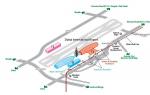
The problem of the Kuril Islands in Russian-Japanese relations. The Kuril Islands in the history of Russian-Japanese relations. Japan and sanctions
Image copyright RIA Image caption Before Putin and Abe, the issue of signing a peace treaty between Russia and Japan was discussed by all their predecessors - to no avail
During a two-day visit to Nagato and Tokyo, the Russian president will agree with Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe on investments. The main question is about ownership. Kuril Islands- as usual, will be postponed indefinitely, experts say.
Abe became the second G7 leader to host Putin after the Russian annexation of Crimea in 2014.
The visit was supposed to take place two years ago, but was canceled due to sanctions against Russia, supported by Japan.
What is the essence of the dispute between Japan and Russia?
Abe is making progress in a multi-year territorial dispute, in which Japan claims the islands of Iturup, Kunashir, Shikotan, as well as the Habomai archipelago (in Russia, this name does not exist, the archipelago, together with Shikotan, are united under the name Malaya Kuril ridge).
The Japanese elite is well aware that Russia will never return two large islands, so they are ready to take a maximum of two small ones. But how to explain to society that they forever refuse big islands? Alexander Gabuev, expert at the Carnegie Moscow Center
At the end of World War II, in which Japan fought on the side of Nazi Germany, the USSR expelled 17,000 Japanese from the islands; no peace treaty was signed between Moscow and Tokyo.
The San Francisco Peace Treaty of 1951 between the countries of the anti-Hitler coalition and Japan established the sovereignty of the USSR over South Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands, but Tokyo and Moscow did not agree on what to understand by the Kuriles.
Tokyo considers Iturup, Kunashir and Habomai to be its illegally occupied "northern territories". Moscow considers these islands part of the Kuril Islands and has repeatedly stated that their current status is not subject to revision.
In 2016, Shinzo Abe flew to Russia twice (to Sochi and Vladivostok), he and Putin also met at the Asia-Pacific economic cooperation in Lima.
In early December, Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov said that Moscow and Tokyo had similar positions on the peace treaty. In an interview with Japanese journalists, Vladimir Putin called the absence of a peace treaty with Japan an anachronism that "should be eliminated."
Image copyright Getty Images Image caption Japanese settlers still live in Japan northern territories", as well as their descendants, who do not mind returning to their historical homelandHe also said that the foreign ministries of the two countries need to decide between themselves "purely technical questions so that the Japanese could visit the southern Kuriles without visas.
However, Moscow is embarrassed that in the event of the return of the southern Kuriles, US military bases may appear there. The head of the Council did not rule out such a possibility. national security Japan Shotaro Yachi in a conversation with the Secretary of the Russian Security Council Nikolai Patrushev, the Japanese newspaper Asahi wrote on Wednesday.
Should we wait for the return of the Kuriles?
The short answer is no. "We should not expect any breakthrough agreements, and ordinary ones too, on the issue of ownership of the southern Kuriles," said former Russian Deputy Foreign Minister Georgy Kunadze.
"The expectations of the Japanese side, as usual, are at odds with the intentions of Russia," Kunadze told the BBC. last days Before leaving for Japan, he repeatedly said that for Russia the problem of belonging to the Kuriles does not exist, that the Kuriles are, in essence, a war trophy following the results of the Second World War, and even that Russia's rights to the Kuriles are secured by international treaties.
The latter, according to Kunadze, is a moot point and depends on the interpretation of these treaties.
“Putin is referring to the agreements reached at Yalta in February 1945. These agreements were of a political nature and assumed the appropriate contractual and legal formalization. It took place in San Francisco in 1951. Soviet Union did not sign a peace treaty with Japan at that time. Therefore, there is no other consolidation of Russia's rights in the territories that Japan renounced under the San Francisco Treaty," the diplomat sums up.
Image copyright Getty Images Image caption The Russians, like the Japanese, do not expect concessions from their authorities on the Kuriles"The parties are trying as much as possible to blow off the ball of mutual expectations of the public and show that there will be no breakthrough," comments Alexander Gabuev, an expert at the Carnegie Moscow Center.
"The red line of Russia: Japan recognizes the results of the Second World War, renounces claims to the southern Kuriles. As a gesture of goodwill, we give Japan two small islands, and on Kunashir and Iturup we can do visa-free entry, free zone joint economic development Anything, he thinks. - Russia can't give up two large islands as it would be a loss, these islands have economic importance, a lot of money has been invested there, there large population, the straits between these islands are used by Russian submarines when they go out to patrol the Pacific."
Japan, according to Gabuev, in last years softened its position on the disputed territories.
