Who discovered Australia in 1644. Who actually discovered Australia? Who discovered Australia according to the official version
Legends that somewhere far to the south, beyond the single World Ocean, there should be a huge land have been known since ancient times. It was to the ancient geographers who called this land “ Terra Australis”, that is, “South Land”, Australia owes its modern name. And although their assumptions were largely erroneous, in the era of the Great geographical discoveries many explorers dreamed not only of the way to India, but also of the vast southern continent.
In the 15th century, the Portuguese, under the leadership of Vasco da Gama, opened the southern route to India and founded their first colonies on the shores of the Indian Ocean. The "maximum task" was completed and many explorers rushed south in search of the "Terra Australis" continent. They managed to discover many islands of Oceania, New Guinea and, most likely, set foot on the land of Australia.
There is a version that the Portuguese Cristovan de Mendonsa was the first to find Australia in 1522. However, there is no reliable evidence of his discovery.
Who is considered the pioneer?
Today it is an indisputable fact that the Dutch were the true discoverers of Australia in the 17th century. The dominance of Portugal in the region at that time came to an end and their place was taken by Holland - one of the most developed and strong European powers of this period. In 1605, the Dutch citizen Willem Janszon set sail on the Deifken ship from the port of Bantam on the island of Java. Its purpose was to study south coast Guinea, but, as in the case of another traveler, Christopher Columbus, he found something completely different from what he was looking for. Unknown land, which the Deifken crew stumbled upon, rounding northern part Guinea was Australia.
Melbourne is located on the territory that John Batman bought in the 18th century. However, the deal was declared invalid and the city was named Melbourne, not Batmania, as the owner of the land had planned.
Willem Janszon, like Columbus, did not understand what he discovered huge continent, naming the discovered Australian peninsula of Cape York "New Zealand". The true scale of what was found became known later. Most likely, Willem Janszoon was not the first European to set foot on the land of the "Southern Continent". However a large number of direct and indirect evidence of his discovery does not leave historians the slightest doubt that he should be considered the pioneer of "Terra Australis".
Who discovered Australia?
It is generally accepted that the discoverer of Australia is James Cook. In 1770 he reached east coast Australia. Cook called just open land New South Wales. He explored the area where modern Sydney is now, that is, Botany Bay. Not far from this place in 1788 the first English colony was formed.
There are hypotheses that suggest that Egyptians and Europeans visited the shores of Australia before Cook.
It is hard to imagine that the ancient Egyptians suspected the existence of Australia. However, many scientists suggest that this is quite possible. When studying the mummies of the ancient Egyptians of the New Kingdom period, it was found that the Egyptians used a special eucalyptus oil to embalm bodies. The plants from which the oil was made grew only on northeast coast Australia. Accurate and indisputable data pointing to this fact is not presented.
Another fact speaks in favor of these hypotheses about the discoverers of Australia. These are silhouettes carved on Australian rocks. The figures are more like inhabitants ancient east but not the Australian Aborigines. These finds were made on the northern coast of Australia. In addition, images of beetles were found that resembled sacred to the Egyptians, scarab beetles.
It is also known that the Dutch were on the shores of Australia before Cook. During their journey between the Netherlands and the island of Java, the Dutch may have accidentally stumbled upon the coast of Australia.
The fact is that the usual route of the Dutch to Java passed through the cape Good Hope, and then straight to the island through Indian Ocean. Some sailors went too far east before turning to the island, and therefore met the coast of Australia on their way. The first European to reach the shores of Australia is Billem Janzson.
Columbus discovered America and Captain Cook discovered Australia. Both of these statements have long been disputed many times, but they continue to live in the minds of the masses. Long before Captain Cook set foot on the coast of Australia on April 20, 1770, navigators from the Old World had already landed here more than once.
According to a number of historians, the Portuguese were the discoverers of Australia. They claim that an expedition led by Cristovan de Mendonça visited the northwest coast of Australia in 1522. It is unknown if this happened intentionally or by accident. The details of this voyage are also unknown. The only material evidence that has come down to us are small bronze cannons with the image of the Portuguese crown minted on them. They were found in 1916 on the shores of Roebuck Bay ( Western Australia) and date back to the beginning of the 16th century.
2 Expedition of Willem Janszon
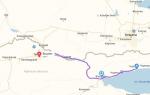
The first European to visit Australia is the Dutchman Willem Janszon. On November 28, 1605, Captain Janszon set off from Bantam on the ship "Dufken" to unknown lands. Bypassing the islands of Kai and Aru from the north, he reached south coast New Guinea, completely unfamiliar to the Dutch. Janszon called it "Marshy Land" and traced the coastline for 400 kilometers. Then rounding the island of Kolepom, Janszon turned to the southeast, crossed central part Arafura Sea and suddenly saw the shore. It was Australia. In the western part of the Cape York Peninsula, near the mouth of a small river, in May 1606 the Dutch made the first documented landing of Europeans on the Australian continent.
