The boundaries of the oceans on the world map contour maps. War of Independence in the Netherlands. Birth of the Republic of the United Provinces
They are different in geographical location, size and shape, which affects the features of their nature.
Geographic location and size of the continents
Continents are placed on the surface of the Earth unevenly. In the Northern Hemisphere, they occupy 39% of the surface, and in the Southern - only 19%. For this reason, the Northern Hemisphere of the Earth is called the continental, and the Southern - the oceanic.
According to the position relative to the equator, the continents are divided into a group of southern and a group of northern continents.
Since the continents are located at different latitudes, they receive an unequal amount of light and heat from the Sun. In shaping the nature of the continent, its area plays an important role: what larger mainland, the more territories on it that are remote from the oceans and do not experience their impact. big geographical importance has a relative position of the continents.
Geographic location and size of the oceans
The separating continents differ from each other in size, properties of waters, systems of currents, features of the organic world.
And they have similar geographical position: they stretch from the Arctic Circle to. almost entirely in the southern hemisphere. Special geographical position y - it is located around the North Pole within the Arctic Circle, covered sea ice and isolated from other oceans.
The border of the continents with the oceans runs along the coastline. It can be straight or indented, that is, having many protrusions. Have rugged coastlines many seas and bays. Going deep into the land, they have a significant impact on the nature of the continents.
Interaction between continents and oceans
Land and water have different properties, while they are constantly in close interaction. The oceans strongly influence the natural processes on the continents, but the continents also take part in the formation of the nature of the oceans.
1. Read and determine if the following statements are correct. If the judgment is incorrect, write it down, correcting the errors.
1) In the German Confederation there was a rivalry between Saxony and Prussia.
In the German Confederation there was a rivalry between Austria and Prussia.
2) The most economically developed regions were the Rhine-Westphalian provinces of Prussia.
The Junker economy gradually became capitalist, the seigneurial duties of the peasants were more and more a thing of the past.
4) In March 1849, the Frankfurt Parliament adopted an imperial constitution that retained estate privileges and feudal duties.
In March 1849, the Frankfurt Parliament adopted an imperial constitution that abolished class privileges and feudal obligations and introduced liberal freedoms.
5) The revolution in Germany ended with the national unification of the country.
The revolution in Germany ended in defeat and failed to unite the country.
1) Draw the borders of the German Confederation.
2) Draw the borders of Prussia by 1864. Sign its name.
3) Mark with different colors: a) the territories captured by Prussia in 1864-1866. Sign their names; b) states included in the North German Confederation. Sign their names.
4) Draw the boundaries of the North German Confederation.
5) Mark the capital of Prussia with the icon. Sign her name.
6) Mark with arrows the offensive of the Prussian troops in the wars with Denmark and Austria.

1. The area from which the kingdom of Piedmont expelled the Austrians with the help of Napoleon III. 2. The English queen, whose name gave the name to an entire era. 3. Name of the representative body of the German Confederation. 4. English diplomat, liberal, Prime Minister of Great Britain in the second half of the 19th century. 5. Chairman of the Government Commission for the Workers of the Provisional Government of France. 6. The name of the constitution of France, which established a constitutional-monarchist regime in the country. 7. One of the organizers of the Society of the Seasons.
4. Write two characteristics of the political figure whose name appeared in the highlighted column of the crossword puzzle in task 3, on behalf of the Prussian (1) and Austrian (2) journalists.
Prussian journalist
This great person, who for many years faithfully served our homeland, was right hand emperor.
Always knowing the right decision, he follows it in spite of any opposition. Always loyal to the monarchy, he does not pay much attention to the prohibitions from the Bundestag, but history, I am sure, will show that he is right, that he will continue to be called the Iron Chancellor.
It was thanks to his efforts that we defeated Austria, won a great victory over France and united Germany.
Austrian journalist
A provincial junker who was accustomed to managing only his estate, he remained such even when he became chancellor. He bosses around the rest of the ministers and even the princes of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation, as if they were his farmhands. The favor of the emperor and the strength of the army allow him to do this, but there is no justice for him.
He destroyed the Holy Roman Empire that existed for centuries and founded a new, German one in its place. But Berlin does not have the rights to rule the empire that Vienna has, and history will prove it.

Answer: A - 4; B - 2; AT 5; G - 5; D - 1; E - 3.