“The Japanese elite is well aware that Russia will never return two large islands, so they are ready to take a maximum of two small ones. But how to explain to society that they are forever abandoning large islands? large. For Russia, this is unacceptable, we want to resolve the issue once and for all. These two red lines are not yet close enough to expect a breakthrough," the expert believes.
What else will be discussed?
The Kuriles are not the only topic discussed by Putin and Abe. Russia needs foreign investment in the Far East.
According to the Japanese edition of Yomiuri, due to sanctions, trade between the two countries has decreased. Thus, imports from Russia to Japan decreased by 27.3% - from 2.61 trillion yen ($23 billion) in 2014 to 1.9 trillion yen ($17 billion) in 2015. And exports to Russia by 36.4% - from 972 billion yen (8.8 billion dollars) in 2014 to 618 billion yen (5.6 billion dollars) in 2015.
Image copyright RIA Image caption As head of the Russian state, Putin last visited Japan 11 years ago.The Japanese government intends to acquire a part of the gas fields of the Russian company Novatek, as well as a part of the shares of Rosneft through the state oil, gas and metals corporation JOGMEC.
It is expected that during the visit dozens of commercial agreements will be signed, and the working breakfast of the Russian president and the Japanese prime minister will be attended, in particular, by the head of Rosatom Alexei Likhachev, the head of Gazprom Alexei Miller, the head of Rosneft Igor Sechin, the head of Russian fund direct investments Kirill Dmitriev, entrepreneurs Oleg Deripaska and Leonid Mikhelson.
So far, Russia and Japan are only exchanging pleasantries. Whether at least part of the economic memorandums will come true, it will become clear whether they can also agree on something.
The conflict over the Kuril Islands began long before World War II.
The dispute over the southernmost Kuril Islands - Iturup, Kunashir, Shikotan and Khabomai - has been a point of tension between Japan and Russia since they were taken over by the Soviet Union in 1945. More than 70 years later, Russian-Japanese relations are still not normal due to the ongoing territorial dispute. To a large extent, it was historical factors that prevented the solution of this issue. These include demographics, mentality, institutions, geography, and economics, all of which encourage tough policies rather than willingness to compromise. The first four factors contribute to the persistence of the stalemate, while the economy in the form of oil policy is associated with some hope of a resolution.
Russia's claims to the Kuriles date back to the 17th century, which occurred as a result of periodic contacts with Japan through Hokkaido. In 1821, a de facto border was established, according to which Iturup became Japanese territory, A Russian land started from the island of Urup. Subsequently, according to the Shimodsky Treaty (1855) and the St. Petersburg Treaty (1875), all four islands were recognized as the territory of Japan. The last time the Kuriles changed their owner as a result of the Second World War - in 1945 in Yalta, the allies, in fact, agreed to transfer these islands to Russia.
The dispute over the islands has become a part of politics cold war during negotiations to conclude the San Francisco Peace Treaty, Article 2c of which forced Japan to renounce all its claims to the Kuril Islands. However, the refusal of the Soviet Union to sign this agreement left these islands in a state of limbo. In 1956, a joint Soviet-Japanese declaration was signed, which de facto meant the end of the state of war, but failed to resolve territorial conflict. After the ratification of the US-Japan Security Treaty in 1960, further negotiations were stopped, and this continued until the 1990s.
However, after the end of the Cold War in 1991, there appeared to be new opportunity to resolve this issue. Despite the tumultuous events in world affairs, the positions of Japan and Russia on the Kuriles have not changed much since 1956, and the reason for this situation was five historical factors that were outside the Cold War.
The first factor is demographic. Japan's population is already declining due to low birth rates and aging, while Russia's population has been declining since 1992 due to excessive drinking and other social ills. This shift, together with the weakening of international influence, has led to the emergence of retrospective tendencies, and both nations are now basically trying to resolve this issue by looking backwards rather than forwards. In the presence of such attitudes, it can be concluded that the aging populations of Japan and Russia are depriving Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and President Vladimir Putin of the opportunity to negotiate because of firmly entrenched views on the issue of the Kuriles.
Context
Is Russia ready to return two islands?
Sankei Shimbun 10/12/2016Military construction in the Kuriles
The Guardian 06/11/2015Is it possible to agree on the Kuril Islands?
BBC Russian service 05/21/2015All this also plays into the hands of the mentality and perception of the outside world, which are formed on the basis of how history is taught, and more broadly on the basis of how it is presented by the media and public opinion. For Russia, the collapse of the Soviet Union was a major psychological blow, accompanied by a loss of status and power as many former Soviet republics seceded. This has significantly altered Russia's borders and created significant uncertainty about the future of the Russian nation. It is well known that in times of crisis, citizens often display stronger patriotic feelings and feelings of defensive nationalism. The Kurile dispute fills a void in Russia and also provides an opportunity to speak out against the perceived emotionally historical injustice committed by Japan.
