Current train schedule. Schedule of passenger and commuter trains
This page provides a detailed timetable for commuter and passenger trains all categories departing from Moscow railway stations.
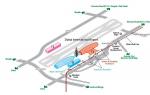
Moscow - the heart of the railway Russian Federation. There are eight major railway stations on the territory of the capital - Belorussky, Kazansky, Kievsky, Kursky, Leningradsky, Paveletsky, Rizhsky and Yaroslavsky, each of which performs specific transport tasks.
WITH Belorussky railway station trains are recovering long distance in a southwestern and western direction. International trains depart in the direction of Brest, Berlin, Bratislava, Warsaw, Vienna, Vilnius, Gomel, Grodno, Kaliningrad, Kaunas, Cologne, Klaipeda, Minsk, Mogilev, Nice, Paris, Polotsk, Prague and others.
Suburban service from the Belorussky railway station it is carried out by electric trains and express trains to the stations of Borodino, Vyazma, Zvenigorod, Mozhaisk, Odintsovo, Usovo, as well as a special express train to Sheremetyevo Airport.
Kazansky railway station is one of the busiest stations in Moscow, which provides the movement of passenger and suburban trains south, southeast and east.
A number of long-distance trains depart from the station, connecting the capital with many cities in Central Russia, the Caucasus and Siberia. International express trains from the Kazansky railway station go to the largest cities of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
Passenger and fast trains depart from the Kievsky railway station in the direction of Ukraine, Moldova, Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania, Serbia and Slovakia. Suburban electric trains connect Moscow with Aprelevka, Bekasovo, Kaluga, Crosses, Lesnoy Gorodok, Maloyaroslavets, Nara, and Vnukovo airport.
Kursky railway station serves as a transit railway point. Trains leave from its platforms towards Donetsk, Dnepropetrovsk, Kerch, Poltava, Simferopol and Kharkov in Ukraine, as well as many major cities Russia. Electric trains follow in the Kursk and Gorky directions.
Leningradsky is the only railway station in Moscow that is not subordinate to the Moscow railway. As a passenger part of the Moscow-Oktyabrskaya station, it is a division of the Oktyabrskaya Railway and serves the northwestern and northern directions.
From Moscow-Oktyabrskaya station, trains run to Veliky Novgorod, Murmansk, Petrozavodsk, Pskov and St. Petersburg in Russia, as well as to Tallinn (Estonia) and Helsinki (Finland). Suburban electric trains run to the stations Klin, Konakovo, Kryukovo, Podsolnechnaya, Skhodnya and Tver.
The Paveletsky railway station connects the capital with the Central Chernozem region, the Lower and Middle Volga regions, and partly with the Caucasus. International trains to Alma-Ata, Baku, Donetsk, Lugansk and Tbilisi start from the station. Commuter trains connect Moscow with Barybino, Biryulyovo, Kashira, Mikhnevo, Ozherelye, Stupino, Uzunovo, Yaganovo and the airport at Domodedovo.
The Rizhsky railway station provides reception of trains from the north-western direction. Trains depart from here in the direction of Velikiye Luki and Pskov, as well as branded trains to the cities of Latvia.
Suburban trains and express trains run regularly to Volokolamsk, Dedovsk, Istra, Krasnogorsk, Nakhabino, Novoyerusalimskaya, Rumyantsevo and Shakhovskaya stations.
Trains northeast direction accepts the Yaroslavsky railway station in Moscow, connecting the capital with the largest cities of the Urals, the North, Siberia and Far East. International trains to Beijing and Ulaanbaatar leave from the Yaroslavsky railway station.
Suburban trains from this station run to Alexandrov, Ivanteevka, Krasnoarmeysk, Korolev, Losino-Petrovsky, Mytishchi, Pushkino, Sergiev Posad, Fryazino, Khotkovo, Schelkovo and Yubileyny stations. Suburban express trains connect Moscow with Aleksandrov, Bolshevo, Monino, Mytishchi, Pushkino and Yaroslavl.
All Moscow railway stations are distinguished by a developed modern infrastructure, which necessarily includes preliminary and suburban ticket offices, a detailed schedule of arrival and departure of trains, service centers, waiting rooms of all categories, rest rooms, and left-luggage offices. This contributes to the high capacity of the Moscow railway junction and ensures the continuous movement of the world's largest passenger traffic.