Janszon sailed his ship along the flat desert coast. Although unknown land, as the Dutch were convinced, stretched further south, on June 6, 1606, at Cape Kerver (“Turn”), the Dufken turned 180º and set off on the return journey. During the landings at Albatros Bay, the Dutch first came into contact with Australian aborigines. Fighting immediately ensued, with several dead on both sides. Continuing north, the sailors traced and charted the coast of the Cape York Peninsula almost to its northern tip. The total length of the explored coast of Australia, which Janszon dubbed New Holland, was about 350 kilometers.
3 Expedition of Jan Carstens
The wreck of the English ship Triel, which occurred on May 25, 1622 on reefs near the islands of Monte Bello and Barrow, showed that the complete lack of knowledge of the waters washing the coast of the Northwestern and Northern Australia, threatens great dangers. The leadership of the Dutch East India Company decided to explore the ocean south of Java and trace the southern coast of New Guinea. To accomplish this task, Jan Carstens' expedition set off from Batavia in January 1623 on two ships, the Pera and the Arnhem. For more than a week, Dutch sailors sailed along the southern coast of New Guinea. On the morning of February 16, Carstens saw a tall mountain range- it was the western part of the Maoke mountains. Five days later, a group of Dutch landed ashore to resupply. Local population was very hostile. As a result of the skirmish, 10 sailors were killed, including the captain of the Arnhem.
On March 20, the expedition reached the southwestern tip of New Guinea. The weather worsened, a storm began. On March 28, Carstens sent a navigator on a boat with 12 sailors to explore the coast that could be seen in the distance. He reported that the sea was getting shallower to the east, and desert land was visible in the distance. Meanwhile, it became dangerous to walk along the coast: shallows and reefs began to come across more and more often. The Dutch turned to the open sea.
On April 12, the earth again appeared on the horizon. It was Australia. For two weeks, Carstens' ships sailed south along the western coast of the Cape York Peninsula, landing several times on land - in estuaries and in bays. The aborigines they met were quite peaceful. The flat and low-lying coast of Northwestern Australia was described by Carstens in his report as "the most barren on Earth." The Dutch were not even able to find here in sufficient quantities fresh water. In addition, the flagship of the Pera expedition was damaged. Carstens instructed Colster, the captain of the Arnhem, to complete the exploration of the coast, while he himself turned north and safely reached the Moluccas. Colster, moving south, managed to reach the Gulf of Carpentaria. Taking advantage of the favorable southeast monsoon, he turned from here to the northwest and, following this course, opened large peninsula, later named the Arnhemland Peninsula after his ship.
4 Expeditions of Abel Tasman
By the beginning of the 1640s. the Dutch knew and mapped the following parts of Australia: in the north - the western coast of the Cape York Peninsula, the protrusion of Arnhemland, the entire western coast of the mainland and western part its southern coast. However, it was still not clear what exactly this mysterious land: a separate continent or giant protrusion of the as yet undiscovered Greater southern mainland? And the pragmatic directors of the East India Company were worried about another question: what are the potential benefits of these newfound lands? What are their commercial prospects? The expedition was supposed to answer these questions. Dutch navigator Abel Tasman, who left Batavia in 1642 on two small ships, the Hemskerk and Zehan. Tasman did not meet any mainland, and only on November 24 from the board of the Zehan did they see a high coast, called Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania). Tasman never figured out whether it was an island or the southern tip of Australia, and Van Diemen's Land was considered a peninsula for more than a century and a half, until Bass Strait was passed. Going further to the south-east of the runoff, Tasman discovered New Zealand, and on this expedition almost ended, leaving a mass unresolved issues.
In 1645, the governor of Batavia, Van Diemen, sent Tasman to new expedition to the coast of Australia. Three Tasman ships surveyed the southern coast of New Guinea for 750 kilometers and completed the discovery of the Gulf of Carpentaria, bypassing its eastern and, for the first time, southern and western coast. Experienced sailors, the Dutch never noticed the entrance to the Torres Strait. In total, the expedition explored and mapped about 5.5 thousand kilometers of coast and found that all the lands previously discovered by the Dutch are parts of a single mainland - New Holland. However, Tasman did not find anything worthy of attention from the point of view of commerce on this mainland, and after 1644 the Dutch completely cooled off towards the Green Continent.
5 James Cook Expedition
In 1768, James Cook set out on his first circumnavigation. In April 1770, Cook approached the east coast of Australia. On the shore of the bay, in the waters of which the Endeavor stopped, the expedition managed to find many previously unknown plant species, so Cook called this bay Botanical. From Botany Bay, Cook headed northwest along the east coast of Australia.
A few kilometers north of Botany Bay, James Cook discovered a wide natural passage into a huge natural harbor - Port Jackson. In his report, the researcher described it as perfect place for the safe parking of many ships. Many years later, the first Australian city, Sydney, was founded here. It took Cook the next four months to climb up to the Gulf of Carpentaria, to the area that bears the name New Holland. Navigator made up detailed map coastline of future Australia.
Not quite happily passing the big barrier reef, Endeavor has finally reached the northern tip of Australia. On August 22, 1770, James Cook, on behalf of King George III, solemnly proclaimed the land he had explored as the possession of Great Britain and named it New South Wales.