The perception of Japan in Russia was largely shaped by the issue of the Kuril Islands, and this continued until the end of the Cold War. Anti-Japanese propaganda became common after the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-1905, and it was reinforced by the Japanese intervention during civil war in Russia (1918-1922). This led many Russians to believe that as a result, all previously concluded treaties were annulled. However, Russia's victory over Japan in World War II ended the previous humiliation and reinforced the symbolic meaning of the Kuril Islands, which came to represent (1) the irreversibility of the results of World War II and (2) Russia's status as a great power. From this point of view, the transfer of territory is seen as a revision of the outcome of the war. Therefore, control over the Kuriles retains an important psychological significance for the Russians.
Japan is trying to define its place in the world as a "normal" state, located next to an increasingly powerful China. The question of the return of the Kuril Islands is directly linked to the national identity of Japan, and these territories themselves are perceived as the last symbol of defeat in World War II. The Russian offensive and the capture of Japan's "inalienable territory" helped reinforce the victim mentality that became the prevailing narrative after the end of the war.
This attitude is reinforced by the Japanese conservative media, which often supports the government's foreign policy. In addition, nationalists often use the media to viciously attack academics and politicians who hint at the possibility of reaching a compromise on this issue, leaving little room for manoeuvre.
This, in turn, has an impact on the political institutions of both Japan and Russia. In the 1990s, President Boris Yeltsin's position was so weak that he feared possible impeachment if the Kuril Islands were handed over to Japan. Simultaneously central Russian government was weakened as a result of the growing influence of regional politicians, including two governors Sakhalin region- Valentina Fedorova (1990 - 1993) and Igor Fakhrutdinov (1995 - 2003), who actively opposed the possible sale of the Kuriles to Japan. They relied on nationalist sentiments, and this was enough to prevent the completion of the treaty and its implementation in the 1990s.
Since President Putin came to power, Moscow has brought regional governments under its influence, but other institutional factors have also contributed to the stalemate. One example is the idea that the situation should mature, and then some issue or problem can be solved. During the initial period of his rule, President Putin was able, but not willing, to negotiate with Japan over the Kuriles. Instead, he decided to spend time and energy on resolving the Sino-Russian border conflict due to the question of the Kuril Islands.
Since returning to the presidency in 2013, Putin has become increasingly dependent on the support of nationalist forces, and it is unlikely that he will be ready to cede the Kuriles in any meaningful way. Recent events in Crimea and Ukraine clearly demonstrate how far Putin is willing to go to defend Russia's national status.
Japanese political institutions, while different from Russia's, also support a hard line of negotiation over the Kuriles. As a result of the reforms carried out after the end of World War II, the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) dominates Japan. With the exception of the period from 1993 to 1995 and from 2009 to 2012, the LDP had and continues to have a majority in the national legislative assembly, and in fact its party platform regarding the return of the four southern islands of the Kuril ridge since 1956 is integral part national policy.
In addition, the real estate crash of 1990-1991 saw the Liberal Democratic Party nominate only two effective prime ministers, Junichiro Koizumi and Shinzo Abe, both of whom rely on nationalist support to maintain their positions. Finally, regional politics in Japan plays an important role, and elected politicians in Hokkaido are pushing the central government to take a assertive stance in this dispute. Taken together, all these factors do not contribute to a compromise that would include the return of all four islands.
Sakhalin and Hokkaido emphasize the importance of geography and regional interests in this dispute. Geography influences how people see the world and how they observe policy making and implementation. The most important Russian interests are in Europe, followed by the Middle East and central Asia, and only after that Japan. Here is one example - Russia devotes a significant part of its time and efforts to the issue of NATO expansion to the east, to the eastern part of Europe, as well as negative consequences related to the events in the Crimea and Ukraine. As far as Japan is concerned, the alliance with the United States, China, and the Korean Peninsula take precedence over relations with Moscow. The Japanese government must also consider public pressure to resolve issues with North Korea over kidnapping and nuclear weapons, which Abe has promised to do on several occasions. As a result, the issue of the Kuriles is often relegated to the background.
Probably the only factor contributing to a possible resolution of the Kuril issue is economic interests. After 1991, both Japan and Russia entered a period of long economic crisis. The Russian economy hit its lowest point during its crisis national currency in 1997, and is currently facing serious difficulties due to the collapse in oil prices and economic sanctions. However, the development of oil and gas fields in Siberia, in the process of which Japanese capital and Russian natural resources are combined, contributes to cooperation and a possible resolution of the Kuriles issue. Despite the sanctions imposed, 8% of Japan's oil consumption in 2014 was imported from Russia, and the increase in oil and natural gas consumption is largely due to the consequences of the disaster at the nuclear power plant in Fukushima.