Information about the schedule of trains and electric trains at Moscow station:
The schedule of trains and electric trains at Moscow station today includes 718 long-distance trains, commuter trains and electric trains (including diesel engines) - 2911, 1009 of them passing and 2620 - start or end their journey in this locality. Most trains arrive in the morning. The first, according to the schedule, departs at 00:00 in the direction of Zheleznodorozhnaya station, and the last one arrives at 23:59. The average parking time on the platform is 0:30.
Some trains passing through Moscow station do not run every day (they have a special timetable).
The schedule of trains and electric trains at the station Moscow, presented on this page takes into account seasonal changes, that is, winter and summer version schedules.
Tickets for trains and electric trains at Moscow station can be purchased online or at the box office.
There are 8 large intercity and international railway stations in Moscow. They depart 817 flights, 194 of which are daily. On this page you will find the current train schedule. Tickets can be purchased online and at the box office.
For a detailed schedule of arrival and departure of trains, see the website
- Belorussky railway station mainly serves the southwestern and western direction of traffic. The international train leaves for Brest, Berlin, Warsaw, Vienna, Vilnius, Cologne, Minsk, Nice, Paris and Prague. Domestic trains go to the stations of Smolensk and Kaliningrad. Electric trains run to Borodino, Odintsovo, Zvenigorod and others. Aeroexpress connects the capital with Sheremetyevo Airport.
- Kyiv railway station carries out international communication with Ukraine, Moldova, Bulgaria, Hungary, Slovakia, etc. Also from the capital you can get to Bryansk and Kaluga. Aeroexpress departs to Vnukovo airport.
- Paveletsky railway station. From here, trains run to stations in the south of the country: Adler, Tambov, Voronezh, Saratov, Astrakhan and Vladikavkaz. international communication affects Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Georgia and Azerbaijan. According to the schedule, Aeroexpress trains depart from Moscow to Domodedovo Airport every half an hour.
- Kursky railway station - the passenger terminal of the Moscow-Passenger-Kurskaya station, train traffic is around the clock. Departure to Donetsk, Dnepr, Simferopol and Kharkiv stations. Passenger trains go to big cities Russia: Tulu, St. Petersburg, Nizhny Novgorod and Samara.
- Kazansky railway station serves the southern, southeastern and eastern directions. It is thanks to him that Moscow is connected with the most distant cities of the country - Novosibirsk, Khabarovsk, Vladivostok. In addition, trains run regularly to major cities in Central Russia, the Caucasus and the Urals: Ufa, Penza, Orenburg, Kazan, Barnaul and Nalchik. The international express travels to the countries of Central Asia.
- Leningradsky Station serves the movement of trains in the north-western and northern directions: Pskov, St. Petersburg, Arkhangelsk, Murmansk. International trains go to Estonia and Finland.
- Rizhsky railway station is the north-western direction. It is from here that you can lay a route from Moscow to Pskov, St. Petersburg and Riga. Passenger electric train stops at the station Volokolamsk, Dedovsk, Istra, Krasnogorsk and others.
- From Yaroslavsky railway station international flights go to Beijing and Ulaanbaatar, internal - to Yaroslavl, Vologda, Vorkuta. Suburban service to stations Alexandrov, Ivanteevka, Krasnoarmeysk and many others. Traffic around the clock.
The UFS.Travel service will help you plan your trip or business trip quickly and comfortably. The train schedule is updated online. Therefore, organizing a trip from any Moscow railway station to a convenient station or city is very simple. Just go to the site and choose the right direction.
MTPPC passengers with subscriptions to regular trains can now pay extra to "Lastochki" at the box office
Passengers of the Moscow-Tver PPK (Leningrad direction) with subscription ticket on a regular train, now they can apply for the service "Additional payment until soon" at the box office and ride on the "Swallow". Previously, this service was available only to single ticket holders.
Holders of unlimited passes can issue an additional payment for any route within the validity of the subscription, and holders of passes "for the number of trips" - only from the starting or final station.
The amount of the surcharge is equal to the difference in the cost of a single ticket for the fast (high-speed) train "Swallow" and a single ticket for a regular train. The fee for the service (subject to registration at the box office) is not charged.
In connection with the work on the construction of track 3 and the reconstruction of the stopping point, from January 14, approximately until June 30, 2019, all commuter trains of the o.p. Victory Kyiv direction will follow without stopping.
