The population of the earth. Groups of countries with different population densities. Educational: to cultivate a benevolent attitude towards each other, tolerance
Geography lesson in grade 10
"Accommodation and Settlement of the World's Population."
Goals and objectives:
To form an idea about the features of the distribution of the population on the planet and to establish the causes of uneven distribution; to acquaint with the main migration phenomena in the world.
To form the concept of urbanization, suburbanization, urbanization, to characterize urbanization as a worldwide process. Define common features urbanization, the relationship between levels and rates of urbanization. Get an idea about the forms of settlement.
Continue developing skills in working with geographical maps, tables, make comparisons.
Equipment:
Textbook "Economic and social geography of the world",
Atlas for 10th grade.
Political map of the world, world population density.
During the classes
IOrganizing time
II Checking homework.
Name the major world religions. And their regions.
How religions influence the peculiarities of national life, lifestyle, as well as the development of industries and agriculture.
Give examples of countries where national religions are widespread.
IIILearning new material.
Knowledge update:
What factors influence the distribution of the world's population?
- How is the population of Russia distributed throughout the country?
At present, all habitable people and their economic activity spaces on Earth are populated. However, the population is distributed extremely unevenly. About 70% of all mankind lives on 7% of the territory. Lives in the Eastern Hemisphere more people than in the Western Hemisphere. More in the northern hemisphere than in the southern.
15% of the land is completely undeveloped by people. These are areas with extreme natural conditions.
1. Features of the settlement of the Earth.
Task -1 Placement of the population
1) Identify the factors that affect the distribution of the population.
2) Define the role natural conditions in the distribution of the population.
3) Describe the distribution of the world's population according to the degree of distance from the sea (ocean).
Conclusion: The distribution of the population is extremely uneven. Main reasons: natural factor, historical conditions, socio-economic conditions.
Task -2 Population density
What is population density?
Which country has the highest population density?
Practical task. Analyze the "World Population Density" map in the atlas, the text of the textbook from 84-85, fill in the table, draw a conclusion.
| Groups of countries with different population densities | Country examples | Causes explaining the population density pattern |
| Countries with low density (less than 2 people/km2) | Niger, Australia, Mongolia, Lebanon, Namibia | Countries that are in an arid climate, except for Australia, have no access to the sea, etc. |
| Countries with very high density (more than 200 people/km2) | India, Germany, Great Britain, Belgium, Israel, Libya, Rep. Korea, Italy, Greece | Favorable living conditions throughout the countries |
| Countries with densities close to the global average | Tunisia, Mexico, Ecuador | Various conditions: natural, social, economic differ greatly in different areas countries. |
Conclusion: The world average population density is 44 people / km. But this indicator does not give an idea of the real population density in various parts of the world, because there are densely populated territories, there are practically undeveloped ones, such as Greenland, Antarctica, the Highlands of the planet, deserts, tundras and Arctic deserts. Almost 15% of the planet's land is uninhabited. And 70% of the population lives on 7% of the area of the continents. 90% of the world's population lives in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres. The density on the continents is: in Asia - 75 people / km, in Europe - 70 people / km, in Africa - 22 people / km, in America - 19 people / km, in Australia and Oceania - 3 people / km.
Population migration.
"People are not migratory birds, and their migration is explained not by biological, but by social laws" N.N. Baransky
Task-3
1) What laws did N.N. Baransky?
2) Using table 16 p. 88 “Types migration processes»remember:
What is "migration"?
Types of migration. What is the difference between external and internal migration. Give examples of external and internal migrations.
What is the difference between the motives of those and other migrations?