In their totality, historical factors largely determine the continued stagnation in resolving the issue of the Kuril Islands. The demographics, geography, political institutions, and attitudes of the citizens of Japan and Russia all contribute to a tough negotiating position. Oil policy provides some incentive for both nations to resolve disputes and normalize relations. However, so far this has not been enough to break the impasse. Despite the possible change of leaders around the world, the main factors that have driven this dispute to a standstill are likely to remain unchanged.
Michael Bacalu is a member of the Council on Asian Affairs. He received his master's degree in international relations from Seoul University, South Korea, as well as a bachelor's degree in history and political science Arcadia University. The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author as an individual and do not necessarily reflect the views of any organization with which he has ties.
The materials of InoSMI contain only assessments of foreign media and do not reflect the position of the editors of InoSMI.
In 2012 visa-free exchange between the South Kuriles and Japanwill start April 24th.
On February 2, 1946, by decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR, the Kuril Islands Iturup, Kunashir, Shikotan and Khabomai were included in the USSR.
On September 8, 1951, at an international conference in San Francisco, a peace treaty was concluded between Japan and 48 countries participating in the anti-fascist coalition, according to which Japan renounced all rights, titles and claims to the Kuril Islands and Sakhalin. The Soviet delegation did not sign this treaty, referring to the fact that it regards it as a separate agreement between the US and Japanese governments. From the point of view of treaty law, the question of the ownership of the South Kuriles remained uncertain. The Kuriles ceased to be Japanese, but did not become Soviet. Using this circumstance, Japan in 1955 presented the USSR with claims to all the Kuril Islands and the southern part of Sakhalin. As a result of two years of negotiations between the USSR and Japan, the positions of the parties drew closer: Japan limited its claims to the islands of Habomai, Shikotan, Kunashir and Iturup.
On October 19, 1956, the Joint Declaration of the USSR and Japan on the termination of the state of war between the two states and the restoration of diplomatic and consular relations was signed in Moscow. In it, in particular, the Soviet government agreed to the transfer of Japan after the conclusion of a peace treaty of the islands of Habomai and Shikotan.
After the conclusion of the Japanese-American security treaty in 1960, the USSR canceled the obligations assumed by the 1956 declaration. During the Cold War, Moscow did not recognize the existence of a territorial problem between the two countries. The presence of this problem was first recorded in the Joint Statement of 1991, signed following the visit of the President of the USSR to Tokyo.
In 1993, in Tokyo, the President of Russia and the Prime Minister of Japan signed the Tokyo Declaration on Russian- Japanese relations, where the consent of the parties to continue negotiations was recorded with the aim of concluding a peace treaty as soon as possible by resolving the issue of ownership of the islands mentioned above.
In recent years, in order to create at the talks an atmosphere conducive to the search for mutually acceptable solutions, the parties have been paying great attention to establishing practical Russian-Japanese interaction and cooperation in the area of the islands.
In 1992, on the basis of an intergovernmental agreement between the inhabitants of the Russian South Kuriles and Japan. Trips are carried out on a national passport with a special insert, without visas.
In September 1999, the implementation of an agreement on the most facilitated procedure for visiting the islands by their former residents from among Japanese citizens and members of their families began.
Cooperation is being carried out in the fishery sector on the basis of the current Russian-Japanese Agreement on fishing near the southern Kuriles dated February 21, 1998.
The material was prepared on the basis of information from RIA Novosti and open sources
Briefly, the history of the "belonging" of the Kuril Islands and Sakhalin Island is as follows.
1.In period 1639-1649. Russian Cossack detachments led by Moskovitinov, Kolobov, Popov explored and began to explore Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands. At the same time, Russian pioneers repeatedly swim to the island of Hokkaido, where they are peacefully met by local natives of the Ainu people. The Japanese appeared on this island a century later, after which they exterminated and partially assimilated the Ainu.
2.B 1701 Cossack constable Vladimir Atlasov reported to Peter I about the "subordination" of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands to the Russian crown, leading to the "wonderful Nipon kingdom."
3.B 1786. by order of Catherine II, a register of Russian possessions in the Pacific Ocean was produced, bringing the register to the attention of all European states as a declaration of Russia's rights to these possessions, including Sakhalin and the Kuriles.
4.B 1792. By decree of Catherine II, the entire ridge of the Kuril Islands (both Northern and Southern), as well as Sakhalin Island officially included in Russian Empire.
5. As a result of the defeat of Russia in the Crimean War 1854—1855 gg. under pressure England and France Russia forced was concluded with Japan on February 7, 1855. Treaty of Shimoda, through which four southern islands of the Kuril chain were transferred to Japan: Habomai, Shikotan, Kunashir and Iturup. Sakhalin remained undivided between Russia and Japan. At the same time, however, the right of entry of Russian ships into Japanese ports, and also proclaimed "permanent peace and sincere friendship between Japan and Russia."
