The content of the work of the investigator. Youth Personnel Center
Description:
An investigator is a lawyer who investigates crimes: criminal, economic, political.
Investigator investigates murders, robberies, thefts and other crimes. But bullets don't usually whistle over his head. Unless, of course, this is an investigator of the military prosecutor's office. A military investigator is a person liable for military service who has received education at a military university. For him, shooting is a common thing, but not in the process of investigation, but at shooting and training camps.
Investigators usually do not participate in detentions. Their job is to collect and analyze information. The investigator coordinates the work of operatives, works with documents, expert opinions, conducts interrogations, and keeps records. The authority of the investigator includes the initiation of a criminal case. And when a case is initiated, he investigates it and takes it to court.
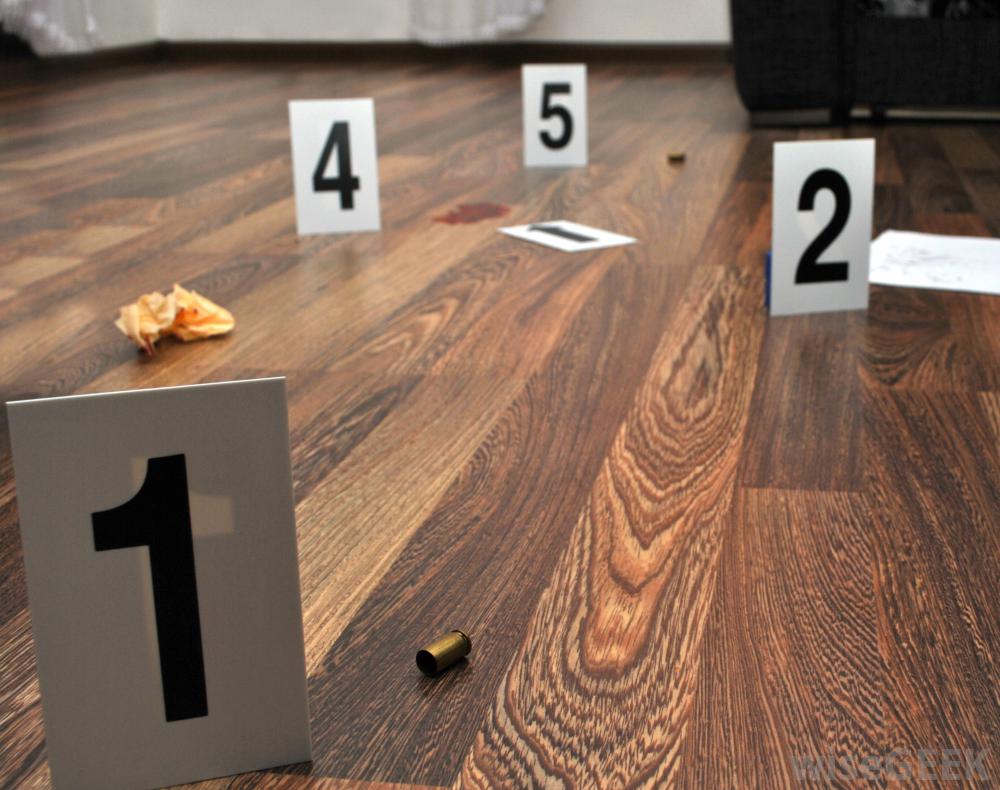
Usually the work of the investigator begins at the scene of the crime. There, forensic experts collect and examine evidence (fingerprints, shell casings, alleged crime weapons, etc.), and already at this stage it is possible to build preliminary versions. In the same place, "in hot pursuit" the first conversations with victims and witnesses take place. The investigator draws up an inspection protocol, determines the direction of the search, and gives tasks to operational workers.
Later, when the initial information is collected, the investigator checks the leads and plans further steps. Sometimes searches are carried out to collect evidence, identifying suspects.