Compensatory buses from/to the Aprelevka station have been assigned, the schedule can be found at the Central Control Center.
July 30: About free travel for pensioners of Moscow and the Moscow region from August 1
From August 1, 2018, pensioners, as well as a number of other residents of Moscow and the Moscow Region, will have the right to free travel on commuter trains.
pensioners Moscow will be able to ride for free in all suburban trains - including fast and high-speed suburban trains: "Satellites", "REKS", suburban "Lastochka" (highlighted on the site in blue, not to be confused with long-distance "Lastochki" highlighted in red - they do not provide benefits) and other express trains.
pensioners Moscow region will be able to travel only in suburban trains of the 6000th numbering. These include ordinary electric trains, the Standard Plus trains of the TsPPK and Comfort trains of the Moscow-Tverskaya PPK.
The benefit will be valid for routes through Moscow, the Moscow Region and adjacent regions, where direct electric trains from Moscow (Moscow Region) run. For example, in the Leningrad direction free tickets can be issued no further than Tver and Konakovo stations.
To be able to issue a non-cash ticket, it is necessary once (before the first use on suburban railway transport) activate social card. According to preliminary information, it will be possible to do this at ticket offices from August 1 at all head stations and some interchange stations in Moscow, as well as at a number of large stations in the Moscow region - Mytishchi, Sergiev Posad, Zheleznodorozhnaya, Domodedovo, Lyubertsy, Podolsk, Nara, Odintsovo, Pavshino, Lobnya. In addition, it will be possible to activate (recode) the card at all stations and stopping points of the Moscow - Tver, Konakovo section (where there is a ticket office), as well as at ticket machines (BPA) of the Moscow-Tverskaya PPK. You don't need to reissue the card.
In the absence of a social card, it is necessary to contact the MFC - they will issue a certificate and a temporary card, upon presentation of which and a passport, it will also be possible to issue a non-cash ticket. Until August 9, it is possible to issue a ticket at the CPPK training ground without a certificate (upon presentation of only a temporary card and passport).
From mid-August, it will be possible to activate the card at other stations.
After the card is activated, it will be possible to issue one-time non-cash tickets in the direction "there" or "there and back" using the social card at the box office or BPA.
Please note that the right to travel free of charge does not give the right to travel without a ticket. Before each trip, you must receive a non-cash ticket at the box office or BPA taking into account the category of the train in which you plan to travel (ticket to regular train does not give right of way in the near future, but a ticket for Express train gives the right to travel on a regular train).
Beneficiaries of Moscow can usually do this on the day of the trip or in advance (up to 10 days), and beneficiaries of the Moscow Region - only on the day of the trip.
If the ticket office is closed (at the time of departure of the train) or there is no BPA, then you need to get a ticket at the ticket printing terminal confirming the fact of landing at this stopping point (only at the Central Control Panel site). And only if there is no such terminal at the station, you can get on without a ticket and get free travel directly on the train or at the destination station.
In other cases, if there is no ticket when checking on the train or at the destination station, the passenger may be charged a service fee of 100 to 200 rubles.
Train timetable - a fundamental long-term technological document that regulates the organization of operational work at all levels and levels of management in railway transport.
The train schedule is a conditional dependence of the distance traveled by the train on the time spent on the route, depicted in the “distance-time” coordinate axes in the form of the so-called “track line” of the train on the graph or the “thread” of the graph (Fig. 8.1).
The conventionality of the image of the line of the train on the graph is that along the distance axis, located vertically on the graph, the speed of the train within one stage is assumed to be uniform. At the same time, when starting off, passing curves, descents and ascents on the stage, braking to stop at the station and fulfilling speed limits, the actual speed of the train changes significantly.
To build a graph, you should put the lines of the course of all trains on the graph, a special template is used, called " grid graphics ". The grid of the graph and the lines of the trains on it are supplied with brief comments, which are called "requisites".
The graph captures three main events occurring with trains. These include
arrival,
departure,
passage by trains of separate points.
The existing classification of trains divides them into freight and passenger, as well as into several categories. Within each category, there are additional train designations that indicate the specifics of their use. The division of trains into freight and passenger trains in the schedule is reflected in the fact that different standards are used for their laying. The main and defining moment in this case is the distillation time of the course, which laid the “thread” of the graph. Passenger trains are laid with passenger travel times, and freight trains with freight ones.
