The population of Japan. Unusual and interesting facts about the population of Japan. The population of Japan, its distribution throughout the country
Japan deserves special attention. This land of the Yellow Sun last years has become very popular among the inhabitants of the world, it is developed at a consistently high level and continues to "move" further towards the ideal. The state produces various household appliances and high-quality equipment, the demand for which is active throughout big world. An interesting circumstance is also that The population of Japan in 2018 is 127 million people. Gradually, the population density continues to grow, which proves the development and stability of this state.
Population of Japan
If you talk about Japan, you can find out a huge number of interesting facts. As is known, given country famous for the active production of modern household appliances, which meets all the parameters of quality and long shelf life. In recent years, the production of equipment has slightly decreased, this is influenced by the instability of the economic policy of the world and the “jumps” in the dollar.
What is still surprising and unusual in this state is its population density. Hundreds of thousands of tourists come to Japan, but few want to stay here forever. Although most The resident population is only indigenous people, the population of the state continues to grow. Population growth is observed due to the birth rate, the value of which is included in the norm. Statistics indicated that the population of Japan in 2018 is 127 million people, there is an increase in the country, but there is also a decrease in the indigenous population. Unfortunately, here the official mortality slightly exceeds the average statistical norms. The main reason for the increased mortality of the population living in Japan is the spread of serious diseases, as well as the advanced and senile age of people.
The statistics of population growth and decline are constantly in changeable limits. In some years, mortality prevails over fertility, in other times the reverse situation occurs. Even in such a developed and economically stable state, young families are not very eager to have a baby a large number kids. In most cases, young parents raise no more than 2 babies in one family, and very few agree to the birth of a third and subsequent children.
Of course, this fact is strange, because in Japan the economic sphere is well established, but people do not want to increase their own number of people living in their own families by increasing the birth rate. However, the bulk of the local residents are working people.
The Japanese are amazing people with an unusual worldview and rich inner world. The people are unlucky with geographic location country and sometimes unbearable natural conditions, but the difficulties only made them stronger, more resourceful. Japanese people never ceases to amaze the world with its colorfulness and a light dose of madness. For a European, the Japanese will forever remain a mystery and mystery. You won't get tired of being surprised by their oddities. Who are they, these inhabitants of the Country rising sun? Let's try to figure it out together.
The national composition of the country
The population of Japan is for the most part a monocultural and homogeneous group of purebred Japanese. Only 1% of the state's inhabitants (1.56 million) are representatives of the Korean diaspora and workers from Asia. As for Americans and Europeans, they live in Japan, but on a non-permanent basis.
A small part of the Ryukyus and Ainu natives live on the islands. There is also a separate burakumin community, which differs from the Japanese society in cultural and everyday features.
Residents communicate mainly in Japanese, and English is additionally studied in schools. It is interesting that the locals consider their native speech to be very difficult, therefore they respect a foreigner who knows at least.
Japan Population Size and Density
The state in terms of population ranks 7th after China, India, Brazil, Indonesia, the United States and Russia. According to UN estimates, at the beginning of this year, the population of Japan was more than 126.5 million people. Of these, 48.7% are males, 51.3% are females. More than 31 thousand are migrants. Behind last year 1,269,374 people died, 1,050,211 were born. Statistics showed that the annual increase decreased by 0.12%. Over the past ten years, the population has remained virtually unchanged. The reason for this phenomenon is due to the decline in the birth rate and low mortality of residents.
But, thanks to immigrants, the number of people has increased slightly, although foreigners are poorly welcomed by the locals due to ignorance Japanese culture and violations of applicable laws and regulations.

Japan is a fairly densely populated country. Average density population is 334 people/km2. But in the north of Hokkaido, less than 70 people / km2 live, and in coastal areas - more than 500 people / km2.
The level of urbanization is impressive: 80% of the inhabitants live in cities. Japan has 655 big cities, of which 11 have a population of more than a million.
Most of the people are employed in the service sector, only 13% work in industry and 20% in the agricultural sector. Labor resources are characterized by a fairly high level of qualification. The Japanese do not know how to relax at all, they work both on weekends and on holidays, they do everything a lot and with high quality. Interesting: would such an approach to work be effective for the economies of European countries? For now, it's a secret.
Difficult demographic situation
In the recent past, the natural increase in population was very high, but a few years later, as a result of political reforms aimed at reducing the birth rate, the population of Japan dropped sharply. Due to improved living conditions and a noticeable leap in the development of medicine, the death rate has fallen significantly. There are only three deaths per 1000 newborns. This is a good indicator.
The average age of residents is 44.6 years. The average life expectancy for men is 77 years, for women - 85 years. Just incredible numbers! But in the country there are only 13% of children and adolescents, 64% of people from 15 to 65 years old and 28% of old people. That is, the pension burden ratio is as much as 35.7%. The question arises: why are young families unable to fully reproduce themselves? At this rate, Japan's population is projected to decline to 97 million by 2050. It is unlikely that the Japanese authorities will allow such a situation. But with the current outlook on life, politicians are forced to work hard to stimulate population growth.