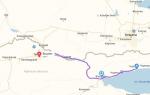
1. Fill in the gaps in the diagram "Background for the liberation war in the Netherlands"
2. Complete the tasks on the contour map "War of Liberation in the Netherlands"
1) Draw the borders of the Netherlands, which were under the rule of Spain (by 1566)
2) Mark the areas covered by the iconoclastic movement
3) Mark with arrows the campaigns of the Spanish troops under the command of the Duke of Alba. Sign them years
4) Mark the port whose capture by the Geuzes led to a general uprising in the northern provinces of the Netherlands. Sign its name and the year of this event
5) Paint over with different colors the territories of the provinces: a) united by the Union of Utrecht; b) remained under the rule of Spain until 1579. Sign the names of the provinces
3. Arrange the following events in chronological order. Specify the answer as a sequence of numbers
1) Signing of the Union of Utrecht; 2) the capture of the city of Bril by sea; 3) the beginning of the Spanish-Dutch war; 4) the entry of the Spanish army under the command of Alba into Brussels; 5) the beginning of the iconoclastic movement; 6) the announcement by the Northern Netherlands of Philip II deposed; 7) the signing of a peace treaty between Spain and Holland; 8) the siege of the city of Haarlem by the Spanish troops
5 4 2 3 8 1 6 7
4. Indicate on the timeline the events highlighted in italics in task 3 by putting their serial numbers in the circles
5. Having solved the ciphertext, you will read a statement about the liberation war in the Netherlands. Complete the task in writing
1) A form of government in which the supreme power belongs to one person - the monarch. 2) The Royal Viceroy in the Netherlands. 3) Participants in a religious movement aimed at destroying objects of worship (including icons). 4) The name of the leader of the liberation movement in the Netherlands. 5) Union of states. 6) The name of the largest northern province of the Netherlands. 7) The city in which the military-political alliance against Spain was concluded
Do you agree with this statement? Justify your opinion
6. Read the notes of the English merchant and economist Thomas Maine on the reasons for the rise of Holland in the early 17th century. Emphasize the reasons for the economic prosperity of the country (note: phrases are written here that must be underlined in the text) and complete the task
They threw off the yoke of Spanish slavery...
their unceasing zeal in trade?...
their provinces are warehouses of goods for most of the countries of Christendom...
really supplies and sells to other states ships, artillery, tackle, grain, gunpowder, bullets, and so on, and everything that only the Dutch collect from all over the world thanks to their diligent bargaining ...
If you want to name other reasons for the rise of Holland, write them down.
Textile industry, development of manufactories, skillful sailors, convenient geographical position
Parts of the oceans.
1. Lay a route on the contour map of the hemispheres world travel so that it passes through all the oceans. Sign the seas, bays, straits through which your route is laid.
2. Find the boundaries of all oceans on the map of the oceans in the atlas. Put them on a contour map. Designate the boundary of the Southern Ocean allocated by some scientists.
3. Name an ocean that has all southern borders
Arctic.
4. Using the map of the hemispheres and the map of the oceans, write a description of one of the oceans.
5. Using a map of the hemispheres, make a description of the Mediterranean Sea.
6. In figure 12, indicate with numbers: 1 - coastline, 2 - bays, 3 - straits, 4 - islands, 5 - peninsulas.
7. In figure 13, indicate:
a) peninsulas: Arabian, Scandinavian, Labrador, Somalia, Hindustan;
b) islands: Greenland, Madagascar, Hawaiian, Big barrier reef, New Guinea;
c) bays: Bengal, Mexican, Guinean;
d) straits: Bering, Gibraltar, Magellan, Drake;
e) seas: Black, Baltic, Barents, Mediterranean, Red, Okhotsk, Japanese, Caribbean.
Some properties of ocean water.
1*. The salinity of the water of which sea is more - Arabian or Okhotsk? Why?
Arabian. flows into the Sea of Okhotsk more rivers, there more precipitation. Arabians have more evaporation.
2. By physical map Russia define:
a) completely freezing seas: Kara, Laptev, East Siberian.
b) partially freezing seas: Baltic, Barents.
c) non-freezing seas: Black, Caspian, Japanese.
3. According to the map of the oceans in the atlas, set:
a) seas with the highest temperature of surface waters - Japanese, South Chinese, Arabian, Caribbean, Red;
b) seas with the lowest surface temperature - Greenland, Barents, Kara, Laptev, East Siberian.
Waves in the ocean.
After studying § 26 of the textbook and reading task 3 after it, fill in the table.
ocean currents.
1. Using the map of the oceans in the atlas, mark in figure 14 five warm and five cold currents. Sign their names.
2*. Why are both warm and cold currents found at the same latitude?
Because the wind drives away the warm surface water, and colder ones rise in their place.
The study of the oceans.
According to the text of the textbook, make a plan for the story "How they studied and study the ocean."
1. What happens on the surface of the ocean and in coastal waters.
2. Jacques Yves Cousteau
3. Explorers of great depths.
4. Special research vessels.