The train number is set according to its category. Depending on the direction of travel, trains are assigned even (as a rule, they follow from south to north and from west to east) or odd (follow in reverse directions) numbers. In this regard, the graph distinguishes between even and odd directions of train movement. The lines of the even trains are laid from the lower left corner to the upper right, and the odd ones - from the upper left to the lower right. The train number is stored along the entire route from the formation station to the disbanding (destination) station and changes from even to odd or vice versa when changing the direction of movement at those points where this is provided for by the train schedule.
Rice. 8.1. Example of a train schedule
8.2. Types of train schedules
The railway network of Russia is characterized by different sizes of traffic, the number of main tracks, the ratio of the speeds of freight and passenger trains, the difference in the size of traffic in directions, etc. As a result, they are different motion graphics, which classified according to several characteristics:
Depending on the number of main tracks on the sections of the railway section:
single track or two-way - the main track on the hauls is used for the movement of trains in both directions alternately; crossing and overtaking of trains is carried out at separate points (Fig. 8.2);
double track or one-way - each main track on the hauls is specialized for the movement of trains in only one direction (Fig. 8.3).

Rice. 8.2. Single Track Parallel Graph

Rice. 8.3. Double track parallel chart
Depending on the ratio of the speeds of trains of various categories:
parallel - all trains of the same direction have the same running speed (Fig. 8.2 and 8.3);
non-parallel - trains of the same direction have different running speeds depending on their category (Fig. 8.4).

Rice. 8.4. Single Track Non-Parallel Graph
Depending on the ratio of the number of trains in each direction to:
paired – with the same number of trains in both directions;
unpaired - with a different number of trains in each of the directions.
Depending on the order of trains in one direction:
batch - used for auto blocking. In this case, trains are delimited by block sections, and several trains can be on the haul at the same time (Fig. 8.5a).
partially packaged - are used for auto-blocking; in this case, some trains follow in a package, others - separately (Fig. 8.5b).
bundled – used for semi-automatic blocking. In this case, trains are delimited by inter-station hauls, and only one train can be on one haul (Fig. 8.5c).
|
|
|
|||
|
|
||||
Rice. 8.5. Train timetable:
a - batch; b - partially packaged; in - batch
The UFS service will help you find out the timetable for the MOSCOW - SAINT PETERSBURG train and buy round-trip tickets for the MOSCOW - SAINT PETERSBURG train. We provide full information about the cost, types of carriages and the availability of seats on the train on the route MOSCOW - SAINT PETERSBURG.
Prices of railway tickets for the train MOSCOW - SAINT PETERSBURG
Price railway tickets depends on three main factors - the time of purchase, the type of train and the type of car in which you want to buy a ticket.
- Firstly, the earlier you decide to buy tickets, the cheaper they will cost.
- Secondly, tickets for branded high speed trains(Strizh, Sapsan, Lastochka) and RZD branded trains are more expensive
- Thirdly, with regard to the type of wagon, the most expensive places- in SV cars and compartments, and the most cheap tickets- in a common carriage
Thus, tickets for Strizh, Sapsan or Lastochka, as well as for RZD branded trains, will cost the most, especially if you want to buy a ticket for a first-class carriage. The cheapest way to travel is in general or reserved seat car on a regular train.
How to buy a train ticket
You don't have to leave your home to buy tickets. All you have to do is visit our website and follow a few simple steps.
Step 1. Choose your travel date.
Step 2. Choose the right train.
Step 3. Select the desired type of car (SV, coupe, reserved seat, general). Look at the scheme of the car, what places are available at the moment. Choose the best for you.
Step 4. Pay for the purchase in a way convenient for you.
Step 5. Get e-ticket.
Step 6. If you have an electronic ticket, it will be enough to present your passport (identity document) to your conductor when boarding the train.
Please note: to buy return tickets, you need to act exactly the same, just change the date and choose the return train
Advantages of UFS.Travel
Are you going on a trip? Our UFS.Travel service will help you quickly pack up and hit the road without wasting a single minute of your precious time
Through UFS.Travel you can:
- find out the timetable of the train MOSCOW - SAINT PETERSBURG;
- check availability;
- choose and buy tickets for the desired seats;
- book return tickets in advance.