6.May 7, 1875 under the Petersburg Treaty, the tsarist government as a very strange act of "good will" makes incomprehensible further territorial concessions to Japan and transfers to it 18 more small islands of the archipelago. In return, Japan finally recognized Russia's right to the whole of Sakhalin. It is for this agreement referred most of all by the Japanese today, slyly silent that the first article of this treaty reads: "... and henceforth eternal peace and friendship will be established between Russia and Japan" ( the Japanese themselves violated this treaty in the 20th century repeatedly). Many Russian statesmen of those years sharply condemned this “exchange” treaty as short-sighted and harmful to the future of Russia, comparing it with the same short-sightedness as the sale of Alaska to the United States of America in 1867 for next to nothing (7 billion 200 million dollars). ), saying that "now we are biting our own elbows."
7. After the Russo-Japanese War 1904—1905 gg. followed another stage of humiliation of Russia. By Portsmouth peace treaty concluded on September 5, 1905, Japan received the southern part of Sakhalin, all the Kuril Islands, and also took away from Russia the right to lease the naval bases of Port Arthur and Dalniy. When Russian diplomats reminded the Japanese that all these provisions are contrary to the 1875 treaty g., those arrogantly and arrogantly answered : « War cancels all treaties. You have failed and let's proceed from the current situation ". Reader, remember this boastful declaration of the invader!
8. Next comes the time of punishment of the aggressor for his eternal greed and territorial expansion. Signed by Stalin and Roosevelt at the Yalta Conference February 10, 1945 G. " Agreement on the Far East"It was envisaged:" ... 2-3 months after the surrender of Germany, the Soviet Union will enter the war against Japan subject to the return to the Soviet Union of the southern part of Sakhalin, all the Kuril Islands, as well as the restoration of the lease of Port Arthur and Dalny(these built and equipped hands of Russian workers, soldiers and sailors back in the late XIX - early XX centuries. very comfortable on their own geographic location naval bases were donated to "fraternal" China. But these bases were so necessary for our fleet in the 60-80s of the rampant "cold war" and intense combat service of the fleet in remote areas of the Pacific and Indian Oceans. I had to equip the forward base Cam Ranh in Vietnam for the fleet from scratch).
9.B July 1945 g. in accordance with Potsdam Declaration heads of the victorious countries the following verdict was passed regarding the future of Japan: "The sovereignty of Japan shall be limited to four islands: Hokkaido, Kyushu, Shikoku, Honshu, and such as WE SPECIFY". August 14, 1945 the Japanese government has publicly confirmed the acceptance of the terms of the Potsdam Declaration, and on September 2 Japan unconditionally surrendered. Article 6 of the Instrument of Surrender reads: "... the Japanese government and its successors will faithfully fulfill the terms of the Potsdam Declaration to give such orders and take such actions as the Commander-in-Chief of the Allied Powers shall require in order to carry out this declaration...”. January 29, 1946 Commander-in-Chief General MacArthur DEMANDED by Directive No. 677: "The Kuril Islands, including Habomai and Shikotan, are excluded from the jurisdiction of Japan." AND only after that legal effect, a Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR of February 2, 1946 was issued, which read: “ All lands, bowels and waters of Sakhalin and the Kul Islands are the property of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ". Thus, the Kuril Islands (both Northern and Southern), as well as about. Sakhalin, legally And in accordance with the regulations international law were returned to Russia . This could put an end to the "problem" of the Southern Kuriles and stop all further verbiage. But the story of the Kuriles continues.
10. After the end of World War II US occupied Japan and turned it into their military base on Far East. In September 1951 USA, UK and a number of other states (total 49) signed San Francisco Peace Treaty with Japan, prepared in violation of the Potsdam agreements without the participation of the Soviet Union . Therefore, our government did not join the treaty. However, Art. 2, chapter II of this treaty, it is fixed in black and white: “ Japan renounces all legal grounds and claims ... to the Kuril Islands and that part of Sakhalin and the islands adjacent to it over which Japan acquired sovereignty under the Treaty of Portsmouth of September 5, 1905. However, even after this, the story with the Kuriles does not end.
October 11.19 1956 d. the government of the Soviet Union, following the principles of friendship with neighboring states, signed with the Japanese government joint declaration, according to which the state of war between the USSR and Japan ended and peace, good neighborliness and friendly relations were restored between them. When signing the Declaration as a gesture of good will and no more promised to give Japan the two southernmost islands of Shikotan and Habomai, but only after the conclusion of a peace treaty between the countries.