Taking a look at Japanese demographic changes, I would like to conclude that a modern Japanese woman often has no time to give birth. She needs more years for, as a result of which she marries late. In addition, financial obstacles lie in wait, such as the high cost of raising children. Lots of young girls and boys Lately decided not to get married at all. And such a decision is followed by the rejection of childbearing, since the Japanese do not welcome extramarital relationships.
Indeed, the able-bodied population preferred a career to marriage. In Japanese society, it is quite difficult to combine work and raising children. An interesting fact is that both sexes doubt family and marital values. 61% of unmarried men and 49.5% of unmarried women aged 18 to 35 did not have a sexual partner. Most didn't even want to. Perhaps, with this view, the population of Japan will not increase soon.
Local authorities are concerned about the state of demography in the country, because after a while, if everything develops at the current pace, the labor force will be greatly reduced.
Japanese Religious Life
In Japan, there are different religious directions that have developed over many centuries. The main currents are Shintoism, Indian Buddhism and Christianity. From the beginning of the 19th century, new Japanese sects appeared on the basis of folk beliefs and rituals.

More than 200 thousand religious institutions and organizations operate on the territory of the country. The number of believers is statistically twice as large as the population of Japan. There is an explanation for that. Many residents of the Land of the Rising Sun are immediately adherents, the existence of which excludes the slightest aggression towards a person. All beliefs are characterized by indulgence, love for one's neighbor, respect for family and ancestors, respect for nature, close interaction between man and God, purification, unity of religious rites with everyday life.
Japanese longevity secrets
The high life expectancy of the people of Japan is due to a proper diet and developed system healthcare.
The Japanese menu includes cereals, soy and seafood. For breakfast, lunch and dinner, the main ingredient, of course, is rice. And its combination with fish wrapped in seaweed is a world-famous delicacy called sushi.
Fruits in the Land of the Rising Sun are very expensive: for two dollars you can buy just one apple or apricot. But, nevertheless, they are eaten in larger quantities and exclusively fresh.
Also, the inhabitants of Japan love greens, vegetables, especially eggplant, spinach, bamboo sprouts, broccoli. Eat food only in season.
It may seem that the variety of food in Japan is very poor, but in a week a Japanese family eats about 50 different dishes, when as a European one - only 30.
The Japanese, in addition to all of the above, move a lot, do physical exercises. Naturally, the result was not long in coming. Only three out of a hundred people in Japan are overweight. For comparison: in America, as many as 34% of the population suffer from this disease.

That's the whole secret of the longevity of the Japanese. By following these principles, we can boast of good health.
Unusual traditions of the Japanese
The population of Japan observes a huge amount. The life of a Japanese is literally permeated with a network of customs and ceremonies, this is especially evident in communication between people.
The Japanese greet not with a handshake, but with a slight bow, the depth and duration of which should correspond to social status counter. When talking, the inhabitants of the Land of the Rising Sun begin their speech with an apology, as if for wasting the interlocutor's time. And they always smile.

Before going outside, the Japanese always take a bath; in general, they are obsessed with personal hygiene. They even go to the toilet in special slippers, so as not to spread dirt around the house.
Even in Japan there is a cult of food. They can talk about food for hours, while tasty smacking their lips. It is considered ignorance not to say “Very tasty” to the hostess. A best souvenir, perhaps, will become a new yummy.
Interestingly, a tip for a Japanese is perceived as an obscene gesture. After all, paying the appointed price for the service, the visitor remains on an equal footing with the workers of the institution. Otherwise, he will show his superiority, which amounts to an insult.
It is unacceptable to enter the house shod. Eat special place for street shoes, on which to step with a toe is equated with a disaster - because it is dirty there.
In general, Japan is a country of naive, sympathetic and very smart people. Many of their actions on the part of the Europeans are not amenable to common sense, but, thanks to such actions, the people of Japan will always retain great interest in themselves.
What interesting or funny facts about the Japanese do you know? Perhaps you noticed something in communication with the inhabitants of the Land of the Rising Sun? Please share.