Australia is the smallest and most distant continent from Eurasia. During the Middle Ages, it was called Terra Australis Incognita, which means "unknown southern land". Who discovered mainland Australia, and in what year did it happen?
Official version
Mankind has become aware of new territory thanks to the traveler - navigator James Cook. His goal was to study the passage of Venus through the solar disk. It is assumed that the true reason for Cook's trip was the search for uncharted lands in the southern latitudes of Terra Australis Incognita. He went to trip around the world and discovered distant lands, reaching the coast of the mainland in 1770. This date is considered historically accurate. But it was known about the existence of a piece of land "on the edge of the earth" much earlier. In addition, there were human settlements. It is difficult to determine the date of their foundation, approximately it happened 40 - 60 thousand years ago. Artifacts found in the western part of Australia on the Swan River belong to that period.
Who discovered mainland Australia in prehistoric times?
Scientists suggest that the first travelers who went to land across the ocean were the ancient Egyptians. They brought eucalyptus oil from these parts.
This version is confirmed cave drawings with insects similar to the Egyptian sacred scarabs. In addition, mummies were found in tombs in Egypt, which were embalmed with oil from eucalyptus trees grown in Australia.
However, all these theories are not officially accepted, since the existence of a continent lost in the sea element in Europe became known much later.
Who first discovered Australia?
Attempts to reach the continent were made several times. In the 16th century in sea route the Portuguese went. In 1509 they reached Moluccas, and in 1522 they ended up in the north west coast. These dates are considered the first time the mainland was founded by Europeans.
There is also a hypothesis that Admiral Willem Jansson, who arrived on the continent on behalf of the Dutch authorities, discovered Australia. He undertook a campaign in 1605. For this purpose, the Dyfken ship was equipped. He followed in the direction of New Guinea and after three months of travel reached the Cape York Peninsula. The navigator made a detailed map of the coastline 320 km long. He had no idea that he had discovered new continent, considering the lands to be the territories of New Guinea. Therefore, they were given the name "New Holland".
Behind him sailed to the mainland Abel Tasman. He explored the islands on the west coast and plotted their outlines on a world map. One of the islands, Tasmania, is named after the discoverer.
Yes, to XVII century, thanks to the efforts of Dutch travelers, the position on the world map of mainland Australia and its islands became known.
Australia - amazing place on the ground. Her nature is unique. Here live animals that you will not find anywhere else. This is the smallest continent and at the same time a country with one of the leading economies in the world. The State of Australia was created by the union of the British colonies into the Commonwealth of Australia in 1901. And after 30 years, she received complete independence in external and internal affairs. Who discovered Australia? More on this later.
Who discovered Australia and in what year?
Australia, although a distant, but attractive place to live. But who was the first to discover this land and move it from the category of legends to a given? All school history textbooks say that the discoverer of the fifth continent is James Cook, a famous navigator and cartographer.
In the middle of the 18th century, Captain Cook explored southern waters World Ocean. After an unsuccessful attempt to discover Antarctica, the Endeavor ship approached the coast of Australia in 1770. After that, James Cook visited the continent twice more. He proved that New Zealand is an archipelago and does not belong to Antarctica. Then the active development of the new land began.
However, the first explorer of Australia was the Dutchman Willem Janszon. This happened 165 years before Cook's expedition. In 1605, the ship of the Dutch fleet "Dyfken" set off from the port of Bantam to the shores of New Guinea.

Without knowing it, Admiral Janszon landed in northwestern Australia. In total, he mapped 320 km of coastline. The explorer decided that this was part of New Guinea, and declared these lands the property of the Netherlands.
Some scientists believe that before the Dutch, the fifth continent was secretly mastered by the Portuguese in the early 20s of the 16th century. In 1916, in the northwest of Australia, scientists found Portuguese cannons of that era. Also in favor of this theory are maps that partially show the coast of the continent south of the island of Java. However, no records of Portuguese expeditions to the region have survived.

Australia: the first people on the mainland
The ancestors of the indigenous population of Australia appeared on the mainland about 70 thousand years ago. This is evidenced by the fossils found at the bottom dry lake Mungo and in the Swan River region.
It is believed that the first people arrived by sea when New Guinea adjoined the continent. Where they came from is unknown. However, archaeologists believe that at that time at least three different nationalities settled on the mainland.
To the east of Darwin is national park Cockatoo. Here you can see the oldest rock art. Ancient drawings are at least 30 thousand years old. In Australia, images of beetles resembling scarabs have also been found.

In this regard, some scholars think that in the era of the pharaohs, the mainland was visited by the Egyptians. Presumably they made this way for the sake of eucalyptus leaves. They were used to make embalming oil.
Today, to visit Australia, you need to go a long way. Even by plane, a flight with transfers will take 15–20 hours. It is difficult to imagine what tests the discoverers of the fifth continent were subjected to. Their courage and ambition can only be envied. They went down in history, and we expanded our knowledge of the world. Would you like to visit Australia?