12. However The United States after 1956 imposed a number of military agreements on Japan, replaced in 1960 by a single "Treaty of Mutual Cooperation and Security", according to which US troops remained on its territory, and thereby Japanese islands turned into a springboard for aggression against the Soviet Union. In connection with this situation, the Soviet government announced to Japan that it was impossible to transfer the promised two islands to it.. And in the same statement it was emphasized that according to the declaration of October 19, 1956, "peace, good neighborliness and friendly relations" between the countries were established. Therefore, an additional peace treaty may not be required.
Thus, the problem of the Southern Kuriles does not exist
. It's been decided a long time ago. AND de jure and de facto the islands belong to Russia
. In this regard, it might be to remind the Japanese of their arrogant statement in 1905 g., and also indicate that Japan was defeated in World War II and therefore has no rights to any territory, even to her ancestral lands, except for those granted to her by the victors.
AND our foreign ministry just as harshly, or in a milder diplomatic form it would be necessary to declare this to the Japanese and put an end to this, FOREVER stopping all negotiations
and even conversations on this non-existent and humiliating problem of the dignity and authority of Russia.
And again the "territorial question"
However, starting from 1991
, repeatedly held meetings of the President Yeltsin and members of the Russian government, diplomats with government circles in Japan, during which the Japanese side every time importunately raises the question of the "Northern Japanese Territories".
Thus, in the Tokyo Declaration 1993
signed by the President of Russia and the Prime Minister of Japan, was again acknowledged the "existence of the territorial issue", and both sides promised to "make efforts" to resolve it. The question arises - could our diplomats really know that such declarations should not be signed, because the recognition of the existence of a “territorial issue” is contrary to the national interests of Russia (Article 275 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “ Treason»)??
As for the peace treaty with Japan, it is de facto and de jure in accordance with the Soviet-Japanese Declaration of October 19, 1956. not really needed. The Japanese do not want to conclude an additional official peace treaty, and there is no need. He Japan needs more, as the side that was defeated in the Second World War, rather than Russia.
A citizens of Russia should know the “problem” of the South Kuriles, sucked from the finger , her exaggeration, periodic hype in the media around her and the litigation of the Japanese - there a consequence of Japan's illegitimate claims in violation of the obligations it has assumed, to strictly comply with the international obligations recognized and signed by it. And such a constant desire of Japan to reconsider the ownership of many territories in the Asia-Pacific region pervades Japanese politics throughout the 20th century.
Why the Japanese, one might say, have seized the South Kuriles with their teeth and are trying to seize them again illegally? But because the economic and military-strategic importance of this region is extremely great for Japan, and even more so for Russia. This an area of colossal seafood riches(fish, living creatures, marine animals, vegetation, etc.), deposits of minerals, and rare earth minerals, energy sources, mineral raw materials.
For example, January 29 of this year. short information slipped through the Vesti (RTR) program: a a large deposit of the rare earth metal Rhenium(75th element in the periodic table, and the only one in the world
).
Scientists allegedly calculated that it would be enough to invest only 35 thousand dollars, but the profit from the extraction of this metal will allow to bring the whole of Russia out of the crisis in 3-4 years
. Apparently, the Japanese know about this and that is why they are so persistently attacking the Russian government with a demand to give them the islands.
It must be said that for 50 years of ownership of the islands, the Japanese have not built or created anything capital on them, except for light temporary buildings. Our border guards had to rebuild barracks and other buildings at the outposts. The entire economic "development" of the islands, which the Japanese are shouting to the whole world today, consisted in the predatory robbery of the riches of the islands . During the Japanese "development" from the islands rookeries of fur seals, habitats of sea otters disappeared . Part of the population of these animals our Kuril residents have already restored .
Today, the economic situation of this entire island zone, like the whole of Russia, is difficult. Of course, significant measures are needed to support this region and take care of the Kuril people. According to the calculations of a group of deputies of the State Duma, it is possible to extract on the islands, as reported in the program "Parliamentary Hour" (RTR) on January 31 of this year, only fish products up to 2000 tons per year, with a net profit of about 3 billion dollars.
In military terms, the ridge of the Northern and Southern Kuriles with Sakhalin constitutes a complete closed infrastructure of the strategic defense of the Far East and the Pacific Fleet. They enclose the Sea of Okhotsk and turn it into an inland one. This is the area deployment and combat positions of our strategic submarines.
Without the South Kuriles, we will get a "hole" in this defense. Control over the Kuriles ensures free access of the fleet to the ocean, because until 1945 our Pacific Fleet, starting from 1905, was practically locked up in its bases in Primorye. The means of detection on the islands provide long-range detection of air and surface enemy, the organization of anti-submarine defense of the approaches to the passages between the islands.
In conclusion, one should note such a feature in the relationship of the Russia-Japan-US triangle. It is the United States that confirms the "legitimacy" of the ownership of the islands of Japan
in spite of all international treaties they have signed
.