How can one explain the outbreak of migration in the 19th-20th centuries?
The biggest "migration explosion" began in the 19th century. Europe remained the main center of emigration, where the development of capitalism was accompanied by the “pushing out” of part of the population to those areas where there were free lands, the economy developed rapidly and created a demand for labor.
The second center of emigration has developed in Asia . Here, Chinese and Indian workers (coolies) became emigrants, who were recruited to work on plantations and mines. The main centers of immigration were the USA, Canada, Brazil, Argentina, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa.
Post World War II dimensions international migrations began to increase again and by the end of the 20th century. have reached the scale of a new "migration explosion" - Work migration .
The main flow of these emigrants was directed from developing to economically developed countries.
main reason- a large gap in living conditions and wages between economically developed and developing countries.
Task-4. Practical task. On contour map color show the three main centers of gravity of labor resources:
First - Western Europe (Germany, France, Great Britain, Switzerland) - working emigrants from the countries of Southern Europe, Eastern Europe.
Second– USA, where legal immigration reached 1 million people (from countries Latin America, Asia and Europe), illegal emigration is much larger.
Third - these are the oil-producing countries of the Persian Gulf (emigrants from Egypt, India, Pakistan).
Urban and rural population
According to the nature of settlement, the world's population can be divided into urban and rural. rural settlement arose with the development of agriculture. Currently, more than half of the world's population lives in rural areas.
There are two forms of rural settlement:
group (village) - most typical for the countries of Central and Southern Europe, Russia, Japan, as well as for most developing countries;
scattered (farm) - most common in the USA, Canada, Australia, the countries of Northern Europe.
Task-5.
With the development of industry began the growth of cities.
1) What is called urbanization?
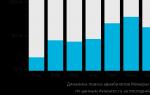
2) Analyze Fig.35 on p.91. How did the proportion of the world's urban population change in the 20th century and draw a conclusion.
Conclusion: The rate of urbanization differs sharply between developed and developing countries. In developing countries, urban population growth is faster than developed countries.
3) What is called agglomeration? Name the largest agglomerations of the world according to Table 17, p.93. In what parts of the world is it concentrated large quantity agglomerations?
Task -6.
According to the text of the textbook p.94, study the processes of "suburbanization", "rurbanization", "false (slum) urbanization". Which countries are characterized by the development of these processes?
IIIConsolidation of the material covered.
Test.
The largest population clusters formed in the lowlands:
1. Central-Eastern Europe;
2. Latin America;
3. East Asia; +
4. North Africa.
Of these lowlands, the most densely populated are:
1. La Platskaya;
2. Indo-Ghanaian; +
3. Orinokskaya;
4. Caspian.
1. Brazil;
2. Netherlands; +
3. Pakistan;
4. Slovakia.
Of these countries, the highest population density is typical for:
1. Belgium and Japan; +
2. Paraguay and Australia;
3. Libya and Finland;
4. Philippines and Botswana.
5. From listed countries lowest density population is characterized by:
1. Indonesia and the Netherlands;
2. UK and Pakistan;
3. Mongolia and Chad; +
4. Italy and South Korea.
6. Agglomerations, which of these cities are the largest in their countries?
2) Rio de Janeiro,
3) Mexico City,+
5) Shanghai.+
7. Which of these countries are highly urbanized?
2) Indonesia,
3) Canada,+
5) Sweden +
IVHomework
1. Study paragraph 15
2. Define the following concepts: Brain drain; white, blue, gold collars.
3. prepare a mini-essay "World cities - the main centers of activity of the world community"
4. Do practical work on p. 95.
LESSON OBJECTIVES
Educational: to provide during the lesson the assimilation of the following concepts: race, sex and age composition of the population, population density, migration
Developing: contribute to the formation of students' intellectual skills: choose the main thing in the material being studied, compare and contrast
Educational: cultivate a friendly attitude towards each other, tolerance