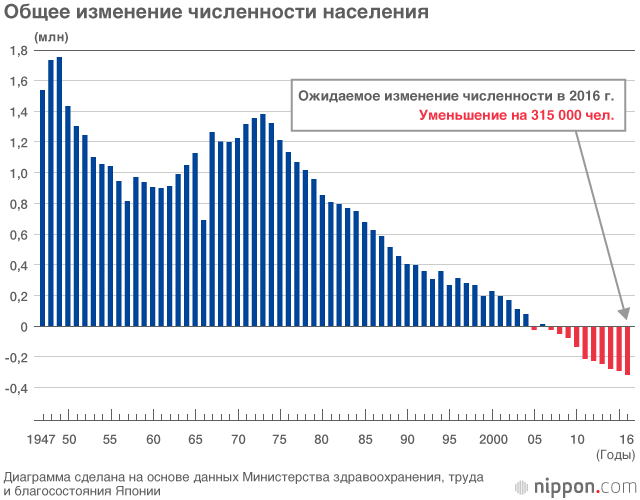
In 2016, the number of deaths is estimated at about 1,296,000, the highest number since World War II. Taking births into account, estimates show that the population has declined by 315,000 people, and Japan's population is decreasing faster and faster.
Demographics of Japan
| Per 1000 people | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 estimate | Data for 2015 | Difference | 2016 estimate | Data for 2015 | |
| birth | 981 000 | 1 005 677 | -25 000 | 7,8 | 8 |
| Of death | 1 296 000 | 1 290 444 | 6 000 | 10,3 | 10,3 |
| Total population change | -315 000 | -284 767 | -30 000 | -2,5 | -2,3 |
| marriages | 621 000 | 635 156 | -14 000 | 5 | 5,1 |
| Divorces | 217 000 | 226 215 | -9 000 | 1,73 | 1,81 |
Note: Calculations are based on population estimates as of October 1, 2016 (125,245,000)
According to the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan
During the first post-war baby boom (1947-1949), 2.5 million births per year were registered. During the second period (1971-1974) - 2 million each. Since then, the number of births has been declining, and in 2007 there were fewer births than deaths.
The number of marriages in 2016 is estimated at 621,000, about 9,000 fewer than the previous year. This is the minimum number for the post-war period, and is only 10 people (5 marriages) per 1000 people.
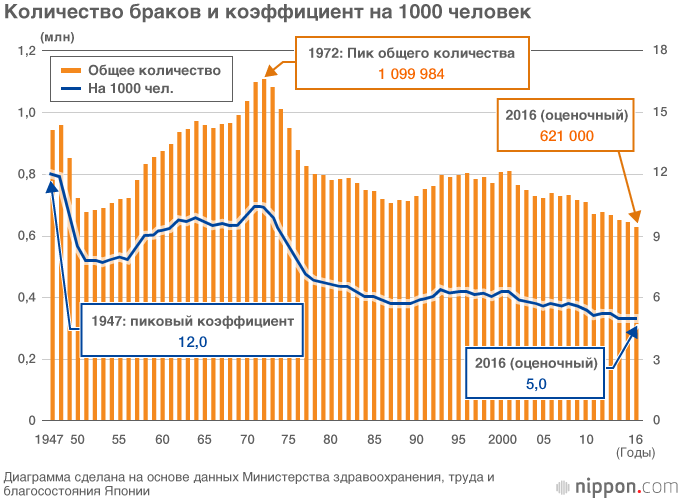
The table below shows the demographics of eight countries in Asia, Europe and North America collected by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. The marriage rate per 1,000 people is still slightly higher than in Europe, but the birth rate is lower than in other countries. This shows that in Japanese society, couples are unable or unwilling to have children even after marriage.
Data on births and deaths, marriages and divorces by country
(Per 1000 people)
| fertility | Mortality | marriages | Divorces | fertility rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | *7,8 | *10,3 | *5,0 | *1,73 | 1,45 |
| South Korea | 8,6 | 5,4 | 5,9 | 2,1 | 1,24 |
| Singapore | 10,9 | 5,0 | 7,3 | 1,77 | 1,25 |
| USA | 12,5 | *8,4 | *6,9 | *3,2 | *1,84 |
| France | *12,0 | *8,5 | 3,5 | 1,91 | 2,01 |
| Germany | *8,7 | *10,8 | 4,6 | 2,11 | 1,47 |
| Italy | 8,3 | 10,0 | 3,2 | 0,86 | 1,37 |
| Sweden | 11,8 | *9,1 | 5,4 | 2,81 | 1,88 |
| Great Britain | *12,1 | 9,0 | 4,5 | 2,05 | *1,81 |
An asterisk indicates preliminary estimates.
Data from the United Nations Demographic Yearbook, US Department of Health and Human Services National Vital Statistics Reports, Eurostat Population and Social Conditions, South Korea National Bureau of Statistics data
The demographic situation in Japan has come under scrutiny due to the population decline that has continued since 2010, along with a sharp increase in the over-65 age group.
According to UN estimates, the population of Japan at the beginning of March 2016 is 126 million 394 thousand people. Japanese government projections say that if current trends continue, by 2050 the country's population will drop to 90 million.
This is only an extrapolation, which will not necessarily become a reality, but it is the beginning of a new trend. Similar situation expects other Asian and developed European countries.
In 1910, Japan had a population of 51 million.