If so, then our Ministry of Foreign Affairs has every right, in response to the claims of the Japanese, to propose that they demand the return of Japan to its "southern territories" - the Caroline, Marshall and Mariana Islands.
These archipelagos former colonies Germany, captured by Japan in 1914. Japan's dominion over these islands was sanctioned by the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. After the defeat of Japan, all these archipelagos came under US control.. So Why shouldn't Japan demand that the United States return the islands to her? Or lack of spirit?
As you can see, there is explicit double standard in Japanese foreign policy.
And one more fact that clarifies the general picture of the return of our Far Eastern territories in September 1945 and the military significance of this region. The Kuril operation of the 2nd Far Eastern Front and the Pacific Fleet (August 18 - September 1, 1945) provided for the liberation of all the Kuril Islands and the capture of the island of Hokkaido.
The accession of this island to Russia would be of great operational and strategic importance, since it would ensure the complete isolation of the "fencing" of the Sea of Okhotsk by our island territories: Kuriles - Hokkaido - Sakhalin. But Stalin canceled this part of the operation, saying that with the liberation of the Kuriles and Sakhalin, we had resolved all our territorial issues in the Far East. A we don't need foreign land . In addition, the capture of Hokkaido will cost us a lot of blood, unnecessary losses of sailors and paratroopers in the very last days of the war.
Stalin here showed himself to be a real statesman, taking care of the country, its soldiers, and not an invader, who coveted foreign territories that were very accessible in that situation for the capture.
Since 1945, the authorities of Russia and Japan have not been able to sign a peace treaty because of a dispute over the ownership of the southern part of the Kuril Islands.
The Northern Territories Issue (北方領土問題 Hoppo: ryō:do mondai) is a territorial dispute between Japan and Russia that Japan considers unresolved since the end of World War II. After the war, all the Kuril Islands came under the administrative control of the USSR, but a number of the southern islands - Iturup, Kunashir and the Lesser Kuril Ridge - are disputed by Japan.
In Russia disputed territories are part of the Kuril and Yuzhno-Kuril urban districts of the Sakhalin Region. Japan claims four islands in the southern part of the Kuril ridge - Iturup, Kunashir, Shikotan and Habomai, referring to the bilateral Treatise on Trade and Borders of 1855. Moscow's position is that the southern Kuriles became part of the USSR (of which Russia became the successor) according to the results of the Second World War, and Russian sovereignty over them, which has the appropriate international legal design, is beyond doubt.
The problem of ownership of the southern Kuril Islands is the main obstacle to the complete settlement of Russian-Japanese relations.
Iturup(Jap. 択捉島 Etorofu) is an island of the southern group of the Great Ridge of the Kuril Islands, the largest island of the archipelago.
Kunashir(Ainu Black Island, Japanese 国後島 Kunashiri-to:) is the southernmost island of the Great Kuril Islands.
Shikotan(jap. 色丹島 Sikotan-to:?, in early sources Sikotan; name from the Ainu language: "shi" - large, significant; "kotan" - village, city) - the largest island small ridge Kuril Islands.
habomai(Jap. 歯舞群島 Habomai-gunto ?, Suisho, "Flat Islands") - Japanese name a group of islands in the northwest Pacific Ocean, together with the island of Shikotan in Soviet and Russian cartography, considered as the Lesser Kuril Ridge. The Habomai group includes the islands of Polonsky, Oskolki, Zeleny, Tanfiliev, Yuri, Demin, Anuchin and a number of small ones. Separated by the Soviet Strait from the island of Hokkaido.
History of the Kuril Islands
17th century
Before the arrival of the Russians and the Japanese, the islands were inhabited by the Ainu. In their language, “kuru” meant “a person who came from nowhere,” from which their second name “smokers” came from, and then the name of the archipelago.
In Russia, the first mention of the Kuril Islands dates back to 1646, when N. I. Kolobov spoke about the bearded people inhabiting the islands Ainakh.
The Japanese first received information about the islands during an expedition [source not specified 238 days] to Hokkaido in 1635. It is not known whether she actually got to the Kuriles or learned about them indirectly, but in 1644 a map was drawn up on which they were designated under the collective name "thousand islands". Candidate of Geographical Sciences T. Adashova notes that the map of 1635 "is considered by many scientists to be very approximate and even incorrect." Then, in 1643, the islands were explored by the Dutch, led by Martin Fries. This expedition was over detailed maps and described the land.
18th century
In 1711, Ivan Kozyrevsky went to the Kuriles. He only visited 2 northern islands: Shumshu and Paramushir, - but he asked in detail the Ainu and Japanese who inhabited them, brought there by a storm. In 1719, Peter I sent an expedition to Kamchatka led by Ivan Evreinov and Fyodor Luzhin, which reached Simushir Island in the south.