When inspecting a place or during searches, great attention is paid to details, which can be quite a lot. But you can't get carried away with trifles. A good investigator knows how to focus his attention precisely on those details that can carry important information. This skill is acquired with experience. True, modern achievements in forensic science help to extract information even from such items that until recently seemed completely useless. For example, a woolen glove mass production, left at the scene of a crime, may carry a sample of the attacker's DNA. And this is serious evidence.
Evidence of guilt must be undeniable, otherwise a completely innocent person may be punished, and a real criminal will celebrate his elusiveness.
The investigator spends a lot of time in conversations with people: with victims, with relatives of victims, with witnesses, and of course, with suspects. Although he does not have the slightest right to take people at their word. Each statement that can affect the course of the investigation must be verified.
Interrogation of a suspect is a very important part of the job. The investigator must structure the conversation in such a way as to get from the suspect truthful information even if he does not intend to reveal his secret.
The task of the investigator is not to force a confession, but to clarify the truth. This difficult task. Logic and physical evidence are the main tools of work.
Often the interrogation turns into a confrontation between two personalities. Success depends on the right tactics. It is pointless to proceed with the interrogation, if not necessary information, serious analytical training. This operation requires the investigator and psychological preparation, emotional stability. Otherwise, it is so easy to retreat under the onslaught of false arguments, aggression, the charm of a criminal. Or vice versa, get carried away by detective excitement and not notice that the answers of the person under investigation destroy the chosen version.
Another emotionally charged operation is a confrontation, at which witnesses are brought face to face, and their testimony may contradict each other.
Responsibilities:
Initiation of criminal cases, cases of administrative and civil offenses;
· work with criminal cases (acceptance into jurisdiction, transfer to the bodies under investigation, etc.);
Deciding on the direction of the investigation, taking necessary and additional measures, appealing judgments, carrying out revisions;
· cooperation with the investigative group, bodies of inquiry, forensic experts, bailiffs, etc.;
Appearance in court as an accuser.
Requirements:
Personal qualities: the investigator must be able to listen and hear, flexibly change assumptions, "versions" and make operational decisions, be able to penetrate the thought beyond the visible. Solving crimes requires great personal initiative, perseverance, perseverance, purposefulness and responsibility for decisions and actions. The work of an investigator is impossible without such personal qualities: analytical thinking, perseverance, quick wits, and sometimes acting skills.
Professional skills:
Thorough knowledge of legislative documents of a criminal, civil and administrative orientation, forensic science
· Availability general information on the functioning of financial, economic, socio-political and other organizations, on the most frequent crimes committed in these areas
psychological skills
Knowledge and skills: the investigator must know the current legislation, the code of criminal procedure, logic, psychology, the basics of economics. And be sure to have the skills of a forensic expert: be able to seize material documents, fix traces of a crime, fill out protocols.
Education: as a rule, to become an investigator, you need to graduate from a law school with a degree in jurisprudence. Preferably with a criminal law background.
To become an investigator of the military prosecutor's office, you must graduate from a military university.
But you can start a career with a secondary vocational education, for example, after graduating from a police school. In this case, higher education can be obtained in absentia.
Additional features: career prospects for investigators - obtaining the position of a prosecutor of the Department for Supervision of Investigation in the Prosecutor's Office or a Counselor of Justice. This requires not only a solid record of successful work, but also the presence of a higher legal education.
�ѽ=���q�� This is the confrontation of two personalities. Success depends on the right tactics. It is pointless to start interrogation if there is no necessary information, serious analytical preparation. This operation requires the investigator and psychological preparation, emotional stability. Otherwise, it is so easy to retreat under the onslaught of false arguments, aggression, the charm of a criminal. Or vice versa, get carried away by detective excitement and not notice that the answers of the person under investigation destroy the chosen version.
Another emotionally charged operation is a confrontation, at which witnesses are brought face to face, and their testimony may contradict each other.
It is also necessary to mention the investigative experiment, during which the defendant demonstrates exactly how he committed his crime.