Historical reference
In the first half of the 20th century, the number of Japanese grew by an average of 5-7% every 5 years, excluding the period of the 2nd World War. The population census of 1950 recorded an increase of 15% compared to 1945, but there is no complete confidence in these figures - in addition to a restorative increase in the birth rate, in 1950 military personnel who returned from the fronts and from captivity were taken into account.
Since 1950, the birth rate began to fall from 28 births per 1,000 people in 1950 to an average figure of 18-19 births per 1,000 in 1955-1975.
The sharp drop in fertility in 1966 was due to the peculiarities of the Japanese zodiac calendar: "Inoe Zuma", the year of bad omens.
After 1980, the fall in the birth rate intensified with a simultaneous decrease in mortality. This led to significant changes in the demographic structure of society, the number of elderly people aged 65 years and above began to increase, while the number of able-bodied population decreased.
Since 2000, the population has increased slightly: an increase of 0.7% over the five-year period between 2005 and 2010.
The peak was recorded by the 2010 census - 128 million people, after which the population began to fall.
On the video population of Japan for 2016:
Largest islands
97% of the population live on four largest islands Japanese archipelago:
- honshu,
- hokkaido,
- Shikoku
Honshu Island- the largest and most populated, more than 97 million people, mainly concentrated in urban agglomerations on west coast.  Most sparsely populated - second largest north islandHokkaido c 5.5 million population.
Most sparsely populated - second largest north islandHokkaido c 5.5 million population.  Kyushu Island with 12 million people - the third largest and southernmost of big islands.
Kyushu Island with 12 million people - the third largest and southernmost of big islands.  The smallest of the four main islands Shikoku with 3.98 million inhabitants.
The smallest of the four main islands Shikoku with 3.98 million inhabitants.  Japan is a highly urbanized country. The 2010 census showed that 90.7% of the population lived in cities. share rural population does not exceed 5%.
Japan is a highly urbanized country. The 2010 census showed that 90.7% of the population lived in cities. share rural population does not exceed 5%.
At the same time, 68.5% of the territory is covered by forests, which is typical for sparsely populated northern countries.
Japan's capital Tokyo, together with Yokohama and Kawasaki, forms the world's largest urban agglomeration, with a population of 35 million people.
Other cities with more than a million inhabitants: Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Kobe, Kyoto, Fukuoka, Saitama, Hiroshima.
On video country density:
Employment
The economically active population is concentrated in cities. 33% of employed Japanese are employed in industry. The country is poor in minerals, so the mining industry is practically not developed.
The developed automotive, electronic and engineering high-tech industry requires highly qualified workers, so there is a shortage of high-class specialists from time to time. 50% work in the service sector, in transport, in construction.
No more than 5% of the able-bodied population is employed in agriculture. In connection with the aging of the population, the employment of older people over 60 years of age is of particular importance. Unemployment is at a low level - 4.4% in 2015.
However, the system of “lifetime employment”, which the country was so proud of until 2000, is gradually giving way to hiring freelancers. The number of freelancers increased from 5% to 24%.
Japan is a rich country.
Net per capita income (income after taxes) was $26,111 at the end of 2014. For comparison, in South Korea this figure was equal to 19510 dollars.
From this article you can find out which and probably now 2016. But looking back at the pace of economic growth developed countries, we can conclude that these countries will be at a low level for many years to come.
The rest of the countries of the Asian region cannot even come close to such indicators. Singapore stands apart, but there is no data on net per capita income.
You might also be interested.
In 2016, the population of Japan will decrease by -149,311 people and at the end of the year will be 126,385,225 people. Natural population growth will be negative and will amount to 218,905 people. For the entire year, approximately 1,048,971 children will be born and 1,267,876 people will die. If the level external migration remains at the level of the previous year, then due to migration reasons, the population will change by 69,594 people. That is, the total number of people entering the country for the purpose of long-term stay (immigrants) will be more quantity people leaving the country (emigrants).
The dynamics of change in the population of Japan in 2016
Below are the coefficients of change in the population of Japan, calculated by us for 2016:
- Birth rate: average 2,874 children per day (119.75 per hour)
- Mortality: average 3,474 per day (144.73 per hour)
- Migration population growth: an average of 191 people per day (7.94 per hour)
Distribution of the population by age groups
According to our calculations, as of the beginning of 2016, the population of Japan had the following age distribution:
In absolute numbers:
- 16,605,127 under 15s (Men: 8,525,897 / Women: 8,080,495)
- 80,982,103 over 14 and under 65 (male: 40,835,225 / female: 40,146,878)
- 28,947,306 over 64 (Men: 12,281,442 / Women: 16,665,864)
We have prepared a simplified model of the age-sex pyramid, in which only three age groups are presented, the data on which were given above:
| 65+ |
| 15-64 |
| 0-14 |
| men | women | |||