In 1738-1739, Martyn Spanberg walked along the entire ridge, putting the islands he met on the map. In the future, the Russians, avoiding dangerous voyages to southern islands, mastered the northern ones, taxed yasak local population. From those who did not want to pay it and went to distant islands, they took amanats - hostages from among close relatives. But soon, in 1766, the centurion Ivan Cherny from Kamchatka was sent to the southern islands. He was ordered to attract the Ainu into citizenship without the use of violence and threats. However, he did not follow this decree, mocked them, poached. All this led to a rebellion of the indigenous population in 1771, during which many Russians were killed.
Great success was achieved by the Siberian nobleman Antipov with the Irkutsk translator Shabalin. They managed to win the favor of the Kuril people, and in 1778-1779 they managed to bring into citizenship more than 1500 people from Iturup, Kunashir and even Matsumaya (now Japanese Hokkaido). In the same 1779, Catherine II by decree freed those who accepted Russian citizenship from all taxes. But relations were not built with the Japanese: they forbade the Russians to go to these three islands.
In the "Extensive land description of the Russian state ..." of 1787, a list was given from the 21st island, owned by Russia. It included islands up to Matsumaya (Hokkaido), whose status was not clearly defined, since Japan had a city in its southern part. At the same time, the Russians had no real control even over the islands south of Urup. There, the Japanese considered the Kurilians their subjects, actively used violence against them, which caused discontent. In May 1788, a Japanese merchant ship that had come to Matsumai was attacked. In 1799, by order of the central government of Japan, two outposts were founded on Kunashir and Iturup, and guards began to be constantly guarded.
19th century
In 1805, a representative of the Russian-American Company, Nikolai Rezanov, who arrived in Nagasaki as the first Russian envoy, tried to resume negotiations on trade with Japan. But he also failed. However, the Japanese officials, who were not satisfied with the despotic policy of the supreme power, gave him hints that it would be nice to carry out a forceful action in these lands, which could push the situation off the ground. This was carried out on behalf of Rezanov in 1806-1807 by an expedition of two ships led by Lieutenant Khvostov and midshipman Davydov. Ships were plundered, a number of trading posts were destroyed, and a Japanese village was burned on Iturup. Later they were tried, but the attack for a while led to a serious deterioration Russo-Japanese relations. In particular, this was the reason for the arrest of Vasily Golovnin's expedition.
In exchange for the right to own southern Sakhalin, Russia transferred to Japan in 1875 all the Kuril Islands.
20th century
After the defeat in 1905 in the Russo-Japanese War, Russia transferred the southern part of Sakhalin to Japan.
In February 1945, the Soviet Union promised the United States and Great Britain to start a war with Japan on the condition that Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands be returned to it.
February 2, 1946. Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR on the inclusion South Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands to the RSFSR.
1947. Deportation of Japanese and Ainu from the islands to Japan. Displaced 17,000 Japanese and an unknown number of Ainu.
November 5, 1952. A powerful tsunami hit the entire coast of the Kuriles, Paramushir suffered the most. giant wave washed away the city of Severo-Kurilsk (formerly Kasivabara). The press was forbidden to mention this catastrophe.
In 1956, the Soviet Union and Japan agreed to a Joint Treaty formally ending the war between the two states and ceding Habomai and Shikotan to Japan. Signing the treaty, however, failed: the United States threatened not to give Japan the island of Okinawa if Tokyo renounces its claims to Iturup and Kunashir.
Maps of the Kuril Islands
Kuril Islands on English map 1893. Plans of the Kuril Islands, from sketches chiefly mand by Mr. H. J. Snow, 1893. (London, Royal Geographical Society, 1897, 54×74 cm)
Map fragment Japan and Korea - Location of Japan in the Western Pacific (1:30,000,000), 1945


Photomap of the Kuril Islands based on space image NASA, April 2010.
List of all islands
View of Habomai from Hokkaido
Green Island (志発島 Shibotsu-to)
Polonsky Island (Jap. 多楽島 Taraku-to)
Tanfiliev Island (Jap. 水晶島 Suisho-jima)
Yuri Island (勇留島 Yuri-to)
Anuchina Island
Demina Islands (Japanese: 春苅島 Harukari-to)
Shard Islands
Kira Rock
Rock Cave (Kanakuso) - a rookery of sea lions on a rock.
Sail Rock (Hokoki)
Candle Rock (Rosoku)
Fox Islands (Todo)
Bump Islands (Kabuto)
Can Dangerous
Watchtower Island (Homosiri or Muika)
Drying Rock (Odoke)
Reef Island (Amagi-sho)
Signal Island (Jap. 貝殻島 Kaigara-jima)
Amazing Rock (Hanare)
Seagull Rock