When the crime is solved, the criminal case with all protocols, expert opinions, etc. goes to court.
Dangerous profession. As the investigators themselves say, anyone with a legal education can become an investigator, but staying in the profession is much more difficult: human grief, death, someone else's anger, criminal deceit, and sometimes a sense of one's own powerlessness - all this is in the profession of an investigator. And for many, such a burden is beyond their strength.
Although the investigator does not participate in the pursuit of criminals, he also takes risks. At least if this is a real investigator, and not a werewolf in uniform. They may try to bribe him, he may be threatened by those who want to interfere with the investigation. He may even be assassinated. Therefore, there are special services responsible for the protection of investigators. And the investigator himself must not succumb to provocations and be vigilant.
Place of work: investigators work in different structures: in the Investigative Committee Russian Federation, in police departments, in the prosecutor's office (including the military prosecutor's office), in the Federal Security Service and in the bodies of the Federal Drug Control Service of the Russian Federation, etc.
The law enforcement system of a country can change. But the essence of the profession always remains the same - the search for a criminal and his exposure.
After working 10-15 years in the public service, you can become a private detective. For such work, professional and life experience is required, which the service provides.
In some countries, police detectives receive a private detective license as a gift when they retire. In Russia, this is not practiced, but if you wish, you can obtain such a license yourself.
Working conditions: their working hours are irregular. The employee must be ready to leave the scene at any time of the day.
Legal advisor
Legal consultant on issues civil law, regular participant of city and all-Ukrainian scientific and practical conferences, forums, manager of several Internet resources of legislative and legal topics
A lawyer who investigates a crime relating to murder, robbery, theft is, no doubt, an investigator. To collect information into one whole, to conduct a thorough analysis of it, to make an examination, to take part in an interrogation, to record all the information, you need to know and understand a lot.


Where do investigators study and work?
All investigators who receive their position graduate from a law school with a specialization in jurisprudence. True, at the beginning of their career, they may not enter the staff of investigators, occupying the niche of interrogators. With time and experience, the investigator gets more privileges in his work field and can control the actions of operational officers.
You should not think that the investigator runs through the streets with a gun in his hands and catches criminals. His actions are the opposite: the initiation and investigation of criminal cases and their subsequent transfer to court.

The investigator must...
The work of many investigators begins at the crime scene. Here they analyze the facts according to fingerprints, hacking or murder weapons. Logical guesses, interrogations, protocols of answers from witnesses and victims - all this will be needed by the investigator in his work to conduct searches and detain suspects.
The investigator must clearly understand that he has no right to make mistakes in his actions. Because, due to his inattention, he can expose a completely innocent person, giving a “green corridor” to an experienced criminal. Thanks to investigative actions in court, the fate of those who, by the will of fate, find themselves in the dock is decided.
A true professional, and such people should work in the investigation, will never allow illegal actions in the investigation of crimes. A logical technique, a tactical move, stress resistance, the ability to separate truth from lies, an emphasis on verified information - without these components, the investigator will not be able to delve into the case and make a fair verdict.

Cons of work
In the work of an investigator, there is almost no such thing as a day off and a holiday. At any time of the day or night, good and bad weather he must take part in investigative actions, sometimes putting his life in danger.
After all, everything that the investigator knows concerns the criminal intentions of those who are interested in eliminating a person capable of solving a crime. Therefore, investigators more often than other law enforcement officers risk their health and face meanness and aggression.
Last resort
This formula applies to investigators as well. The more evidence they collect and fundamentally substantiate their assumptions, the faster retribution will come for those involved in criminal acts.

And an important help in your work will be such qualities as:
- knowledge of the law
- knowledge of the criminal code,
- psychological skills,
- logics.
Without them, even specialists with a “red” diploma will not be able to act. Only in practice the investigator shows what he is capable of.