The population of the Earth is 7 billion people


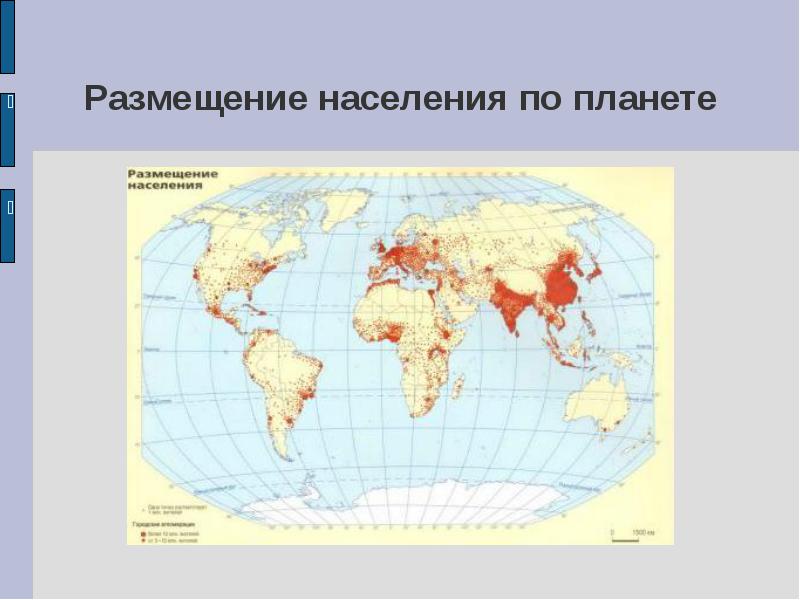
Distribution of the population on the planet
Independent work with cards
1. Analyze the "Population Distribution" map and draw a conclusion!
2. Determine the areas populated minimum and maximum. Determine the reason for the diversity of density by comparing this map with the physical map of the world.

populated countries of the world

human races
Caucasoid Mongoloid Negroid

Working with the text of the textbook
Carefully read the text of the textbook on page 157,
highlight the features of the races and fill in the table
Race equality
Nikolai Nikolaevich Miklukho - Maklai-
fighter against all "theories" postulating racial inequality, against the concepts of "inferior" and "superior" races

Tolerance is...

Gender composition of the population

Analyze the age structure of the world population
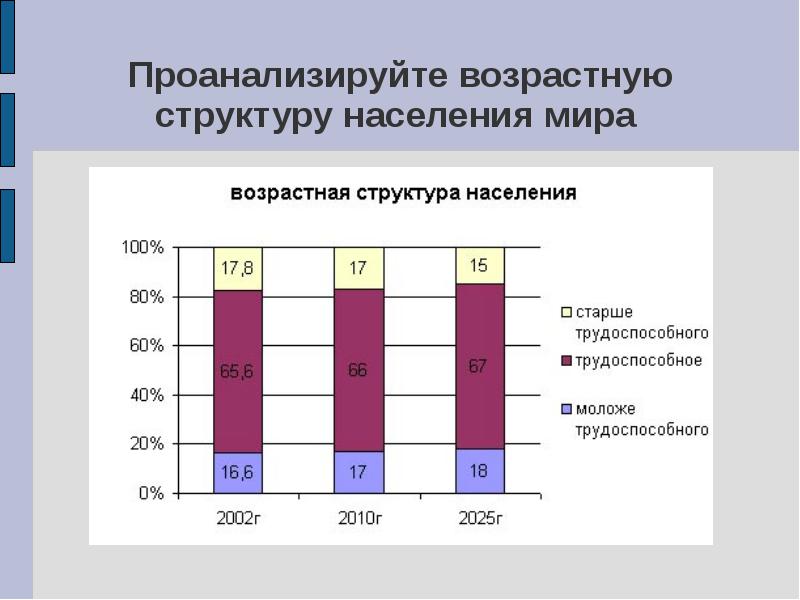
Summing up the lesson

MOSCOW STUDIES
11,551,930 people live in Moscow
Men - 46.3% Women - 53.7%

Homework
1. Paragraph 51-52, read and answer questions
2. Prepare a report on the population of Moscow using the data of the last population census http://www.perepis-2010.ru/

7 GEF class
Earth population
Dyrova L.B. MBOU secondary school № 1 Timashevsk Krasnodar region

You will learn
1. How many people live on Earth.
2. When rapid population growth began.
3. What are the features of the distribution of the population.
4. What is race and how are they different human races from each other.
5. What is the people.
6. How many peoples on Earth.
7. What religions are called world.

