nutrients. The fish knows this, so it eats wholesome food with pleasure. But in order for the maggot to attract fish in the form of bait on a hook, it must look natural.
The larva should emit a natural aroma and squirm. This moment must be taken into account by the angler before putting the maggot on the hook. If he is motionless, and only a shell remains of the body, then such a bait will not interest even a stupid trifle.
Not all fish behavior can be explained. It is not clear why red maggot is in demand among representatives of the ichthyofauna. This color is not natural, and the resemblance to a bloodworm is far from ideal. But the fact is, the fish often ignores the natural coloring, preferring the red color.
Also, the predilection of fish for a canned larva becomes incomprehensible. This is used by experienced anglers when the fish is naughty.
Hook selection
In order for maggot fishing to be successful, it is important to choose a hook that matches the bait used. Large models must be left in the box immediately. When the larva is pierced, the nutrient fluid flows out of it, and only the skin remains on the hook. Therefore, the angler should purchase a set of thin wire hooks with a sharp sting.
- For planting one larva, model No. 18-20 is suitable.
- Fishing for two maggots can be carried out on hook No. 16-18.
- If purposeful hunting for large fish is carried out, then volumetric bait is often formed. For such purposes, hook No. 8-14 is required.
The maggot is highly mobile, often it manages to slide off the hook onto the fishing line. To prevent such cases, the knot is varnished or a drop of synthetic paste is applied. It happens that the fish with impunity removes the larva. Then you should tie a hook with a beard on the forearm.
The color of the hook should also be chosen according to the color of the larva. Today it will not be difficult to find white, yellow or red hooks in a fishing store.
Planting methods
There are several working ways to put a larva on a hook. Each of them can be used in certain fishing conditions.
Classic variant
Since ancient times, maggot fishing has been carried out with the classic version of planting. To do this, you must perform the following manipulations.
- Take the larva with two fingers and squeeze so that the maggot does not slip out. Here it is necessary to dose the compression force, otherwise the bait can be crushed.
- The tip of the hook is inserted from the side of the head (the thicker end) under the skin and immediately brought out. The distance between the punctures should not exceed 5 mm.

Photo 1. Bait for the head.
This type of planting is suitable for fishing such fish as roach, silver bream, crucian carp, bleak, dace, gudgeon, ruff, perch.
Fit along the body
Large fish are careful and should use a different mounting option.
- The sting of the hook is inserted into the area of the head of the larva, which is firmly held with two fingers.
- Then the bait is carefully put on the hook, and when the tip reaches the middle of the body, it is brought out. It is advisable not to go deep into the bait, placing the forend near the skin itself.

Photo 2. Baiting along the body.
This method is suitable for carp, bream, ide, sabrefish.
Option from athletes
Professional anglers bait the maggot in the middle of the body. However, unlike the classic version, the hook is inserted not along the body, but across.
- The larva must be placed horizontally.
- The larva is pierced with a sharp sting from top to bottom. The hook should pass near the skin.

Photo 3. Sports option.
In this position, the larva behaves naturally and freely. Perch and roach, goby and silver bream, gudgeon and dace, bleak and rudd are pecking well at such an installation.
"Unhooked"
Mounting "non-hook" is used when catching a wire is used. The bait with a hook constantly moves along the bottom, clinging to various obstacles. Therefore, the tip of the sting is hidden in the body of the bait.
- The larva is held in a vertical position with its head up.
- The hook is threaded from top to bottom, the puncture is made only in the head.
If the hook is large, then several larvae can be strung on the forearm. Such installation may be of interest to bream, carp and other bottom fish.
ringlet
When the fish is naughty or cautious, the method of planting with a ring is used. With this option, you can save bait.
- First, a puncture is made in the head area.
- Then the sting is inserted into the tail.
A fish cannot pluck such a ring with impunity. You can catch any fish.
Stocking
A popular type of putting larvae on a hook is a stocking.
- After piercing the head with a sting, the forearm is drawn along the entire body.
- The point is displayed near the tail, while the body of the larva should straighten up.
During the second puncture, do not put pressure on the larva so that it does not burst. Carp and crucian carp, roach and rudd, silver bream and chub willingly bite on such a bait.
Planting a few grubs and sandwiches
If it’s easy to deal with one larva, it’s time to get acquainted with how to put a maggot on a hook when creating a bulk or combined bait. There are several ways here.
bundle
Large fish may not covet one larva. Therefore, it makes sense to create a whole bunch of maggots.
- This requires a large but sharp hook. 3-5 larvae cling to it by the head or middle.
- You should get a necklace of plain or multi-colored baits.

Photo 4. Red and white sandwich.
This method of obtaining volumetric bait is good for angling grass carp and large perch, carp and crucian carp, bream and carp.
Sandwich
Combinations of different baits often help out anglers with a bad bite. Maggot can be used to create a sandwich with a worm, corn, bloodworm, peas, etc. There are different mounting options.
- If one of the baits is a bloodworm, then the red mosquito larva is planted first. There may be several (2-3). And the maggot clings in the classic way or with a stocking for better fixation of the sandwich.
- When using other baits, one or more maggots are first baited on the hook with a puncture in the head area. Following the larva, a worm, corn or barley is planted.
All methods of putting a maggot on a hook are quite simple. But skills cannot be developed without practice. Therefore, armed with a fishing rod and baits, you need to go to the pond and experiment.
One of the best varieties of bait for the inhabitants of the reservoir is maggot. The larva is popular with fishermen due to its affordability and ease of use. It is most effective to use a tandem of maggot and bloodworm as a nozzle for catching large fish. The bait does not lose its effectiveness at any time of the year; it is very good to use it to attract trophy specimens. There are many popular ways to put a maggot on a hook. To choose the right one, it is necessary to take into account the conditions of fishing on a particular reservoir.
The bait is a blowfly larva with a dense leathery cover, which provides it with unhindered movement and existence in a rather aggressive environment. In case of violation of this cover, the maggot as a bait loses its value, it simply “flows out” and turns into a kind of translucent “stocking”. It is important not to damage this dense shell. A correctly planted larva remains mobile longer and retains its integrity even after repeated use.
The head of the bait has a pointed shape, its tip is dark in color. Its back part, on the contrary, is blunt, and at the end there are two small black dots. The length of the larvae does not exceed 4-12 mm. They appear from eggs laid by bluish-green flies on pieces of meat or fish.
When in comfortable conditions for existence, blowfly larvae can remain at this stage of development for 10-14 days, then the pupation period begins. If you keep the bait in the refrigerator, its shelf life is extended to six months.

What is the attraction of maggot for fish
The value of fly larvae is in the high content of useful microelements, in particular, protein. It is especially good to use such bait for catching crucian carp, perch, carp, large roach, rudd, bream. The main thing is that the bait on the hook looks natural, wriggles and exudes a characteristic smell that underwater inhabitants like so much.