Tags:What is an INVESTIGATOR? The meaning and interpretation of the word sledovatel, the definition of the term
INVESTIGATOR- INVESTIGATOR - an official of the prosecutor's office, internal affairs bodies, the federal security service, the tax police, whose task is to conduct a preliminary investigation in criminal cases. S. is entrusted with the duty of a comprehensive, complete and objective study of the circumstances of the crime: All his decisions in the case must be based on the collected evidence, the assessment of which he makes according to his inner conviction, based on a comprehensive, complete and objective consideration of all the circumstances of the case in their totality, guided by law and justice. C., regardless of departmental affiliation, during the preliminary investigation are guided by the norms of the criminal procedural legislation without any exceptions. Supervision over the activities of S. is carried out by the prosecutor. The Code of Criminal Procedure determines the competence of the S. of each body in accordance with the jurisdiction in criminal proceedings. In cases under investigation, S. has the right to give orders (in writing) to the bodies of inquiry, which are binding on them, on the performance of search and investigative actions and require their cooperation in carrying out a number of investigative actions. S. takes all decisions on the direction of the investigation and the performance of investigative actions independently, except in cases where the law provides for the need to obtain a sanction from the prosecutor (detention, search, seizure of correspondence, etc.), and bears full responsibility for their legal and timely execution. S.'s resolutions are obligatory for all officials and citizens. S. bears criminal liability for knowingly unlawful detention (Article 301 of the Criminal Code), bringing a knowingly innocent person to criminal responsibility (Article 299 of the Criminal Code). unlawful exemption from criminal liability (Article 300 of the Criminal Code), coercion to testify (Article 302 of the Criminal Code). falsification of evidence (Article 303 of the Criminal Code). According to part 2 of Art. 294 of the Criminal Code, it is also criminally punishable to interfere in any form in the activities of S. in order to impede a comprehensive, complete and objective investigation of the case (see also Criminal case. on business). Krutskakh V.E.
INVESTIGATOR
INVESTIGATOR - an official of the prosecutor's office, internal affairs bodies, the federal security service, the tax police, whose task is to conduct a preliminary investigation in criminal cases. S. is entrusted with the duty of a comprehensive, complete and objective study of the circumstances of the crime: All his decisions in the case must be based on the collected evidence, the assessment of which he makes according to his inner conviction, based on a comprehensive, complete and objective consideration of all the circumstances of the case in their totality, guided by law and justice. C., regardless of departmental affiliation, during the preliminary investigation are guided by the norms of the criminal procedural legislation without any exceptions. Supervision over the activities of S. is carried out by the prosecutor. The Code of Criminal Procedure determines the competence of the S. of each body in accordance with the jurisdiction in criminal proceedings. In cases under investigation, S. has the right to give orders (in writing) to the bodies of inquiry, which are binding on them, on the performance of search and investigative actions and require their cooperation in carrying out a number of investigative actions. S. takes all decisions on the direction of the investigation and the performance of investigative actions independently, except in cases where the law provides for the need to obtain a sanction from the prosecutor (detention, search, seizure of correspondence, etc.), and bears full responsibility for their legal and timely execution. S.'s resolutions are obligatory for all officials and citizens. S. bears criminal liability for knowingly unlawful detention (Article 301 of the Criminal Code), bringing a knowingly innocent person to criminal responsibility (Article 299 of the Criminal Code). unlawful exemption from criminal liability (Article 300 of the Criminal Code), coercion to testify (Article 302 of the Criminal Code). falsification of evidence (Article 303 of the Criminal Code). According to part 2 of Art. 294 of the Criminal Code, it is also criminally punishable to interfere in any form in the activities of S. in order to impede a comprehensive, complete and objective investigation of the case (see also Criminal case. on business). Krutskakh V.E.
You may be interested to know the lexical, direct or figurative meaning of these words:
STATE LANGUAGE - LANGUAGE Official language where work is being done...
LANGUAGE OF INTERNATIONAL COMMUNICATION - LANGUAGE OF INTERNATIONAL COMMUNICATION a concept used in relation to ...