1. How many people live on Earth ?
7.248 billion people
http://priroda.inc.ru/naselenie.html
2. When did the rapid population growth start?
With XIX V .

3. What are the features of the distribution of the population?
Uneven!
main area population concentration is southeastern part Eurasia.


4. What is race and how do human races differ from each other?
Race is a large historical group of people who has characteristic external signs inherited.
There are three main large races: Caucasoid, Mongoloid and Equatorial (or Negroid).



5. What is a people? How many nations?
Everyone has it people(or ethnos) their own language, their own culture, their own characteristics, their own territory of residence; several thousand...








7. What religions called world ?
Christianity, Islam and Buddhism.

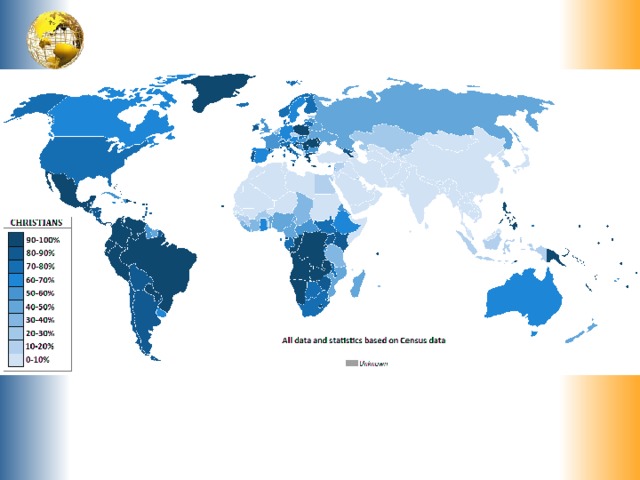
Christianity
The most common

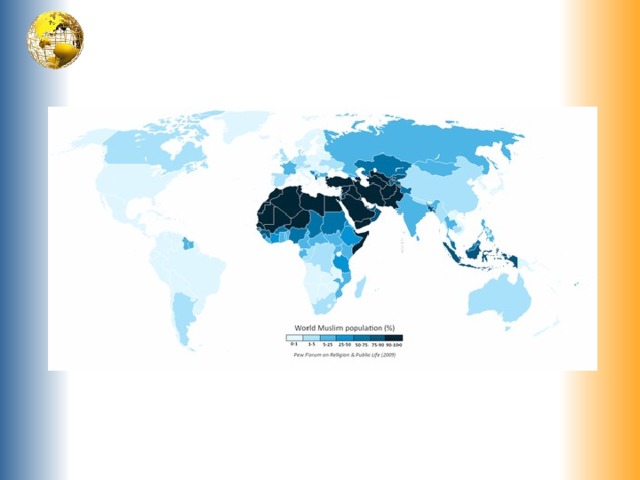
Islam
The youngest

Buddhism.
The most ancient

- Shintoism Japanese religion,
- Hinduism is the religion of the people of India.
- Paganism - this is the deification of the forces of nature and the worship of spirits, including the spirits of dead ancestors.

≪ Be honest, fair and hardworking!≫

Let's repeat the main thing
1. The population of the planet since the XIX century. is growing rapidly and is now about 7.2 billion people.
2. Man has populated the entire planet, but most people live in the most comfortable conditions: on the plains near sea coasts or along rivers. The polar, high mountain and desert regions are much less populated.
3. Humanity is divided into several dozen races. Among them stand out main races. These include Caucasoid, Mongoloid, Negroid.
4. The main part of the world's population professes one of the three world Religions: Buddhism, Christianity and Islam. In total, there are several dozen different religions on Earth.